Sleep is a complex and mysterious process, and while we sleep, our bodies cycle through different stages of sleep. One of these stages is REM sleep, which stands for rapid eye movement sleep. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, and the brain activity is similar to its activity when awake. Dreams typically occur during this stage of sleep, and it is considered a more wakeful state. REM sleep is important for learning and memory, mood regulation, and brain development.
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep is a stage of the sleep cycle, along with non-REM (NREM) sleep
- During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly and your brain is active
- Your muscles become temporarily paralysed so you don't act out your dreams
- REM sleep is important for learning and memory, and helps with mood regulation
- If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience symptoms like trouble coping with emotions and concentrating

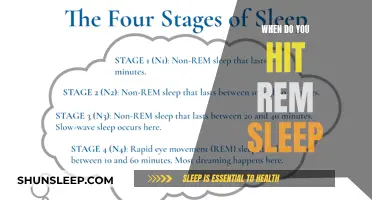
REM sleep is a stage of the sleep cycle, along with non-REM (NREM) sleep
Sleep is generally divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). NREM is further split into three parts: starting to fall asleep, light sleep, and deep sleep. During the deep sleep stage of NREM, your breathing slows down, your blood pressure drops, and your energy is renewed.
During a typical night, your sleep alternates through cycles of REM and NREM sleep about every 90 minutes. The length of these cycles can vary between 90 and 120 minutes, and each cycle includes three stages of NREM sleep and a stage of REM sleep. The REM stage accounts for approximately 25% of sleep time, while the NREM stage takes up the remaining 75%. If you get the recommended seven to nine hours of sleep each night, you might move through five to six full sleep cycles.
During the REM stage, your eyes move rapidly behind your eyelids, giving this stage its name. It is during this stage that most of your vivid dreaming takes place. Your muscles become temporarily paralysed, which is important so that you don't act out your dreams. REM sleep involves more brain activity than NREM sleep and is considered a more "wakeful" state, as your heart rate and blood pressure increase to levels close to what you experience when you are awake.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory. During this stage, your brain repairs itself and processes emotional experiences, helping with mood regulation. It also transfers short-term memories into long-term memories. A lack of REM sleep can lead to negative effects on overall health, including brain function and cellular repair.
The amount of REM sleep you need changes as you age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, which starts to decrease around six months of age and continues to decline throughout childhood and the teen years. By the age of 20, most people spend just over 20% of their total sleep time in REM sleep, and this decreases slightly to about 17% by the age of 80.
Smartwatches: Unlocking the Mystery of REM Sleep
You may want to see also

During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly and your brain is active
Sleep is divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep. During the REM stage, your eyes move rapidly and your brain is active. This stage of sleep has a major impact on your memory, mental focus, and mood.
During REM sleep, your closed eyes move rapidly back and forth under your eyelids. This is where most of your vivid dreaming takes place. Your muscles become temporarily paralysed, which is important so that you don't act out your dreams. REM sleep involves more brain activity than the NREM stage and is considered a more "wakeful" state, as your heart rate and blood pressure increase to levels closer to those when you are awake.
Each sleep cycle includes three stages of NREM sleep and a stage of REM sleep. After falling asleep, you first enter the NREM stage, followed by a shorter period of REM sleep, and then the cycle starts over again. A typical sleep cycle lasts between 90 and 120 minutes, and you will go through four to six of these cycles in a full eight-hour night of sleep.
REM sleep is important for several reasons. Firstly, it stimulates the areas of your brain that help with learning and memory. It also aids in brain development, particularly the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. Additionally, REM sleep helps your brain process emotional experiences and regulate your mood. Research suggests that a lack of REM sleep may increase the risk of developing dementia.
Heart Rate in REM Sleep: Faster or Slower?
You may want to see also

Your muscles become temporarily paralysed so you don't act out your dreams
Sleep is generally divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). During the REM stage, your eyes move rapidly and your brain activity is similar to its activity when you're awake. This is when most of your vivid dreaming takes place. Your muscles become temporarily paralysed, which is important so that you don't act out your dreams.
During REM sleep, your brain sends signals that relax the muscles in your arms and legs. This muscle relaxation is called muscle atonia and it helps you remain still during REM sleep. This paralysis is caused by two powerful brain chemical systems: the neurotransmitters gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine. These neurotransmitters switch off the specialised cells in the brain that allow muscles to be active.
REM sleep behaviour disorder occurs when the body maintains relatively increased muscle tone during REM sleep, allowing the sleeper to move and act out their dreams. This can cause serious injury to the sleeper or their bed partner. It is also often an early indicator of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's.
Prozac and REM Sleep: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also

REM sleep is important for learning and memory, and helps with mood regulation
Sleep is generally divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). During the REM stage, the eyes move rapidly, and the brain is active, with brain activity similar to when we are awake. This is when most of our vivid dreaming takes place. At the same time, our muscles become temporarily paralysed, preventing us from acting out our dreams. REM sleep is considered a more "wakeful" state, as heart rate and blood pressure increase to levels comparable to when we are awake.
REM sleep also strengthens our ability to solve complex problems. A study found that participants who were woken up during REM sleep could solve 15-35% more anagram puzzles than when they were woken up during NREM sleep. Another study found that REM sleep may play a role in linking together related memories, which can help with problem-solving.
The negative effects of a lack of REM sleep are serious. Poor REM sleep can be caused by sleep disorders such as insomnia or obstructive sleep apnea, which cause you to wake during the night. Without sufficient REM sleep, you may experience trouble coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and a general feeling of grogginess in the morning.
Alcohol's Effect on REM Sleep: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience symptoms like trouble coping with emotions and concentrating
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that is essential for our mental and physical health and well-being. Sleep is generally divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). During the REM stage, your eyes move rapidly, your muscles are relaxed, your breathing is irregular, your heart rate is elevated, and your brain activity is similar to when you are awake. This stage usually occurs
How Unisom Affects REM Sleep and Dreams
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. It is a stage of sleep during which your eyes move around rapidly in different directions, and your brain is active.
During REM sleep, your brain activity is similar to when you are awake. Your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing increase, and your muscles become temporarily paralysed. Most of your vivid dreaming occurs during this stage.
REM sleep plays a significant role in helping your brain consolidate and process new information. It also ensures better mental concentration and mood regulation, which are critical to your daily work performance and overall quality of life.
The amount of REM sleep you need shifts as you age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, which gradually decreases to about 20% by age 20. In older adults, it decreases further to around 17% by age 80.