Sleep is a complex and dynamic process that affects how we function in ways scientists are only beginning to understand. A good night's sleep is essential to survival, as important as food and water. Sleep is when the body and brain recuperate from the day and support multiple functions.
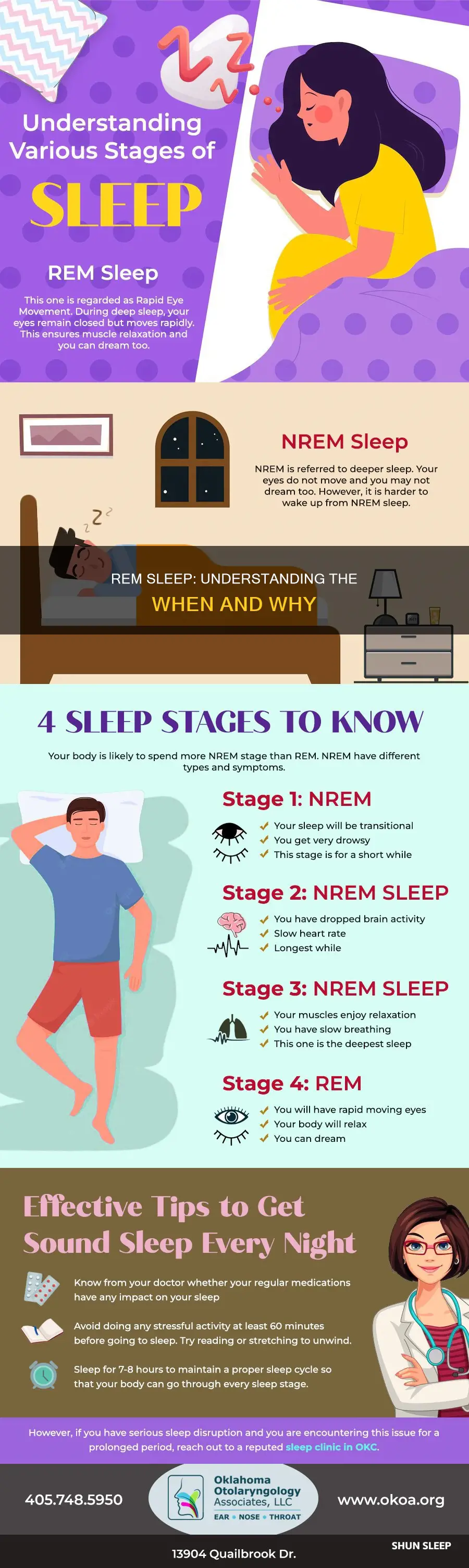
During sleep, the body cycles between non-REM and REM sleep. Non-REM sleep has three stages, and is followed by a shorter period of REM sleep, after which the cycle starts over again. Typically, a person will go through four to six sleep cycles per night.
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly, the brain is active, and dreams typically occur. After falling asleep, it takes about 90 minutes to enter the first period of REM sleep, which usually lasts about 10 minutes.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Time to enter REM sleep | Usually 90 minutes after falling asleep |
| First REM sleep duration | Around 10 minutes |
| Total REM sleep duration | 2 hours |
| REM sleep percentage | 25% of total sleep time |
| REM sleep frequency | 4-6 cycles per night |
| Brain activity | High |
| Eye movement | Rapid |
| Muscle tone | Relaxed |
| Breathing | Irregular |
| Heart rate | Elevated |
| Blood pressure | Increased |
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep occurs 90 minutes after falling asleep
- It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
- It is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming
- The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting around 10 minutes
- The final REM cycle may last up to an hour

REM sleep occurs 90 minutes after falling asleep
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth out of four sleep stages. It is preceded by three stages of non-REM sleep. Typically, REM sleep occurs 90 minutes after falling asleep. This is when the first cycle of REM sleep takes place, lasting for about 10 minutes.
During REM sleep, your brain activity is similar to its activity when you are awake. Your eyes move rapidly from side to side behind closed eyelids, your heart rate speeds up, and your breathing becomes irregular. Your muscles become temporarily paralysed, which prevents you from acting out your dreams.
Each sleep cycle, which includes three stages of non-REM sleep and one stage of REM sleep, takes 90 to 120 minutes to complete. As you progress through the cycles, you spend increasing amounts of time in REM sleep. Most of your REM sleep occurs in the second half of the night.
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. It stimulates the areas of your brain that help with learning and memory. Your brain also repairs itself and processes emotional experiences during this stage.
If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience symptoms such as trouble coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and grogginess in the morning.
Apple Watch: Tracking Your REM Sleep?
You may want to see also

It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
During REM sleep, the body and brain undergo a unique set of changes that distinguish this stage from non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep. Characterised by a combination of physical relaxation and cognitive activity, REM sleep plays a crucial role in various physiological and psychological processes.
Relaxed Muscles
During REM sleep, the body experiences a temporary loss of muscle tone, resulting in a state of muscle relaxation. This paralysis ensures that sleepers don't act out their dreams and injure themselves. However, this paralysis doesn't extend to the eyes, which exhibit rapid movements during this stage.
Quick Eye Movement
The "REM" in REM sleep refers to the rapid eye movements that occur during this stage. The eyes move rapidly in different directions behind closed eyelids. This characteristic is so distinctive that it gave the stage its name.
Irregular Breathing
Breathing patterns during REM sleep become irregular and differ from the steady, slower breathing associated with non-REM sleep. This irregular breathing pattern is another feature that sets REM sleep apart from other stages.
Elevated Heart Rate
In contrast to non-REM sleep, where heart rate slows down, REM sleep is characterised by an increased heart rate. The heart rate can vary significantly, reflecting the activity level occurring in the sleeper's dreams. Intense or scary dreams can lead to a higher heart rate, similar to when a person is awake.
Increased Brain Activity
While brain activity decreases during non-REM sleep, REM sleep is marked by heightened brain activity that resembles the brain's activity during wakefulness. This increased brain activity is associated with dreaming, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. The brain processes new learnings, commits some to memory, and decides which ones to delete.
Unlocking REM Sleep: A Guide to Enhancing Your Sleep Quality
You may want to see also

It is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming.
Memory Consolidation
REM sleep is thought to play a role in memory consolidation. During this stage of sleep, the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, deciding which ones to commit to memory, which ones to maintain, and which ones to delete. This is supported by studies that show increased REM sleep after learning a new task. However, other studies have found no link between REM sleep and memory consolidation, and the overall evidence is weak and contradictory. Some researchers suggest that REM sleep may only be important for certain types of memory, such as procedural memory, while others claim that it has a key role in language or emotional learning.
Emotional Processing
REM sleep is also involved in emotional processing. The brain processes emotions during this sleep stage, and dreams—which are You may want to see also REM sleep usually happens 90 minutes after falling asleep, so it is important to understand the stages that come before it. After falling asleep, an individual enters non-rapid eye movement sleep, which has three stages. The first stage, N1, occurs right after falling asleep and usually lasts less than 10 minutes. During this stage, the body has not fully relaxed, but body and brain activities start to slow, with periods of brief movements and light changes in brain activity. The second stage, N2, lasts from about 30 to 60 minutes. During this stage, muscles become more relaxed, and the body temperature drops. Brain waves show a new pattern, and eye movement stops. The third stage, N3 or deep sleep, lasts about 20 to 40 minutes. During this stage, delta brain activity increases, and it is very hard to wake someone up. After progressing through these three stages of non-REM sleep, the body then enters REM sleep, which is typically the shortest during the first cycle, lasting about 10 minutes. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, the heart rate speeds up, and breathing becomes irregular. The brain is also highly active, with brain waves becoming more variable. You may want to see also The lengthening of the REM cycles throughout the night is part of the natural progression of sleep. Sleep is divided into non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Non-REM sleep has three stages, and you typically move through all three before entering REM sleep. The first sleep cycle is often the shortest, ranging from 70 to 100 minutes, while later cycles tend to be longer, falling between 90 and 120 minutes. During the REM stage, your brain activity increases and resembles the brain activity of someone who is awake. Your eyes move rapidly from side to side behind closed eyelids, and your breathing becomes irregular. Your heart rate rises, and your blood pressure increases to near-waking levels. Most dreaming occurs during the REM stage, and it is also associated with memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. The length of the final REM cycle is an important part of the sleep architecture, which refers to the breakdown of a person's sleep into various cycles and stages. Achieving healthy sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, getting natural daylight exposure, and avoiding alcohol before bedtime, can help promote a proper sleep architecture and improve your overall sleep quality. You may want to see also You enter REM sleep about 90 minutes after falling asleep. It takes about 1 to 2 hours to enter REM sleep after falling asleep. The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting only a few minutes. However, each subsequent REM cycle gets longer, with the final one lasting up to an hour.Understanding REM Sleep: Timing and Its Importance

The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting around 10 minutes
Understanding REM Rebound: A Sleep Mystery Explained

The final REM cycle may last up to an hour
Understanding Non-REM Sleep: A Vital Sleep Stage
Frequently asked questions