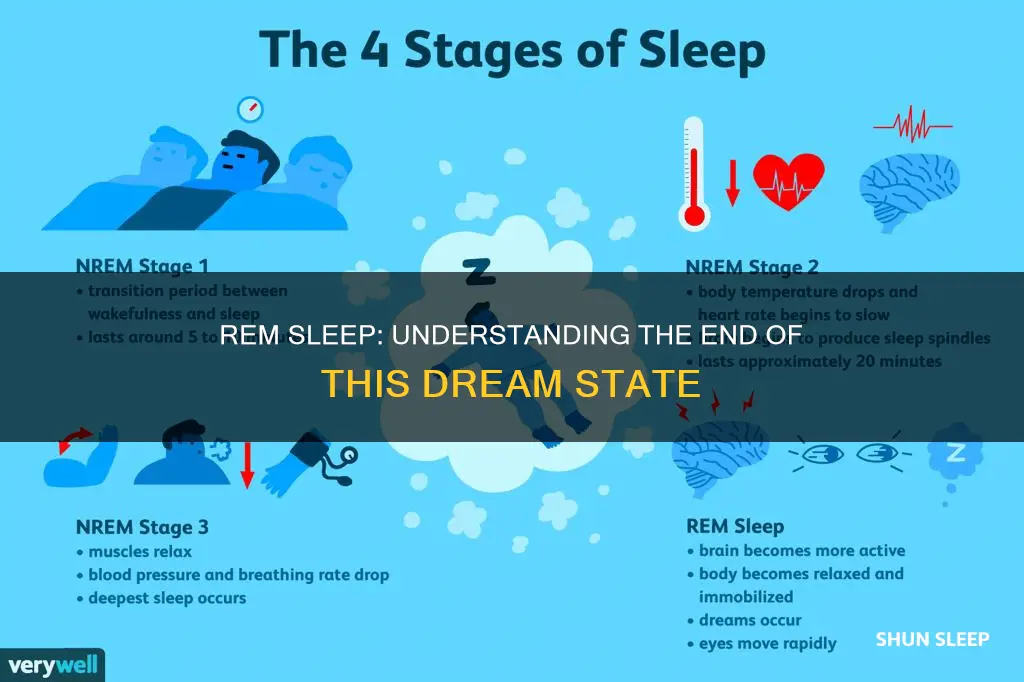
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and repair. During sleep, the body cycles through different stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which is known for its role in dreaming and memory consolidation. REM sleep is characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, and a temporary loss of muscle tone. While the duration of REM sleep can vary, it typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep, with each cycle lasting around 90 to 120 minutes.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| First cycle of REM sleep | 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep |
| Total sleep cycles per night | 4 to 5 |
| First REM cycle duration | 10 minutes |
| Final REM cycle duration | Up to an hour |
| Total REM sleep needed per night | 2 hours |
| REM sleep percentage of total sleep time | 25% |
| REM sleep percentage of total sleep time for babies | 50% |
| REM sleep percentage of total sleep time for adults | 20% |
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep occurs 60-90 minutes after falling asleep
- During REM sleep, the body is temporarily paralysed
- REM sleep is important for memory, mental focus and mood
- Lack of REM sleep can cause grogginess, trouble concentrating and a weakened immune system
- To increase REM sleep, improve your overall sleep quality and quantity

REM sleep occurs 60-90 minutes after falling asleep
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. During sleep, the body cycles through different stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep.
REM sleep is a crucial stage of sleep that typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. It is characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, and a temporary loss of muscle tone. This stage of sleep is associated with dreaming, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development.
During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, and the brain activity resembles that of being awake. The first cycle of REM sleep is usually the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes. Subsequent REM cycles lengthen, with the final one lasting up to an hour.
The amount of REM sleep an individual needs varies with age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, which gradually decreases to about 20% by adulthood. As people age, the time spent in REM sleep decreases slightly, reaching about 17% by the age of 80.
Overall, REM sleep plays a vital role in maintaining mental and physical health. It helps with learning, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. Disruptions in REM sleep can have negative consequences for overall health and cognitive performance.
REM and Deep Sleep: What's the Difference?
You may want to see also

During REM sleep, the body is temporarily paralysed
During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, and the heart rate speeds up. The breathing becomes irregular, and the body experiences a temporary loss of muscle tone. This loss of muscle tone, or paralysis, is a protective measure to stop sleepers from acting out their dreams and injuring themselves.
However, this hypothesis has been challenged by the discovery that people can also dream during non-REM sleep stages when their bodies are not paralysed. Researchers have also found that some birds only lose muscle tone in certain areas, such as the neck, allowing their heads to rest while standing on one foot.
REM sleep typically occurs 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep, with the first cycle being the shortest at around 10 minutes. Subsequent REM cycles lengthen, with the final one lasting up to an hour. The amount of REM sleep needed changes throughout a person's life, with newborns spending eight hours in REM sleep daily, while adults require only two hours on average.
REM sleep is important for several reasons. Firstly, it plays a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. It stimulates areas of the brain that aid in learning and memory, and the brain repairs itself and processes emotional experiences during this stage. Secondly, REM sleep helps ensure better mental concentration and mood regulation, which are critical for daily work performance and overall quality of life.
The negative effects of insufficient REM sleep can be serious, impacting overall health, including brain function and cellular repair. Lack of REM sleep may be due to sleep disorders such as insomnia or obstructive sleep apnea.
Brain Activity During REM Sleep: An Intriguing Mystery
You may want to see also

REM sleep is important for memory, mental focus and mood
REM sleep is the fourth stage of sleep, characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. It is important for memory, mental focus, and mood.
Memory
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, maintaining others, and deciding which ones to delete. This is sometimes referred to as "memory processing".
Mental Focus
REM sleep is also important for mental focus and cognitive performance. Sleep deprivation can lead to difficulty concentrating during the day and forgetfulness or poor memory.
Mood
REM sleep is important for mood regulation. Sleep deprivation can cause mood effects, including feelings of irritability, depression, or anxiety. During REM sleep, the brain processes emotions and dreams, which are thought to be involved in emotional processing.
REM Sleep: A Deep Dive into the Dream State
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep can cause grogginess, trouble concentrating and a weakened immune system
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that is essential for the proper functioning of the body and brain. While asleep, the body "powers down", allowing various systems, including the brain, to become less active and conserve energy. This energy conservation helps the body repair any issues that arose while awake.
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth of four stages of sleep. It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. The first cycle of REM sleep occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. The first period is typically the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes, with each subsequent REM stage getting longer, with the final one lasting up to an hour.
REM sleep is important for brain development, dreaming, memory, and emotional processing. During this stage, the brain repairs itself and processes emotional experiences, transferring short-term memories into long-term memories.
A lack of REM sleep can cause grogginess, trouble concentrating, and a weakened immune system. Other symptoms of inadequate REM sleep include trouble coping with emotions and vivid dreams or nightmares.
To increase REM sleep, it is important to get more sleep overall. This can be achieved by creating a relaxing bedtime routine, setting a sleep schedule, avoiding nicotine and caffeine, and getting daily exercise and sunlight. Additionally, it is best to avoid alcohol, meals, TV, and electronics close to bedtime, as these can interfere with sleep.
REM Sleep: Can You Be Woken Up Mid-Dream?
You may want to see also

To increase REM sleep, improve your overall sleep quality and quantity
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle. It is characterised by increased brain activity, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and relaxed muscles. Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night, which plays a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming.
Develop and Maintain a Sleep Schedule
It is important to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Keeping a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate your sleep/wake cycle, making it easier to fall asleep at night. If you can't fall asleep within 20 to 30 minutes, get out of bed and do something relaxing in another room until you feel sleepy again.
Treat Sleep Disorders
If you suspect that your lack of REM sleep is due to an underlying sleep disorder, consult a doctor or sleep specialist to develop an appropriate treatment plan. For example, treating obstructive sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy can lead to REM rebound sleep, improving mood and overall sleep quality.
Stop Taking Sleep Aids
Certain medications, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics, can reduce or suppress REM sleep. If the lack of REM sleep is affecting your quality of life, consult your doctor about alternative medications or lower doses.
Avoid Alcohol, Caffeine, and Tobacco
Consuming alcohol, especially in moderate to high amounts, can delay the onset of REM sleep and reduce the overall time spent in this stage. Caffeine and tobacco can also interfere with normal sleep progression, especially when consumed in the evening or close to bedtime. Try to cut down on these substances and avoid them in the late afternoon or evening.
Adopt Sleep Hygiene Techniques
- Exercise regularly, preferably in the morning or several hours before bedtime.
- Maintain a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom environment.
- Establish a relaxing bedtime routine with activities such as reading or taking a warm bath.
- Keep gadgets and screens out of the bedroom, as the light from electronic devices can disrupt your sleep.
- If you can't fall asleep, get up and do something quietly in another room until you feel sleepy again.
Recovering from Mid-REM Sleep Waking: Tips for a Better Night
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes. Each subsequent cycle gets longer, with the final one lasting up to an hour. A full sleep cycle is generally 90-120 minutes long.
On average, there are four to six REM cycles in a night.
During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, your heart rate increases, and your breathing becomes irregular. Your brain is highly active and dreams usually occur during this stage.







