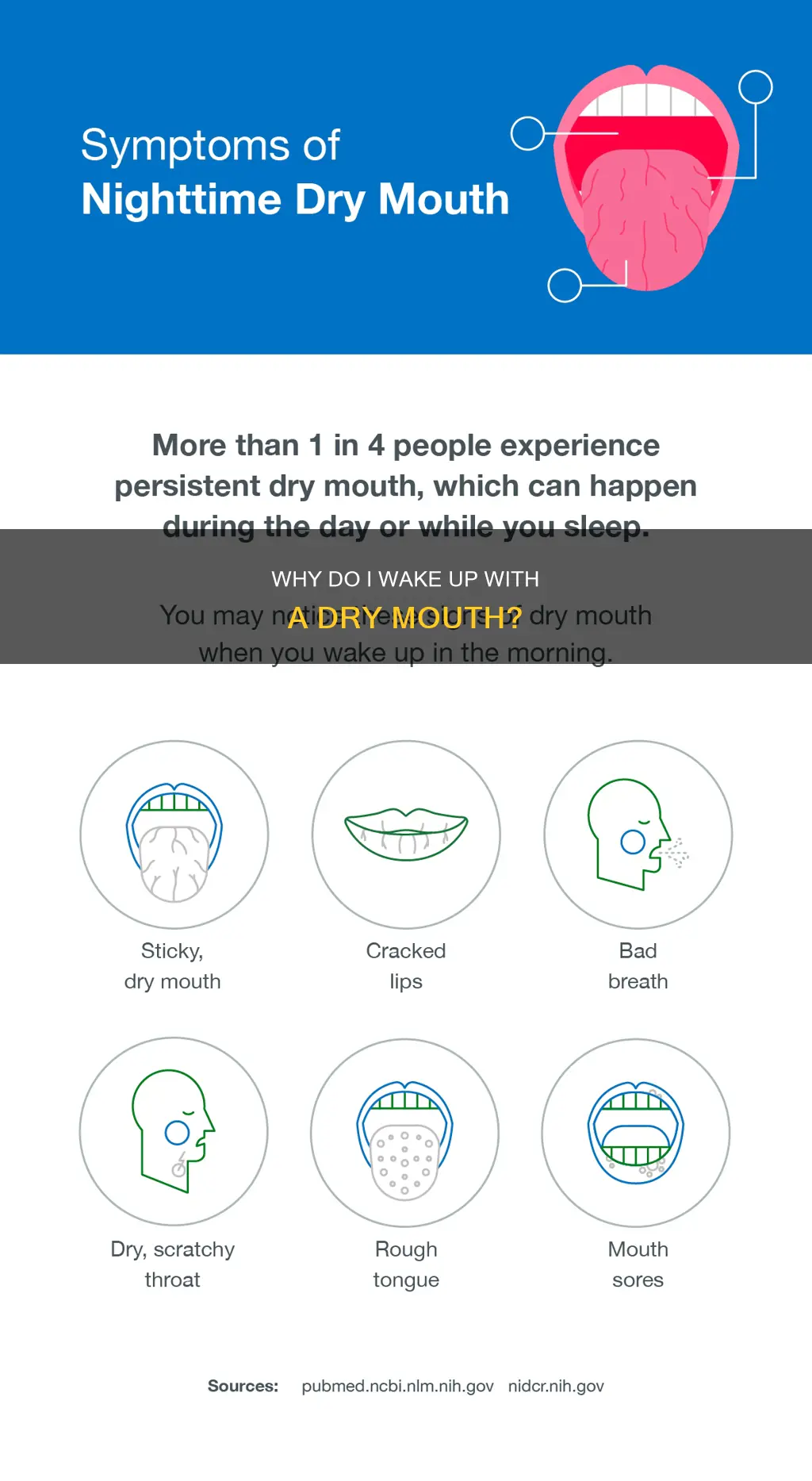
Many people experience a dry mouth upon waking up, which can be an uncomfortable and sometimes concerning symptom. This phenomenon is often attributed to a variety of factors, including the body's natural processes during sleep. During the night, the body conserves water, leading to reduced saliva production, which can result in a dry mouth when you wake up. Additionally, certain sleeping positions, medications, and even the environment in which you sleep can contribute to this issue. Understanding the causes and potential remedies for this condition can help individuals manage and alleviate the discomfort associated with waking up with a dry mouth.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Common Condition | Yes |
| Medical Term | Nocturnal Dry Mouth |
| Causes | - Sleep apnea - Mouth breathing - Dehydration - Medications - Snoring |
| Symptoms | - Dry mouth - Sore throat - Difficulty swallowing - Morning headaches |
| Treatment | - Stay hydrated - Use a humidifier - Avoid alcohol and tobacco - Practice good oral hygiene - Consult a doctor for sleep apnea |
| Prevention | - Maintain a healthy weight - Avoid alcohol and sedatives before bed - Sleep on your side |
| When to Consult a Doctor | - Persistent dry mouth - Discomfort during sleep - Snoring and pauses in breathing |
What You'll Learn
- Saliva Production: Reduced saliva flow during sleep, leading to dry mouth
- Oral Hygiene: Poor oral care may contribute to morning dryness
- Sleep Position: Lying on your back can restrict saliva drainage
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake before sleep can exacerbate dry mouth
- Medications: Certain drugs can cause dry mouth as a side effect

Saliva Production: Reduced saliva flow during sleep, leading to dry mouth
Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health and comfort. It is a natural lubricant that helps to keep the mouth moist, facilitating speech and swallowing while also acting as a protective barrier against bacteria and acids. However, a common issue that many people experience is waking up with a dry mouth, a condition often referred to as xerostomia. This phenomenon can be particularly disruptive and uncomfortable, leaving individuals feeling parched and uncomfortable upon waking.
The primary cause of this dry mouth sensation is the reduced production of saliva during sleep. Saliva flow naturally decreases as the body enters a state of rest, and this reduction can be more pronounced in certain individuals or under specific circumstances. During sleep, the body's metabolic rate slows down, and various physiological processes change, including the activity of salivary glands. These glands, responsible for producing saliva, may become less active, leading to a decrease in saliva secretion.
Several factors contribute to this reduced saliva flow during sleep. Firstly, the position of the body can impact saliva production. Sleeping on the back can cause the tongue to rest against the roof of the mouth, potentially reducing the stimulation of salivary glands. Additionally, certain sleep positions may compress the salivary ducts, hindering the normal flow of saliva. Another factor is the body's natural circadian rhythm, which regulates various bodily functions, including saliva production. This rhythm may influence the timing and amount of saliva secreted throughout the day and night.
Environmental factors also play a role in this sleep-related dry mouth issue. For instance, dry indoor air, often a result of heating or air conditioning, can contribute to reduced saliva flow. The air inside buildings is often drier during winter months, and this can lead to a faster evaporation of saliva, leaving the mouth feeling dry. Similarly, breathing through the mouth during sleep, which is common in individuals with snoring or sleep apnea, can further exacerbate dry mouth as it reduces the stimulation of salivary glands.
Understanding the causes of dry mouth upon waking can help individuals take appropriate measures to alleviate this discomfort. Simple solutions include maintaining a consistent sleep position that encourages optimal saliva flow, using a humidifier to add moisture to the bedroom air, and staying hydrated before bed. For those with sleep disorders like snoring or sleep apnea, seeking medical advice is essential to manage these conditions and potentially reduce the occurrence of dry mouth.
Break the Sleep Cycle: Tips for Waking Up Refreshing
You may want to see also

Oral Hygiene: Poor oral care may contribute to morning dryness
Poor oral hygiene can significantly impact your oral health and may be a contributing factor to the issue of waking up with a dry mouth. When you sleep, your mouth produces less saliva, which naturally helps to keep your mouth moist and wash away food particles and bacteria. However, if your oral care routine is inadequate, it can lead to a buildup of bacteria and debris, resulting in morning dryness and other oral discomforts.
One of the primary reasons for this is the lack of proper brushing and flossing. During sleep, bacteria in the mouth can multiply, and without regular cleaning, these bacteria can form plaque and tartar, leading to gum disease and tooth decay. This bacterial growth can cause inflammation and irritation, which may trigger the body's natural response to reduce saliva production, leaving your mouth feeling dry upon waking.
Additionally, the use of mouthwash or oral care products that contain alcohol can contribute to this problem. Alcohol is a drying agent and can reduce saliva flow, making your mouth feel parched. It is advisable to choose mouthwashes and oral care products that are alcohol-free, especially if you experience frequent morning dryness.
To combat this issue, it is essential to establish a consistent oral hygiene routine. Start by brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, ensuring you cover all surfaces of the teeth and along the gum line. Flossing is equally important to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and under the gum line. Consider using an oral irrigator or water flosser for added effectiveness.
Furthermore, staying hydrated throughout the day can help maintain saliva production. Drinking plenty of water not only keeps you hydrated but also helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of oral dryness. Finally, regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial to maintaining oral health and addressing any potential issues before they become more serious. By prioritizing oral hygiene, you can minimize the occurrence of morning dryness and ensure a healthier, more comfortable mouth.
Dell XPS 15: Quick Tips to Wake from Sleep
You may want to see also

Sleep Position: Lying on your back can restrict saliva drainage
Lying on your back during sleep can have an unexpected consequence: it may contribute to waking up with a dry mouth. This phenomenon occurs because when you lie flat, saliva tends to pool at the back of your throat, and it can be challenging for it to drain effectively. As a result, the saliva can accumulate, leading to a feeling of dryness and discomfort upon awakening. This issue is particularly common for individuals who breathe through their mouths while sleeping, as it exacerbates the problem by further reducing saliva production and drainage.
The position of your body during sleep plays a crucial role in saliva flow. When you lie on your back, gravity works against the natural flow of saliva, making it harder for it to reach the front of your throat and exit through the mouth. This can lead to a buildup of saliva, especially if you tend to breathe through your mouth, which is a common habit for many people. The lack of movement and the relaxed state of the body during sleep further contribute to this issue, as the muscles responsible for saliva drainage may not function optimally in this position.
To mitigate the effects of dry mouth upon waking, consider adjusting your sleep position. Sleeping on your side with an elevated head can help promote better saliva drainage. This position allows gravity to assist in the natural flow of saliva, reducing the likelihood of a dry mouth. Additionally, using extra pillows to elevate your head can open up your airways and reduce the tendency to breathe through your mouth, further alleviating the problem.
Another effective strategy is to maintain a consistent sleep position throughout the night. Frequent changes in position can disrupt the natural flow of saliva, leading to the accumulation of saliva and subsequent dryness. By being mindful of your sleep posture, you can take control of this issue and ensure a more comfortable and hydrated start to each day.
In summary, lying on your back during sleep can restrict saliva drainage, leading to a dry mouth upon awakening. This can be managed by adjusting sleep positions, such as sleeping on your side with an elevated head, and maintaining a consistent posture throughout the night. Simple changes in sleep habits can significantly improve morning hydration and overall sleep quality.
Facetime Tips: Gently Waking Up a Sleeping Friend
You may want to see also

Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake before sleep can exacerbate dry mouth
Dehydration is a common issue that can significantly impact our overall health and well-being. When we don't drink enough fluids throughout the day, our bodies may not have enough water to perform essential functions, including maintaining optimal saliva production. Saliva plays a crucial role in keeping our mouths moist, aiding in digestion, and protecting our teeth from decay. However, when we are dehydrated, our bodies may compensate by reducing saliva production, leading to a dry mouth upon waking up.
The link between dehydration and dry mouth is particularly noticeable during sleep. As we rest, our bodies conserve energy and focus on repairing and restoring. This process can sometimes disrupt the natural fluid balance in our bodies. If you've been dehydrated during the day, your body may not have enough fluids to maintain optimal saliva levels overnight. As a result, you might wake up feeling parched and experiencing the discomfort of a dry mouth.
To prevent this, it is essential to stay well-hydrated throughout the day. Drinking an adequate amount of water not only helps maintain overall health but also ensures that your body has the necessary fluids to produce saliva effectively. Aim to drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily, and consider increasing your fluid intake if you engage in physical activities or live in a hot climate.
Additionally, establishing a consistent bedtime routine can be beneficial. Before going to bed, make sure to drink a glass of water to ensure you start the night with optimal hydration. This simple practice can significantly reduce the likelihood of waking up with a dry mouth. By staying hydrated, you give your body the resources it needs to maintain saliva production, even during sleep.
In summary, dehydration is a key factor in experiencing dry mouth upon waking. By staying properly hydrated during the day and adopting a consistent bedtime hydration routine, you can effectively manage and prevent this issue. Remember, maintaining a healthy fluid balance is essential for overall well-being and can significantly improve the quality of your sleep.
Remote Wake-Up: Tips for Waking Your Computer from Sleep Mode
You may want to see also

Medications: Certain drugs can cause dry mouth as a side effect
Many medications can contribute to dry mouth, a condition known as xerostomia, as a side effect. This occurs due to the impact of these drugs on the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by lubricating the mouth, aiding in digestion, and protecting the teeth and gums from decay. When the production of saliva is reduced, it can lead to discomfort and various oral health issues.
One common class of drugs associated with dry mouth is antidepressants. These medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants, can affect the central nervous system and alter the body's natural processes, including saliva production. As a result, individuals taking these medications may experience a decrease in saliva flow, leading to a dry mouth sensation upon waking up.
Another group of drugs that can cause dry mouth is diuretics, often prescribed for hypertension or heart conditions. Diuretics promote fluid loss from the body, which can disrupt the balance of fluids in the mouth, leading to reduced saliva production. This side effect may be more pronounced in individuals who are already predisposed to dehydration or those who consume diuretic beverages like coffee or alcohol.
Additionally, certain medications used to treat Parkinson's disease, such as trihexyphenidyl, can cause dry mouth. These drugs work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which can affect the salivary glands' function. As a result, individuals with Parkinson's disease may experience dry mouth as a side effect of their medication.
It is important for individuals experiencing dry mouth as a result of medication to consult their healthcare provider. They can assess the specific medications being taken and explore alternative options or strategies to manage this side effect. Staying hydrated, using saliva substitutes, and practicing good oral hygiene can help alleviate the discomfort caused by dry mouth.
Understanding the Eat, Wake, Sleep Cycle: A Guide to Healthy Habits
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Waking up with a dry mouth is a common occurrence and can be attributed to several factors. One primary reason is the decrease in saliva production during sleep, especially in the deeper stages of the sleep cycle. Saliva helps to lubricate the mouth and throat, and when its production diminishes, it can lead to a feeling of dryness. Additionally, breathing through the mouth during sleep can contribute to this issue, as the air passes over the tongue and soft palate, potentially causing them to dry out.
Yes, certain sleeping positions can make a difference. Sleeping on your back is generally recommended as it allows saliva to accumulate in the mouth, reducing the likelihood of waking up with a dry mouth. If you tend to sleep on your side, try to keep your mouth slightly open to allow for better saliva distribution. However, if you find it uncomfortable, consider using a humidifier in your bedroom to add moisture to the air and potentially reduce the sensation of dryness.
Yes, staying well-hydrated is essential for maintaining saliva production. Drinking a glass of water before bed can help ensure that your mouth is moistened while you sleep. Additionally, staying hydrated throughout the day is crucial. Aim to drink enough water to keep your urine pale in color, as this is a simple indicator of proper hydration. However, it's worth noting that excessive fluid intake close to bedtime might lead to more frequent bathroom trips during the night, so find a balance that works best for you.
Yes, certain medical conditions and medications can contribute to dry mouth. Conditions such as sleep apnea, which cause interruptions in breathing during sleep, can lead to increased mouth breathing and subsequent dryness. Additionally, some medications, including antihistamines, decongestants, and certain antidepressants, have a side effect of reducing saliva production. If you suspect that your medication is causing this issue, it's best to consult your healthcare provider for alternative options or solutions.







