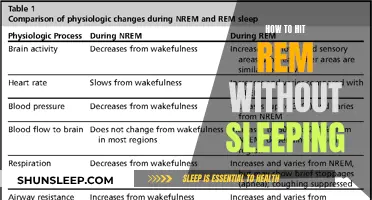
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process, and while we sleep, our bodies cycle through different stages. One of these stages is REM sleep, which is characterised by rapid eye movement, relaxed muscles, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. This stage of sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming.
During a full night's sleep, we cycle through four stages of sleep multiple times: three stages of non-REM sleep, followed by one stage of REM sleep. Each cycle through all the sleep stages takes 90 to 120 minutes to complete, and as the night progresses, we spend increasing amounts of time in REM sleep.
If you want to increase your REM sleep, there are several strategies you can try. These include improving your overall sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a sleep schedule and creating a bedtime routine, as well as avoiding substances like alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine close to bedtime.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of sleep cycles per night | 4 to 6 |
| Length of each sleep cycle | 90 to 120 minutes |
| First sleep cycle length | 70 to 100 minutes |
| Later sleep cycles length | 90 to 120 minutes |
| First REM stage length | 10 minutes |
| Later REM stage length | Up to an hour |
| Total REM sleep for adults | 25% of sleep time |
| Total REM sleep for newborns | 50% of sleep time |
| Total REM sleep for babies and children | More than adults |
| Total deep sleep for adults | 25% of sleep time |
| Total deep sleep for newborns | 25-30% of sleep time |
| Total deep sleep for children | More than adults |
| Total deep sleep for teenagers | Less than children |
What You'll Learn

How to increase REM sleep
REM sleep is important for brain health and function. It is involved in dreaming, memory, emotional processing, and healthy brain development.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to help you wind down each night. Try taking a warm bath or shower, reading a book, or listening to soft music.
- Stick to a sleep schedule and try to wake up and go to bed at the same time every day, even on weekends and holidays. This will help regulate your sleep/wake cycle.
- Avoid nicotine and caffeine, especially close to bedtime. Caffeine blocks brain chemicals that promote sleep.
- Exercise and spend some time outside in natural sunlight every day. Try to exercise outside in the morning, as the natural light will help set your body's sleep/wake cycle.
- Avoid alcohol and large meals close to bedtime. Alcohol and food can disrupt sleep, especially when consumed in large quantities.
- Avoid TV and electronics before bed as the light from these screens can interfere with your sleep.
Trazodone's Effect on REM Sleep: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

The benefits of REM sleep
REM sleep is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle. It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. It is important for several reasons, including:
- Memory consolidation: REM sleep helps the brain process new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, maintaining others, and deciding which ones to delete.
- Emotional processing: The brain processes emotions during REM sleep. Dreams, which are more vivid in this stage, may be involved in emotional processing. The amygdala, the part of the brain that processes emotions, activates during REM sleep.
- Brain development: Researchers hypothesise that REM sleep promotes brain development, as newborns spend most of their sleep time in this stage.
- Wakefulness preparation: REM sleep, through its activation of the central nervous system, might help us prepare to wake up. This may explain why we spend increasing amounts of time in REM sleep as the night progresses and why we are easier to wake up during this stage.
- Bone health and muscle growth: REM sleep is crucial for bone health and muscle growth, irrespective of age.
- Immune system: Quality sleep is important for several brain functions, including how nerve cells (neurons) communicate with each other. It also boosts the immune system by triggering hormone production, which is beneficial in maintaining a good body temperature.
- Learning and cognitive abilities: REM sleep may play a role in learning and memory. It directly influences your cognitive abilities and memory retention. Lack of REM sleep can lead to long-term memory loss and affect the functioning of neurons.
Enhancing REM Sleep: Strategies for Deeper Rest
You may want to see also

The stages of sleep
Sleep is a complex process that involves various stages, and understanding these stages is crucial for optimising sleep quality. Sleep can be broadly categorised into two types: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Each sleep cycle, lasting around 90 to 120 minutes, consists of three stages of NREM sleep followed by a stage of REM sleep.
The first stage of NREM sleep, known as N1, occurs when a person first falls asleep. This stage usually lasts from one to seven minutes, during which the body and brain activities start to slow down, and there are brief periods of muscle movements. It is relatively easy to wake someone during this stage, but if uninterrupted, they quickly progress to the next stage.
The second stage, N2, is characterised by a further decrease in body temperature, muscle relaxation, and slower breathing and heart rate. Brain activity slows down, but there are short bursts of electrical activity, which experts believe are involved in memory consolidation. N2 accounts for about 45% of total sleep time, with each subsequent N2 stage becoming longer.
The third stage, N3 or deep sleep, is the deepest stage of slumber. It is more challenging to wake someone during this phase, and if they do, they may experience sleep inertia, feeling disoriented for up to 30 minutes. N3 is vital for bodily recovery and growth, immune system enhancement, and other key physiological processes. This stage makes up about 25% of total sleep time in adults, but the proportion decreases with age.
Following NREM sleep is the REM stage, characterised by increased brain activity, rapid eye movements, irregular breathing, and elevated heart rate. The muscles become temporarily paralysed, except for those controlling breathing and eye movements. REM sleep is associated with dreaming and plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. The first REM stage is typically the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes, with subsequent stages lengthening throughout the night.
Throughout the night, individuals cycle through these four stages multiple times, with each cycle progressing from light sleep in N1 to deep sleep in N3, followed by REM sleep, before starting the cycle anew. The duration and composition of each cycle can vary based on factors such as age, recent sleep patterns, and even alcohol consumption.
Alcohol and REM Sleep: A Troubling Relationship
You may want to see also

How to get a good night's sleep
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process, but there are some steps you can take to improve your sleep quality and get a good night's rest.
Firstly, it's important to understand the sleep cycle. A typical night of sleep consists of four to six sleep cycles, each lasting around 90 minutes. Each cycle includes three stages of non-REM sleep, which is deeper and more restorative, followed by a stage of REM sleep, which is when dreams occur and the brain is more active.
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends and vacations. This will help regulate your body's sleep/wake cycle.
- Avoid bright lights and electronics before bed, as the light from screens can disrupt your sleep.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime, as these substances can interfere with your sleep.
- Exercise regularly, preferably outside in natural light, as this can improve your sleep quality and boost your mood and energy levels.
- Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to help you wind down, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath.
- Make sure your bedroom is comfortable, dark, and quiet.
- Avoid large meals, caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Opt for a light snack if you're hungry.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation.
- If you can't sleep, get up and do something relaxing until you feel sleepy again.
Does Cannabis Affect Your REM Sleep?
You may want to see also

The importance of REM sleep
REM sleep is important for several reasons. Firstly, it plays a role in memory consolidation, helping your brain to process and store new information. This is essential for learning and improving your ability to concentrate. Secondly, REM sleep is involved in emotional processing, which is crucial for mood regulation and overall mental health. Thirdly, REM sleep may contribute to brain development, especially in infants and children. Newborns spend most of their sleep time in REM, and the amount of REM sleep gradually decreases as the brain matures. Finally, REM sleep is associated with dreaming, and it is during this stage that most of your vivid dreams occur.
The negative effects of insufficient REM sleep can be serious. Lack of REM sleep can lead to trouble coping with emotions, difficulty concentrating, a weakened immune system, and a grogy feeling in the morning. Over time, chronic REM sleep deprivation has been linked to health conditions such as diabetes, depression, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, getting adequate REM sleep is crucial for maintaining physical and mental well-being.
The Mystery of REM Sleep: Can You Survive Without It?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. It is a stage of sleep where your eyes move rapidly behind closed eyes, your heart rate speeds up, and your breathing becomes irregular. It is also the stage of sleep where your brain is most active and dreams occur.
Most adults need around 20% to 25% of REM sleep, which is approximately two hours for a full night's sleep.
If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience symptoms such as trouble coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and feeling groggy in the morning.
To increase your REM sleep, focus on getting more sleep overall. Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, avoid caffeine and nicotine, exercise regularly, and avoid screens before bed.
During non-REM sleep, your brain is less active, your heart rate and body temperature decrease, and your breathing slows down. Non-REM sleep includes three stages of increasingly deeper sleep, while REM sleep is the final stage of the cycle.