Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for maintaining good health. During sleep, our bodies cycle through different stages, including non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep, the focus of this discussion, typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep and is characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, and a temporary paralysis of the body. This stage is particularly important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| First occurrence | 60-90 minutes after falling asleep |
| Time spent in REM sleep | First cycle: 10 minutes; Final cycle: up to an hour |
| Frequency | Every 90-120 minutes |
| Progression | More time spent in REM sleep as the night progresses |
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep occurs 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep
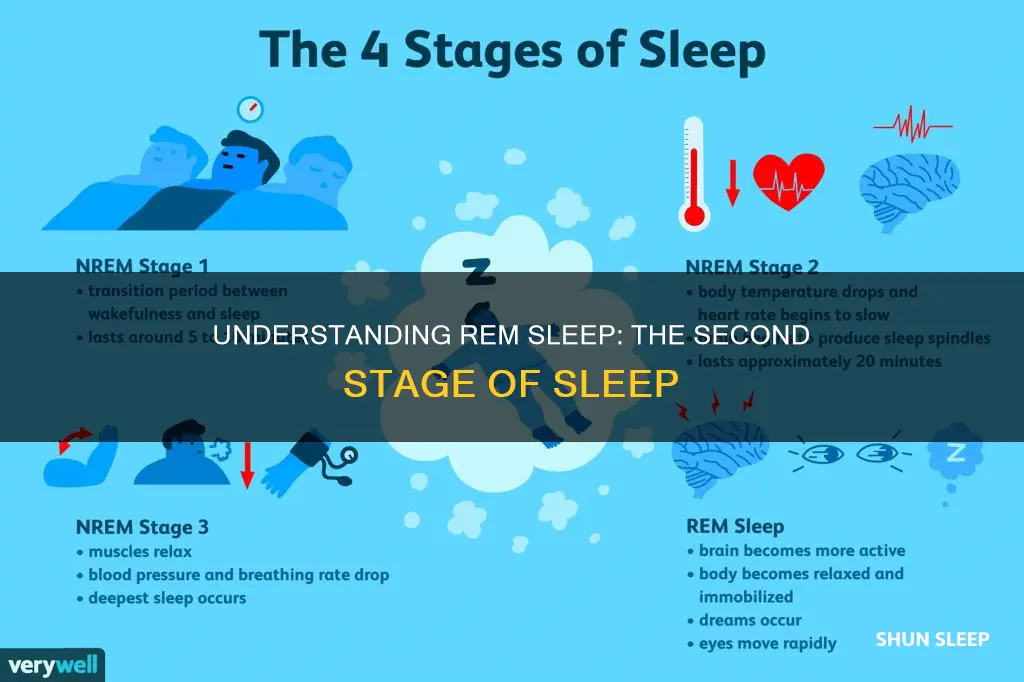
- It is the fourth stage of sleep
- It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
- It is important for learning, memory, emotional processing, and brain development
- Lack of REM sleep can cause grogginess, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and difficulty coping with emotions

REM sleep occurs 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. During sleep, individuals cycle through various stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep.
REM sleep is a fascinating stage characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, and elevated heart rate. It occurs approximately 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep and is associated with dreaming and memory consolidation. This stage typically lasts for 10 minutes during the first cycle and increases in duration with each subsequent cycle, with the final REM stage lasting up to an hour.
During REM sleep, the body experiences atonia, a temporary paralysis of the muscles, except for the eyes and breathing muscles. This stage is believed to be crucial for cognitive functions, including memory, learning, emotional processing, and creativity. The significant increase in brain activity during REM sleep leads to more vivid dreams compared to the NREM stages.
The duration of REM sleep changes throughout an individual's lifetime. Newborns spend a significant amount of their sleep in the REM stage, which may occur immediately after falling asleep. As people age, the amount of REM sleep decreases, and older adults tend to spend less time in this stage.
Overall, REM sleep is vital for brain development, emotional processing, and memory consolidation. The transition through the different sleep stages, including REM, is essential for a restorative and refreshing sleep experience.
How Well Does the Fenix 3HR Track REM Sleep?
You may want to see also

It is the fourth stage of sleep
REM sleep is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle. It typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep, and the first cycle usually lasts around 10 minutes. As the night progresses, the time spent in REM sleep increases, with the final cycle lasting up to an hour. During this stage, the brain's activity is similar to how it looks when you are awake.
REM sleep is characterised by increased brain activity, rapid eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and relaxed muscles. It is also known as "active sleep" due to the high level of brain activity. This is the primary stage of sleep during which dreaming occurs, and dreams are usually more vivid during REM sleep.
REM sleep plays a crucial role in several important functions, including memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. It accounts for about 25% of total sleep time in adults.
During REM sleep, the brain processes and consolidates new memories, making it an important stage for learning and memory retention. It is also believed that REM sleep aids in the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord.
Furthermore, REM sleep helps in the emotional processing of memories, particularly those associated with fear. Studies have shown that a lack of REM sleep can interfere with memory formation and increase the risk of developing dementia.
In summary, REM sleep, as the fourth stage of the sleep cycle, is essential for maintaining cognitive performance and overall brain health. It is characterised by distinct physiological changes and plays a vital role in memory, learning, and emotional regulation.
Understanding REM Sleep: Essential for Adult Health
You may want to see also

It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
During REM sleep, the body experiences a unique combination of physical and mental changes that distinguish it from non-REM sleep. This stage is characterised by a contrast between physical relaxation and mental alertness.
Firstly, the muscles become relaxed and immobilised. This temporary paralysis is believed to be a protective mechanism to prevent people from acting out their dreams. While the body's muscles are relaxed, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, exhibiting quick eye movement.
The breathing pattern during REM sleep is irregular and faster than during non-REM sleep. Additionally, the heart rate increases, resembling the elevated heart rate experienced during wakefulness.
The brain displays heightened activity during this stage, similar to the brain activity observed when a person is awake. This increased brain activity is associated with dreaming, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. The combination of relaxed muscles, rapid eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and heightened brain activity during REM sleep creates a state that is both physically restful and mentally active.
The progression through these stages of sleep is not always linear, and the duration of each stage can vary throughout the night. However, the cycle repeats approximately four to six times during a full night's sleep, with each cycle lasting around 80 to 120 minutes.
The Mystery of REM Sleep: Can You Survive Without It?
You may want to see also

It is important for learning, memory, emotional processing, and brain development
REM sleep is important for learning, memory, emotional processing, and brain development. During REM sleep, the brain prunes its synapses, the spaces in which brain cells communicate with one another, improving memory and problem-solving abilities. Dreams, which are more vivid during REM sleep, may be involved in emotional processing. The amygdala, the part of the brain that processes emotions, activates during REM sleep.
REM sleep is also when the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, maintaining others, and deciding which ones to delete. This is important for brain development, particularly in newborns, who spend most of their sleep time in REM. Research shows that animals born with less developed brains, such as humans and puppies, spend more time in REM sleep during infancy than those born with more developed brains, like horses and birds.
Additionally, people who get less REM sleep may have a greater risk of developing dementia. A study published in the journal Neurology found that for every 1% reduction in REM sleep, there was a 9% increase in the risk of dementia.
Does ZzzQuil Help You Get a Good Night's Rest?
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep can cause grogginess, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and difficulty coping with emotions
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the proper functioning of the body and brain. While sleeping, the body cycles between REM (rapid-eye movement) and non-REM sleep, each serving distinct purposes. During the REM stage, the eyes move rapidly, the heart rate increases, and brain activity is heightened. Dreams typically occur during this stage, and it stimulates areas of the brain that aid in learning and memory consolidation.
REM sleep usually occurs 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep, with the first cycle lasting about 10 minutes. Subsequent cycles lengthen, with the final one possibly lasting an hour. Now, let's delve into the consequences of missing out on this vital stage of sleep:
Grogginess and Trouble Concentrating
The lack of REM sleep can leave you feeling groggy and disoriented in the morning. This is because your brain hasn't had a chance to fully recharge and process information effectively. You may find it challenging to concentrate and learn new things. The brain feels exhausted, and its ability to perform cognitive tasks is impaired.
Weakened Immune System
During sleep, the immune system produces antibodies and cytokines, which are essential for fighting off bacteria and viruses. Sleep deprivation hinders this process, leaving your body vulnerable to illnesses and prolonging recovery. Additionally, long-term sleep deprivation increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
Difficulty Coping with Emotions
REM sleep is crucial for emotional processing. It is the stage when your brain processes emotions and consolidates emotional memories. A lack of REM sleep can lead to difficulty regulating emotions and increased mood swings. This, in turn, can impact your overall mental health and well-being.
Exploring the Intricacies of REM Sleep Duration
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. It is a stage of sleep where your eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, your heart rate increases, and your breathing becomes irregular.
REM sleep occurs about 90 minutes after falling asleep. Each sleep cycle is about 90-120 minutes, and the first cycle of REM sleep is typically the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes.
On average, a person will go through four to five sleep cycles in a full night of uninterrupted sleep.
During REM sleep, your brain is highly active and resembles brain activity when you are awake. It is also the stage when most dreams occur, and your body temporarily paralyses itself to prevent you from acting out these dreams.
To increase your REM sleep, you need to get more sleep overall. Sticking to a sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, and spending time outside in natural sunlight are some ways to improve your sleep.