When I Sleep, I Can't Wake Up is a mysterious and intriguing phenomenon that has captivated many. It involves experiencing a state of deep sleep where one feels unable to be awakened, even when physically stimulated. This condition, often referred to as 'sleep paralysis,' can be both a fascinating and potentially alarming experience, leaving individuals trapped in a state of awareness within a dream-like state. It raises questions about the boundaries between sleep and wakefulness and the intricate workings of the human mind.
What You'll Learn
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, despite having the opportunity
- Nightmares: Frightening dreams that cause intense fear and distress upon waking
- Sleepwalking: Walking or performing other activities while still asleep, often without awareness
- Sleep Paralysis: Temporary inability to move or speak when waking up or falling asleep
- Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders: Conditions like snoring or sleep apnea that disrupt sleep quality

Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, despite having the opportunity
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by the persistent difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep, even when an individual has ample time and opportunity to rest. It can be a frustrating and exhausting condition, leaving people feeling tired and unrefreshed during the day. This disorder can significantly impact one's quality of life, affecting work, relationships, and overall health. Understanding the causes and implementing effective strategies can help manage and overcome insomnia.
The causes of insomnia are multifaceted and can vary from person to person. Often, it is a combination of factors that contribute to this sleep disorder. Stress and anxiety are common triggers, as they can keep the mind active and racing, making it challenging to relax and fall asleep. For example, worrying about work deadlines or personal issues can lead to a constant state of mental alertness, making it difficult to unwind. Additionally, certain lifestyle factors play a significant role. Irregular sleep schedules, excessive caffeine consumption, and exposure to bright screens before bedtime can disrupt the body's natural sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Environmental factors also contribute to insomnia. A bedroom environment that is not conducive to sleep can exacerbate the issue. Noisy surroundings, an uncomfortable bed, or an overly warm or cold room can disrupt sleep patterns. It is essential to create a relaxing and comfortable sleep environment. This includes ensuring the bedroom is quiet, dark, and at a pleasant temperature. Investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows can significantly improve sleep quality.
Cognitive and behavioral factors are other significant contributors to insomnia. Racing thoughts, worry, and negative self-talk can keep the mind active at night. For instance, lying awake, counting the hours, and feeling frustrated can create a cycle of insomnia. It is crucial to develop healthy sleep habits and practices. This includes establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and learning relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
Managing insomnia often involves a combination of these strategies. Firstly, identifying and addressing the underlying causes is essential. This may include stress management techniques, such as exercise, yoga, or therapy, to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Limiting caffeine and screen time before bed can also significantly improve sleep. Creating a soothing sleep environment and sticking to a consistent sleep schedule are practical steps. Additionally, seeking professional help is beneficial, as sleep specialists can provide personalized advice and guidance. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is a highly effective treatment, offering techniques to improve sleep hygiene and manage sleep-related thoughts and behaviors.
Unleash the Magic: Secrets to Wake a Sleeping Fairy
You may want to see also

Nightmares: Frightening dreams that cause intense fear and distress upon waking
Nightmares are vivid, terrifying dreams that often leave individuals feeling distressed and anxious long after they wake up. These dreams can be so intense that they may even cause a person to feel paralyzed or unable to move, leading to a sense of dread and panic. The experience of a nightmare can be so overwhelming that it may take a significant amount of time to feel calm and safe again.
The content of nightmares can vary greatly, often reflecting an individual's deepest fears, anxieties, or unresolved emotional issues. Common themes include falling from great heights, being chased by unknown entities, being trapped in a confined space, or experiencing a sense of impending doom. These dreams can be so realistic and emotionally charged that they may even trigger a fight-or-flight response, causing the body to release stress hormones and leading to physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and hyperventilation.
Understanding and managing nightmares can be a challenging but important task. Here are some strategies that may help:
- Keep a Dream Journal: Writing down your dreams immediately upon waking can help you process and analyze them. Over time, you may identify recurring themes or triggers, which can provide valuable insights into your subconscious mind.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Before bed, engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle stretching. This can help reduce overall stress and improve sleep quality, potentially decreasing the frequency of nightmares.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Consider using white noise machines or earplugs to minimize disturbances. A comfortable and safe sleep environment can contribute to more restful sleep and potentially reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
- Seek Professional Help: If nightmares persist and significantly impact your daily life, consider consulting a mental health professional. Therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals understand and manage their nightmares by addressing underlying fears and developing coping mechanisms.
Nightmares can be a distressing aspect of sleep, but understanding and managing them is possible. By implementing these strategies and seeking support when needed, individuals can work towards improving their sleep quality and overall well-being.
iPhone X Sleep/Wake Function: Unlocking the Power of Rest
You may want to see also

Sleepwalking: Walking or performing other activities while still asleep, often without awareness
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a sleep disorder that involves a person performing complex actions while in a state of sleepwalking. This phenomenon typically occurs during the first third of the night, during the non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep stages. Individuals experiencing sleepwalking often appear to be awake and aware of their surroundings but are still in a semi-sleep state, making them difficult to rouse. They may walk around, perform daily activities, or even engage in more complex behaviors such as dressing, undressing, or leaving the house, all without any recollection of the event upon waking.
The exact cause of sleepwalking is not fully understood, but it is believed to be associated with a disruption in the brain's sleep-wake cycle. During sleepwalking episodes, the brain's prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making and complex behavior, is less active, while the brainstem, which controls basic functions like breathing and heart rate, is more active. This imbalance can lead to a person's body moving and acting as if they were fully awake, even though they are still in a state of sleep.
Sleepwalking episodes can vary in duration and intensity. Some individuals may sleepwalk for a few minutes, while others can remain in this state for an extended period. The behaviors exhibited during sleepwalking can range from simple actions like sitting up and stretching to more complex tasks such as driving a car, preparing meals, or even engaging in violent or aggressive acts. It is important to note that sleepwalkers often have no memory of these activities upon waking, which can be concerning for both the individual and those around them.
There are several factors that can contribute to sleepwalking. Sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions can all increase the risk of developing this disorder. Additionally, genetic predisposition plays a role, as sleepwalking tends to run in families. Stress, anxiety, and emotional disturbances can also trigger sleepwalking episodes, as they can disrupt the normal sleep-wake cycle.
If you or someone you know experiences sleepwalking, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management. Treatment options may include improving sleep hygiene, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and addressing any underlying medical or psychological conditions. In some cases, a sleep specialist may recommend a polysomnogram, a sleep study that monitors brain activity and body functions during sleep, to better understand the pattern and frequency of sleepwalking episodes. Early intervention and proper management can help ensure the safety of the individual and those around them during these episodes.
Troubleshoot: Revive Your Frozen Windows 7 Program with These Tips
You may want to see also

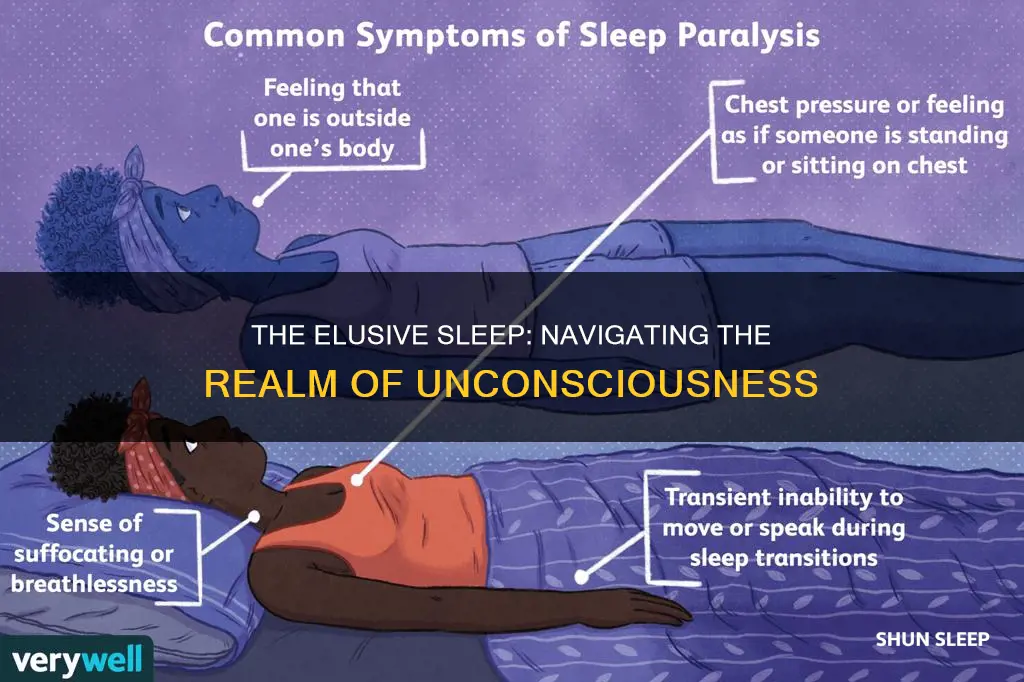
Sleep Paralysis: Temporary inability to move or speak when waking up or falling asleep
Sleep paralysis is a fascinating yet often terrifying phenomenon that can occur during the transition between sleep and wakefulness. It is a state where an individual becomes conscious but is temporarily unable to move or speak, sometimes accompanied by a sense of fear or a feeling of being trapped. This condition can be a distressing experience, leaving individuals feeling vulnerable and confused.
During sleep paralysis, a person's body enters a state of muscle atonia, where the muscles are temporarily paralyzed, similar to the state experienced during REM sleep. This paralysis is a natural mechanism to prevent acting out dreams and potential harm to oneself or others. However, when this paralysis occurs when waking up or falling asleep, it can lead to a terrifying experience. The individual may feel like they are unable to breathe, as if something is pressing down on them, or even experiencing a sense of presence in the room, often described as a malevolent force. These hallucinations can be incredibly realistic and distressing, causing a heightened sense of anxiety and panic.
The duration of sleep paralysis episodes can vary, lasting from a few seconds to several minutes. It often begins with a feeling of drifting off to sleep or waking up, but instead of progressing normally, the individual becomes aware of their surroundings but is unable to move or speak. The experience can be so intense that it may lead to a fight-or-flight response, causing the person to struggle to breathe or experience a rapid heart rate.
Understanding the causes of sleep paralysis is essential in managing and preventing these episodes. It is often associated with sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules, and certain sleep disorders. People who suffer from narcolepsy, a condition characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden muscle weakness, are more prone to experiencing sleep paralysis. Additionally, sleep position can play a role, as lying on the back during sleep may increase the likelihood of experiencing this phenomenon.
Managing sleep paralysis involves improving sleep hygiene and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. Ensuring adequate sleep duration and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can help reduce the occurrence of these episodes. For those who experience frequent or severe sleep paralysis, seeking medical advice is recommended to rule out any underlying sleep disorders and to receive appropriate treatment.
Awaken Windows 10: Tips for a Smooth Wake-Up
You may want to see also

Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders: Conditions like snoring or sleep apnea that disrupt sleep quality
Sleep-related breathing disorders are a group of conditions that affect the quality of sleep and can have significant impacts on an individual's health and well-being. These disorders are characterized by disruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. Understanding these disorders is crucial as they are quite common and can often go unnoticed, affecting both the affected individual and their sleep partners.
One of the most well-known sleep-related breathing disorders is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA occurs when the airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing the individual to wake up repeatedly to breathe. This interruption in sleep can lead to a constant state of fatigue and a lack of restorative sleep. Snoring, a common symptom of OSA, is the result of the airway being partially blocked, causing vibrations in the tissues. While snoring is often dismissed as a harmless habit, it can be a sign of a more serious underlying issue.
Sleep apnea can have numerous consequences on a person's health. During episodes of apnea, the body's oxygen levels drop significantly, leading to arousals that may not be conscious but can still cause fragmented sleep. Over time, this can result in excessive daytime sleepiness, affecting work performance, cognitive abilities, and overall quality of life. Additionally, the repeated arousals can lead to changes in brain function, including memory and learning difficulties.
Another disorder under this category is central sleep apnea, which is less common but equally significant. Unlike OSA, central sleep apnea is caused by a disruption in the brain's signaling to the muscles involved in breathing. This type of apnea is often associated with certain medical conditions, such as heart failure or stroke, and can be a result of the body's natural sleep-wake cycle. Both types of sleep apnea require medical attention and treatment to ensure adequate sleep and improve overall health.
Managing sleep-related breathing disorders typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. For snoring and mild cases of sleep apnea, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, avoiding alcohol before bed, and sleeping on one's side can help reduce symptoms. However, more severe cases may require the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines, which deliver pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep. Oral appliances and, in some cases, surgical interventions can also be effective treatments.
In summary, sleep-related breathing disorders, including snoring and sleep apnea, are conditions that can significantly impact sleep quality and overall health. Recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate medical advice is essential for effective management and treatment. With the right approach, individuals can improve their sleep, enhance their daily functioning, and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
Escape Sleep Paralysis: Effective Methods to Awaken from the Nightmare
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Sleep paralysis is a real condition where a person becomes conscious while still unable to move or speak, often accompanied by hallucinations. It occurs when the body's muscles are temporarily paralyzed at the beginning or end of sleep, allowing the mind to wake up while the body remains asleep. This can lead to feelings of being unable to wake up or a sense of being trapped.
While both can be frightening, sleep paralysis is distinct. During sleep paralysis, you are fully awake and aware but cannot move, and you might experience hallucinations. Nightmares, on the other hand, typically occur during REM sleep and involve vivid, scary dreams. You may wake up suddenly and remember the dream, but you will be able to move and speak normally.
Yes, sleep paralysis can be triggered by various factors. These include sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules, narcolepsy, and certain medications. It is more common in people who experience sleep disorders or have a family history of sleep paralysis. Maintaining a consistent sleep routine and getting adequate rest can help reduce the risk.
Managing sleep paralysis involves improving sleep hygiene and addressing any underlying sleep disorders. Here are some tips:
- Stick to a regular sleep schedule.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Avoid stimulants like caffeine close to bedtime.
- Practice relaxation techniques before sleep.
- If episodes are frequent, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
While it might not be possible to prevent sleep paralysis entirely, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing it. Ensuring you get enough sleep, maintaining a consistent sleep routine, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help. Additionally, keeping a sleep diary can help identify patterns and triggers, allowing you to make informed adjustments to your sleep habits.







