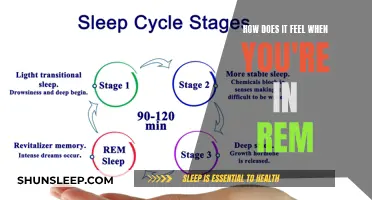
Sleep is divided into two main types: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). NREM is further split into three parts: starting to fall asleep, light sleep, and deep sleep. REM sleep, on the other hand, is the deepest stage of sleep and is associated with a variety of important physiological and cognitive processes. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly, the heart rate and blood pressure rise, and the brain is highly active. This is the stage of sleep where most dreams occur and it is believed to play a crucial role in memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and learning. While REM sleep is generally considered beneficial, it is important to note that a healthy sleep pattern requires a balance of both REM and non-REM sleep stages.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Eye Movement | Rapid |
| Dreaming | Vivid |
| Muscle Tone | Loss |
| Brain Activity | Increased |
| Heart Rate | Increased |
| Blood Pressure | Increased |
| Respiration | Faster and erratic |
| Oxygen Consumption | Increased |
| Limb Movement | Twitching |
What You'll Learn

REM sleep is important for brain development and learning
REM sleep is also associated with dreaming, and it is believed that dreams may help with emotional processing. While the purpose of dreaming is not fully understood, it is thought that it may aid in processing emotions. This is supported by the fact that the amygdala, the part of the brain responsible for processing emotions, is highly active during REM sleep.
Research has shown that a lack of REM sleep can negatively impact memory formation and cognitive performance. For instance, studies on sleep deprivation have found that it can lead to difficulties with concentration and memory retention. Furthermore, animal studies have indicated that REM sleep is particularly important for infants, as it is linked to neural stimulation and brain development.
In summary, REM sleep is crucial for brain development and learning due to its role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, and its potential impact on neural stimulation in infants.
REM Sleep and Dreams: Can We Recall Them?
You may want to see also

It helps with memory consolidation
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation and processing new information. It helps with mental concentration and mood regulation, which are critical to daily work performance and overall quality of life.
The brain processes information and consolidates memories during sleep. Sleep deprivation can negatively impact a person's working memory. A 2016 study involving healthy adolescents also found that sleep deprivation could increase the risk of forming false memories.
REM sleep is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. It is during this state that most vivid dreaming takes place.
During REM sleep, the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, maintaining others, and deciding which ones to delete.
The negative effects of a lack of REM sleep are serious. Without this critical sleep stage, overall health, including brain function and cellular repair, can suffer. Poor REM sleep may be due to sleep disorders such as insomnia or obstructive sleep apnea, which causes people to wake up during the night.
Michael J. Fox's Sleep Disorder: REM Behavior Explored
You may want to see also

It aids emotional processing
REM sleep is essential for emotional processing. This stage of sleep stimulates brain areas that are crucial for learning, memory formation, and retention. It is during REM sleep that the amygdala, the brain region responsible for processing emotions, is activated.
REM sleep is also when the brain exhibits high levels of activity, similar to the wakeful state, and this increased brain activity is associated with dreaming. Dreams, particularly those experienced during REM sleep, are thought to be involved in emotional processing.
The role of REM sleep in emotional processing is so significant that a lack of it can reduce an individual's ability to differentiate between threatening and non-threatening stimuli and respond appropriately. This can have adverse effects on physical and mental health, with links to conditions like obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, dementia, depression, and cardiovascular disease.
The importance of REM sleep for emotional processing is further highlighted by the fact that a healthy sleep pattern requires adequate amounts of both REM and non-REM sleep. While non-REM sleep is crucial for physical restoration, REM sleep is vital for cognitive and emotional processing.
Additionally, the amount of REM sleep an individual needs changes with age. Infants, for instance, spend more than 50% of their sleep time in the REM stage, which gradually decreases as they get older.
Overall, REM sleep is essential for emotional processing, and a lack of it can have negative consequences for both physical and mental health.
REM Sleep: Second Cycle Mystery Explored
You may want to see also

REM sleep is linked to dreaming
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth stage of the sleep cycle, following three stages of non-REM sleep. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly, the heart rate and blood pressure rise, breathing becomes erratic, and brain activity increases. This stage of sleep is associated with dreaming, memory consolidation, and learning.
REM sleep typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep and lasts for about 10 minutes. This cycle repeats every 90 to 120 minutes, with each subsequent REM stage becoming longer, and the final one lasting about an hour. On average, a healthy adult will go through 3 to 5 REM cycles per night, with 20-25% of their sleep time spent in the REM stage.
The REM stage of sleep is crucial for memory and learning. During this stage, the brain processes and consolidates new information, converting short-term memories into long-term ones. Studies have shown that sleep deprivation, specifically a lack of REM sleep, can interfere with memory formation and learning. Additionally, REM sleep is associated with more vivid dreaming due to the increase in brain activity.
The negative effects of insufficient REM sleep are significant. It can impact overall health, including brain function and cellular repair. Chronic sleep deprivation, which includes a lack of REM sleep, has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, dementia, depression, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Overall, REM sleep plays a vital role in maintaining physical and mental health, and ensuring adequate REM sleep is essential for overall well-being.
REM Sleep: Brain Repair and Restoration
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep can have negative health consequences
Sleep is generally divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). NREM is further split into three parts: starting to fall asleep, light sleep, and deep sleep. During a typical night, your sleep alternates through cycles of REM and NREM sleep about every 90 minutes. The REM stage accounts for approximately 20-25% of sleep time, while the NREM stage takes up the other 75%.
REM sleep is important for brain development, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and dreaming. It is also associated with daytime function and wakefulness. A lack of REM sleep can lead to various negative health consequences, including:
- Fatigue and irritability
- Changes in mood and memory
- Issues with cognition and problem-solving
- Cardiovascular health issues
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes
- Increased risk of obesity
- Increased risk of certain types of depression
- Potential contribution to cancer, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's
Additionally, a lack of REM sleep can affect an individual's ability to differentiate between threatening and non-threatening stimuli and respond appropriately, leading to reduced coping skills. It may also increase the risk of experiencing migraines in the following days.
It is important to note that the purpose of REM sleep is still unknown, and more research is needed to fully understand the effects of REM sleep deprivation. However, addressing sleep disorders, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and improving overall sleep quality can help increase REM sleep and mitigate these negative health consequences.
REM Sleep: Healthy or Harmful?
You may want to see also