A good night's sleep is just as important for your health as regular exercise and a healthy diet. Poor sleep can negatively affect your thinking ability, mood, heart health, immune health, and more. It can also increase your chances of developing obesity, diabetes, and other health conditions.
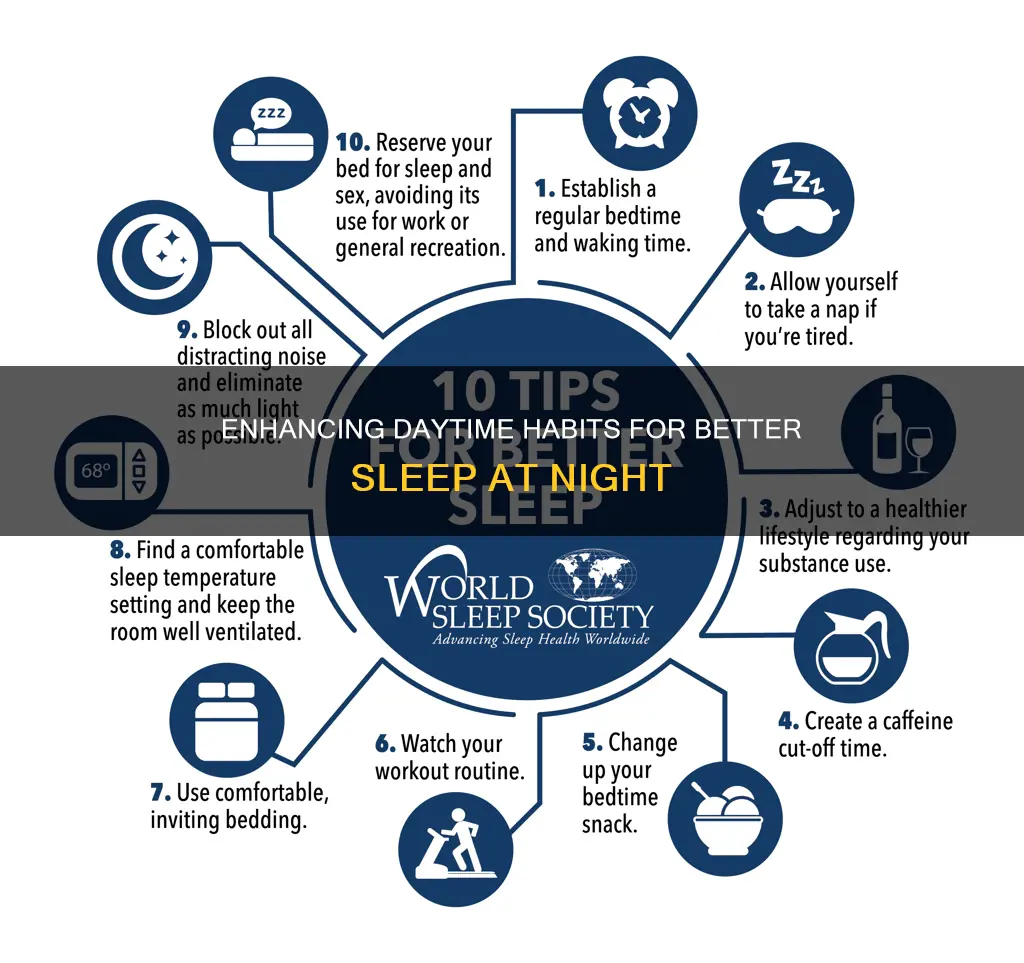
- Increase bright light exposure during the day: Spending time in natural sunlight or bright light during the day can help keep your circadian rhythm healthy and improve your daytime energy and nighttime sleep quality and duration.
- Reduce blue light exposure in the evening: Blue light from electronic devices like smartphones and computers can reduce your levels of melatonin, a hormone that helps you relax and get deep sleep. Try wearing blue light-blocking glasses or turning off your devices a few hours before bed.
- Avoid caffeine late in the day: Caffeine can enhance focus and energy, but it can also reduce your total sleep time and sleep efficiency. Avoid caffeinated beverages at least 8 hours before bedtime.
- Limit daytime naps: While short power naps can be beneficial, long or irregular naps during the day can negatively affect your nighttime sleep.
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule: Your body's circadian rhythm functions on a set loop, so going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can aid long-term sleep quality.
- Optimize your bedroom environment: Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet to minimize distractions and promote better sleep.
- Avoid eating late at night: Eating a big meal close to bedtime can negatively affect your sleep quality. Try to finish dinner a few hours before bed and limit heavy, rich foods within two hours of sleeping.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical exercise can improve sleep quality, but avoid intense exercise close to bedtime as it may hinder your body's ability to settle down before sleep.
- Avoid alcohol: Alcohol can induce drowsiness, but it also affects the brain in ways that lower sleep quality.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Light exposure | Get at least 30 minutes of natural light exposure during the day. Avoid blue light exposure in the evening. |
| Caffeine | Avoid caffeine after 2 p.m. or at least 8 hours before bedtime. |
| Alcohol | Avoid drinking alcohol close to bedtime. |
| Food | Avoid eating late at night. If you need to eat, opt for a light snack. |
| Liquids | Avoid drinking liquids 1-2 hours before bed. |
| Relaxation | Practice relaxation techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, or reading before bed. |
| Sleep schedule | Maintain a consistent sleep schedule. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. |
| Naps | Keep naps short (around 20 minutes) and in the early afternoon. |
| Exercise | Exercise daily, but not too close to bedtime. |
| Bedroom environment | Keep the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. |
| Supplements | Consider taking melatonin or other natural sleep aids such as valerian, chamomile, or glycine. |
What You'll Learn

Avoid caffeine, especially in the latter part of the day
Caffeine is a stimulant that can have a detrimental effect on your sleep, even in small amounts. It is known to negatively impact REM sleep, and a 2023 review found that late caffeine consumption reduced total sleep time by 45 minutes and overall sleep efficiency by 7%.
To avoid this, it is recommended that you do not consume caffeine at least 8 hours before bedtime. If you are taking a caffeine supplement, this time frame increases to 13 hours. This means that if you have a cup of coffee at 2 pm, you could still be affected when you go to bed at midnight.
If you are craving a hot drink in the late afternoon or evening, opt for decaffeinated coffee or tea. You could also try warm milk, which is believed to contain chemicals that simulate the effects of tryptophan in the brain, a building block for serotonin, which is involved in the sleep-wake transition.
Caffeine can be hidden in foods such as chocolate, and even some pain relievers and weight loss pills, so it is important to read labels if you are trying to cut down.
If you are a regular caffeine consumer, it is worth noting that it can be difficult to cut down or quit, and you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and irritability. However, these symptoms should pass within a few days to a week.
Pugs: Sleeping Beauty or Something More Concerning?
You may want to see also

Avoid bright lights before bed
Light is the most important external factor when it comes to getting a good night's sleep. While most people know that it's easier to sleep when it's dark, the link between light and sleep goes deeper than that.
Light plays a central role in regulating the circadian rhythm, the body's internal clock that signals when to be alert and when to rest. Light also affects the production of melatonin, a sleep-promoting hormone.
During the day, spending time in natural sunlight or bright light can help keep your circadian rhythm healthy and improve your daytime energy, as well as your nighttime sleep quality and duration. A 2017 study of office workers found that those exposed to a lot of light in the morning fell asleep more quickly at night and experienced better sleep quality.
However, it's important to avoid bright lights before bed. Exposure to light suppresses the secretion of melatonin, and even dim light can interfere with your circadian rhythm and melatonin secretion. Light at night is one of the reasons many people don't get enough sleep, and researchers have linked a lack of sleep to an increased risk of depression, as well as diabetes and cardiovascular problems.
Blue light, in particular, has a powerful impact on sleep. Blue wavelengths boost attention, reaction times, and mood during the day, but they seem to be the most disruptive at night. The use of electronic devices with screens, as well as energy-efficient lighting, has increased our exposure to blue light in the evening.
To improve your sleep, it's recommended to avoid looking at bright screens beginning two to three hours before bed. If you use a lot of electronic devices at night, consider wearing blue-light-blocking glasses or installing an app that filters blue/green wavelengths.
Additionally, you can make your bedroom as dark as possible by using blackout curtains or a sleep mask to block out light. When preparing for bed, keep the lights dim, and use a small, low-power lamp to help transition to bedtime. Reducing or eliminating technology in your bedroom can also help improve your sleep quality.
Keep Your Computer Awake and Productive
You may want to see also

Exercise daily, but not too close to bedtime
Exercise is a great way to improve your sleep quality and overall health. However, the timing of your workout matters if you want to get a good night's rest. While exercising at any time of day is beneficial, working out too late in the day or too close to bedtime can interfere with your sleep.
The Stimulatory Effect of Exercise
Exercise increases alertness and the levels of stimulating hormones like epinephrine and adrenaline in the body. This can make it difficult to fall asleep and impact your sleep quality. It's recommended to leave a few hours between your workout and bedtime to give your body time to wind down.
Core Body Temperature
Exercise raises your core body temperature, which signals to your body clock that it's time to be awake. It takes about 30 to 90 minutes for your core body temperature to start falling again, facilitating sleepiness. Therefore, exercising too close to bedtime can disrupt your body's natural sleep signals.
Endorphin Release
Aerobic exercise causes the body to release endorphins, creating a level of brain activity that may keep some people awake. If you find that exercise stimulates your brain and makes it difficult to fall asleep, try to exercise at least one to two hours before bedtime to give your body enough time to relax.
Tips for Better Sleep:
- Daily Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise daily. This can include activities like power walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Listen to Your Body: Everyone is different, so pay attention to how your body responds to the timing of your workouts. You may find that morning or afternoon workouts suit your sleep schedule better.
- Consistency: Try to maintain a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Adopt a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it's time to wind down. This can include activities like reading, listening to soothing music, or practicing relaxation techniques.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens for at least 30 minutes before bedtime, as the blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with your sleep.
- Comfortable Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. A comfortable environment can help you fall asleep more easily and improve your sleep quality.
Tie Shoes Securely, Keep Toes Awake
You may want to see also

Avoid eating heavy meals late at night
Eating a heavy meal late at night can have a negative impact on your sleep quality and overall health. Firstly, it can affect your digestion and sleep quality. Consuming a large meal close to bedtime can disrupt your body's natural rhythm, which is evolved to process nutrients during the day and conserve energy at night. This disruption can lead to problems such as heartburn, acid reflux, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
To reduce the risk of these issues, it is recommended to avoid eating a full meal two to four hours before bedtime. This allows for proper digestion and reduces the likelihood of experiencing GERD symptoms and poor sleep. Eating a large meal late at night can also increase your risk of weight gain and obesity over time, as it may lead to consuming more calories than your body needs.
Additionally, late-night meals can negatively impact your blood sugar levels, making it difficult to fall asleep and affecting your overall sleep quality. Eating high-calorie, high-fat, or high-carb meals less than an hour before bedtime can extend the time it takes to fall asleep. On the other hand, eating meals high in carbohydrates at least four hours before bedtime can help you fall asleep faster.
The relationship between late-night eating and obesity is complex and depends on various factors, including the types of food, portion sizes, individual calorie needs, and other health conditions. However, by avoiding heavy meals late at night, you can maintain a healthier weight and lower your risk of obesity and related health issues.
In summary, avoiding heavy meals late at night is crucial for maintaining good sleep hygiene and overall health. It helps prevent digestion issues, improves sleep quality, and reduces the risk of weight gain and obesity. By timing your meals appropriately and opting for lighter, nutrient-dense snacks in the evening, you can set yourself up for a better night's sleep and promote long-term health.
How Birds Sleep Peacefully on Branches
You may want to see also

Keep your bedroom cool, dark and quiet
Keeping your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet is essential for a good night's sleep. Here are some tips to achieve that:
Cool
- Set your thermostat to between 62 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit. The ideal temperature varies between individuals, but most research recommends a cooler room, around 65 to 68 degrees.
- Use a dehumidifier to circulate chilled air and remove moisture from the room. This is especially helpful in humid climates.
- Open the windows at night to let in cooler air, especially if your room is on an upper floor.
- Create a cross-breeze by opening two windows diagonally across from each other and placing fans on the windowsills to blow air in and out.
- Avoid using hot appliances, such as dryers, stoves, or incandescent and halogen lighting, as they can contribute to a rise in room temperature.
- Invest in cooling bedding materials and mattresses designed to regulate body temperature, such as those made with latex, hybrid, or innerspring technology.
Dark
- Limit your exposure to natural and artificial light before bed. This includes televisions, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Install blackout curtains or use thick drapes to block out sunlight and street lights. Alternatively, cover the windows with aluminium foil for a low-cost solution.
- Place a rolled-up towel against the gap between the door and the floor to block light from entering the room.
- If you can't block out all the light, wear an eye mask to cover your eyes while you sleep.
Quiet
- Turn off or move anything that is loud, such as televisions or other electronic devices.
- Ask family members or roommates to keep noise to a minimum.
- Use a noise machine to drown out any disruptive sounds from outside or within the home, such as a snoring partner or a loud air conditioner. These machines produce white, pink, or brown noise, as well as nature sounds like rain or waves.
Why Jabari Parker Deserves Your Attention
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A good diet and regular physical exercise can help us relax and get better sleep. Try to avoid eating large meals, caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine close to bedtime. The general advice is to avoid stimulants 1 to 2 hours before bed. Regular exercise helps with sleep, but avoid anything too energetic in the 90 minutes before bedtime.
It is generally easier to fall asleep when it is quiet, dark, and cool. Good curtains or blinds can help keep a room dark, and earplugs or white noise machines can be used to keep things quiet. Most people find it easier to sleep in a cooler room, with the ideal temperature between 65 and 72 degrees Fahrenheit.
Having a regular sleep routine can help improve sleep. This includes having a set time to start winding down and a fixed bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends. It is also important to relax before bed, and you can do this by reading, listening to music, or practicing meditation or relaxation techniques.
There are several natural sleep aids that can help you fall asleep. These include warm milk, chamomile tea, tart cherry juice, and melatonin supplements.







