Sleep is divided into several cycles, each consisting of different stages, including REM sleep and deep sleep. While REM sleep is often associated with the mind and cognitive functions, deep sleep is all about physical restoration and health. Both are essential for overall health and well-being, and getting a balanced cycle of REM and deep sleep is key to waking up feeling refreshed and ready to tackle the day.
REM sleep is called so because during this stage, our eyes move rapidly in various directions, even though they're closed. This stage is strongly associated with vivid dreams. During REM sleep, our brain activity spikes, resembling activity patterns from when we are awake.
Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, is the stage of sleep when our brain waves slow down significantly. This is the most restorative phase of sleep, ensuring we wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.
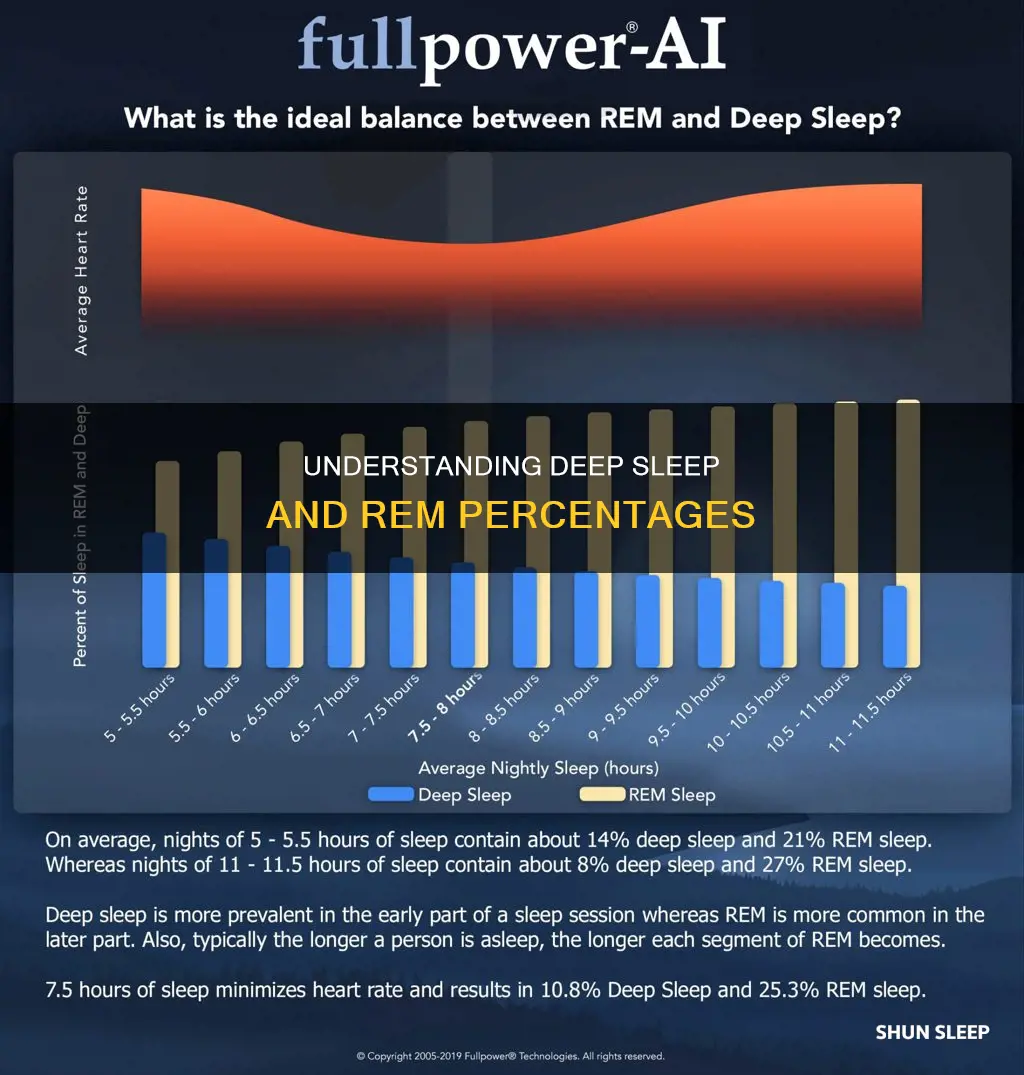
On average, adults should aim for about 20-25% of their sleep to be REM sleep and 13-23% to be deep sleep.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Percentage of sleep that should be REM sleep | 20-25% |
| Percentage of sleep that should be deep sleep | 13-23% |
| Percentage of sleep that should be light sleep | 50-60% |
What You'll Learn

Deep sleep is when the body repairs and restores itself
Sleep is divided into several cycles, each consisting of different stages, including REM sleep and deep sleep. Deep sleep is the stage of sleep when our brain waves slow down significantly. This is the most restorative phase of sleep, ensuring we wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.
Deep sleep typically occurs in longer periods during the first half of the night. Typically, you descend into deep sleep within an hour of falling asleep and experience progressively shorter periods of deep sleep as the night wears on. During this stage, automatic body functions like breathing and heart rate are also very slow, and your muscles are relaxed. It can be difficult for someone to wake you up, and waking up out of deep sleep may make you feel mentally foggy for up to an hour.
Deep sleep is essential for health and wellbeing. Most adults need around 1.5–2 hours of deep sleep per night. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advise adults aged 18–60 years to aim for at least 7 hours of sleep per night, with around 25% of this being deep sleep.
Apple Watch: Tracking Your REM Sleep?
You may want to see also

Deep sleep is essential for growth and development
Sleep is divided into several cycles, each consisting of different stages, including REM sleep and deep sleep. Deep sleep is the most restorative phase of sleep, ensuring we wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated. It is all about physical restoration and health, while REM sleep is associated with the mind and cognitive functions.
Deep sleep is when the body's restorative functions are at their peak. It is when the body strengthens muscle, bones, tissue, and immune function. It is also when the body secretes growth hormones, which are associated with cellular rebuilding and repair.
Deep sleep is particularly important for children and adolescents, who need more of it to support their growth and development. For adults, deep sleep typically makes up about 13-23% of their sleep, which equates to about 1-2 hours per night in a 7-9 hour sleep period.
Not getting enough deep sleep can have several negative consequences. It can cause learning difficulties, make you susceptible to infection, and put you at risk for long-term health concerns such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. It can also lead to a higher risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Ensuring you get sufficient sleep overall can help you get the deep sleep you need. Establishing a healthy sleep schedule and practicing good sleep hygiene, such as exercising regularly, reducing caffeine intake, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can all contribute to getting more deep sleep.
Exploring the Intriguing World of REM Sleep
You may want to see also

REM sleep is important for emotional regulation and memory
REM sleep is also when most dreaming occurs, and dreams are more vivid during this stage of sleep. Dreams may be involved in emotional processing, and the amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions, is activated during REM sleep.
The amount of REM sleep a person needs changes throughout their life. Newborn babies spend eight hours in REM sleep each day, while adults only need around two hours of REM sleep each night.
If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience problems with memory formation. Studies suggest that REM sleep deprivation disrupts the brain's ability to generate new cells. However, it's important to note that the memory problems associated with a lack of REM sleep could also be due to overall sleep disruption, as these two factors often occur together.
Triggering REM Sleep: Techniques for Dreaming and Memory Formation
You may want to see also

A good night's sleep is about quality, not just quantity
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that is essential for our health and well-being. While the quantity of sleep is important, the quality of sleep also plays a crucial role in ensuring we wake up feeling refreshed and ready to tackle the day.
Our sleep consists of different stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and deep sleep. REM sleep is associated with cognitive functions, such as enhancing learning, memory, emotional regulation, creativity, and problem-solving. On the other hand, deep sleep is crucial for physical restoration and repair. During this stage, our brain waves slow down significantly, and our body repairs and regenerates tissues, builds bones and muscles, and strengthens the immune system.
A good night's sleep is about achieving a balance between REM and deep sleep. Most adults should aim for about 20-25% of their sleep to be REM sleep and 13-23% to be deep sleep. However, these percentages can vary depending on age, lifestyle, and overall health. For example, children and adolescents typically need more REM and deep sleep to support their growth and development.
To improve the quality of your sleep, it is essential to establish a consistent sleep schedule, maintain a relaxing bedtime routine, and create a quiet, cool, and dark sleep environment. Additionally, reducing caffeine intake, especially in the afternoon and evening, and incorporating regular physical activity can also promote better sleep quality.
By prioritizing sleep quality and ensuring we get adequate amounts of REM and deep sleep, we can enhance our overall health, well-being, and daily functioning.
The Intriguing Nature of REM Sleep Characteristics
You may want to see also

Sleep disorders can impact your sleep stages
Sleep disorders can significantly impact the quality of your sleep and the time you spend in each sleep stage. Sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and REM sleep behaviour disorder can interrupt your healthy sleep cycle and prevent you from getting restful sleep.
Sleep apnea, for example, is a condition where a person experiences lapses in breathing during sleep. When these breathing lapses occur during REM sleep, people with sleep apnea often move to a lighter sleep stage so they can continue breathing. As a result, they tend to spend less time in REM sleep than those without the disorder and experience excessive daytime sleepiness.
Similarly, restless leg syndrome (RLS) can cause multiple awakenings throughout the night, disrupting the sleep cycle and making it harder to get restful sleep. The more awakenings a person experiences, the less time they will spend in deep sleep and REM sleep, which are crucial for physical restoration and cognitive functions, respectively.
REM sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) is a condition where people don't experience the usual muscle paralysis during REM sleep, causing them to act out their dreams. This can lead to violent movements and sleep talking, interrupting their sleep and that of their bed partner. RBD is often associated with other neurological conditions, such as Parkinson's disease and dementia, and can increase the risk of injury to the person and their bed partner.
Age-related changes in sleep patterns can also impact the time spent in each sleep stage. As people get older, they tend to need less REM sleep and deep sleep. Older adults may experience shorter durations of deep sleep due to factors such as pain, illness, medical problems, and sleep disorders.
Additionally, certain medications can interfere with sleep stages. For instance, antidepressants have been found to suppress REM sleep, and some drugs, like alcohol, can alter the way people enter the various sleep stages.
Overall, sleep disorders and other factors can significantly impact the time spent in each sleep stage, affecting both physical restoration and cognitive functions.
Smartwatches: Unlocking the Mystery of REM Sleep
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM sleep should make up about 20-25% of your total nightly sleep. This equates to roughly 1.5 to 2 hours per night if you're getting the recommended 7-9 hours of total sleep.
For deep sleep, adults typically need about 13-23% of their sleep in this stage, which equates to about 1 to 2 hours per night in a 7-9 hour sleep period.
Signs that you are not getting enough REM or deep sleep include daytime fatigue, mood swings, difficulty concentrating, memory issues, and a general feeling of not being well-rested.
You can influence your sleep stages through lifestyle choices and sleep habits. Creating a consistent sleep routine, optimizing your sleep environment, managing stress, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and electronics before bed can help increase the quality of your sleep.







