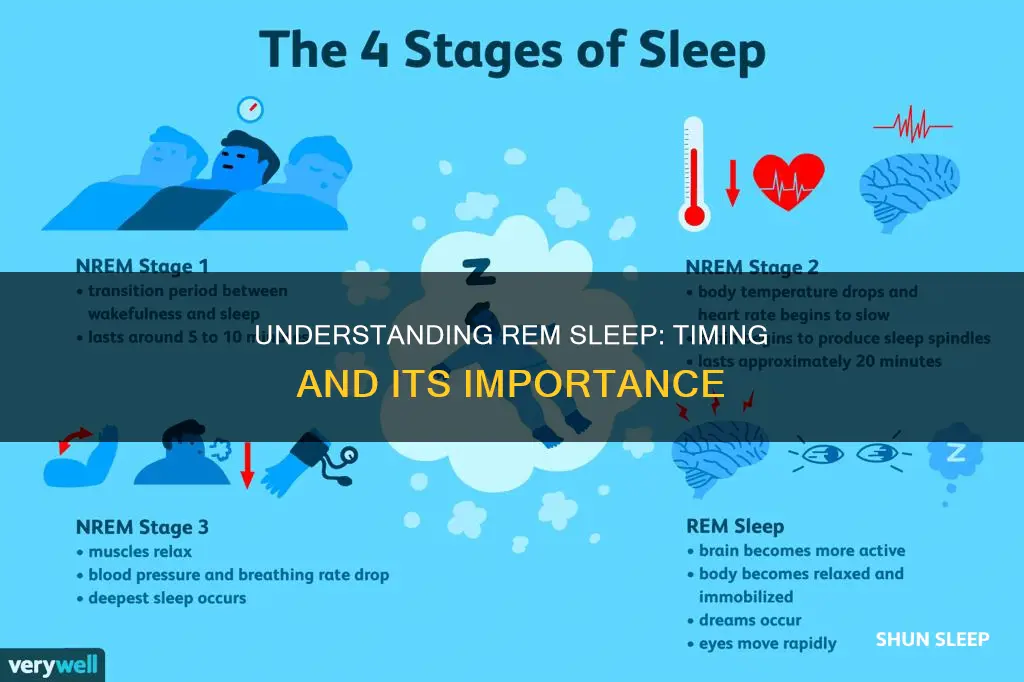
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. During sleep, the body cycles between non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep, marking the end of the first sleep cycle. Each cycle, which includes three stages of non-REM sleep and a stage of REM sleep, lasts between 80 to 120 minutes, with four to six cycles occurring per night.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of sleep cycles per night | 4 to 6 |
| Time to enter REM sleep | 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep |
| First REM sleep duration | 10 minutes |
| Final REM sleep duration | Up to an hour |
| Total REM sleep duration | 2 hours |
| REM sleep percentage in a night | 20% to 25% |
| REM sleep brain activity | Similar to brain activity when awake |
| REM sleep occurrence | Later in the night |
| REM sleep frequency | More frequent during sleep deprivation |
| REM sleep depth | Deeper during sleep deprivation |
| REM sleep intensity | More intense during sleep deprivation |
What You'll Learn

REM sleep occurs 60-90 minutes after falling asleep
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. During sleep, the body cycles between non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The first cycle of REM sleep typically occurs around 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. This initial REM period is usually brief, lasting about 10 minutes, but subsequent cycles become longer, with the final one potentially lasting up to an hour.
REM sleep is characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, and a faster heart rate. The body's muscles also become temporarily paralysed during this stage, preventing individuals from acting out their dreams. Dreams are typically more vivid during REM sleep due to the heightened brain activity, which is similar to the brain activity experienced during wakefulness.
The duration of REM sleep varies across different age groups. Newborns spend approximately half of their sleep time in this stage, while adults average around 20-25% of their total sleep in REM. As people age, the amount of REM sleep slightly decreases, with older adults experiencing around 17% of their sleep in this stage by the age of 80.
The sleep cycle, which includes both non-REM and REM stages, repeats about 4 to 6 times each night. Each cycle lasts between 80 to 120 minutes, and the first REM episode usually occurs about an hour to two hours after falling asleep.
Overall, REM sleep is crucial for brain health and function. It aids in learning, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. Additionally, REM sleep may offer protection against dementia, as lower REM levels have been associated with an increased risk of developing dementia.
Enhancing REM Sleep: Simple Strategies for Deeper Rest
You may want to see also

It is the fourth stage of sleep
Sleep is divided into four distinct stages, and REM sleep is indeed the fourth and final stage. This stage is characterised by a number of unique physical attributes, including rapid eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity.
During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids, and the heart rate speeds up. Breathing also becomes irregular, and the brain is highly active. In fact, brain activity during this stage is similar to that of when we are awake.
The first cycle of REM sleep occurs around 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. As part of a full night's sleep, sleepers cycle through the four stages multiple times: three stages of non-REM sleep, followed by one stage of REM sleep. Each cycle through all the sleep stages takes 90 to 120 minutes to complete. With each new cycle, sleepers spend increasing amounts of time in REM sleep, with most of it taking place in the second half of the night.
REM sleep is important for several reasons. Firstly, it plays a role in memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory and deciding which ones to delete. Secondly, it aids in emotional processing. Dreams, which are more vivid during REM sleep, may be involved in this process, and the amygdala (the part of the brain that processes emotions) is activated during this stage. Thirdly, REM sleep is thought to be important for brain development, especially in newborns, who spend most of their sleep time in this stage. Finally, REM sleep may help prepare the body for wakefulness, which could explain why it becomes more prevalent in the second half of the night, and why people are easier to wake up during this stage.
Lack of REM Sleep: Potential Health Risks and Consequences
You may want to see also

It is characterised by relaxed muscles and quick eye movement
During REM sleep, the body is characterised by relaxed muscles and quick eye movement. This is the fourth stage of sleep, and it is also known as active sleep, paradoxical sleep, or dream sleep. During this stage, the body's muscles become temporarily paralysed, preventing sleepers from acting out their dreams. This paralysis is not complete, however, as the eyes continue to move rapidly behind closed eyelids.
REM sleep is important for brain health and function. It is associated with dreaming, memory, emotional processing, and brain development. Dreaming occurs mostly during REM sleep, and the dreams are usually more vivid than those during non-REM sleep. The brain also processes emotions during REM sleep, and the amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions, is activated during this stage.
The brain further processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, maintaining others, and deciding which ones to delete. This stage is also thought to aid in the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. This may explain why infants, particularly newborns, require a lot of REM sleep.
The amount of REM sleep needed changes as we age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, but this decreases to just over 20% by age 20. In older adults, time spent in REM sleep decreases to about 17% by age 80.
REM sleep can be affected by factors such as stress, drug withdrawal, and sleep deprivation. When the body is deprived of REM sleep, it will naturally increase it the next night, a phenomenon known as REM rebound.
THC and Sleep: Does It Affect Your REM?
You may want to see also

Dreaming usually happens during REM sleep
During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly in different directions, and the brain is active. Brain activity during this stage is similar to its activity when a person is awake. The muscles in the arms and legs become temporarily unable to move, which prevents sleepers from acting out their dreams.
The first cycle of REM sleep usually occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. The first period of REM sleep is typically the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes. Each subsequent REM stage gets longer, with the final one lasting up to an hour.
REM sleep stimulates areas of the brain that help with learning and memory. It is important for brain development, especially in infants and children. It also aids in emotional processing and mood regulation. Studies have shown that people who get less REM sleep may have a greater risk of developing dementia.
Overall, the amount of REM sleep a person needs depends on their age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, while adults spend about 20% of their sleep in this stage.
Diphenhydramine: Preventing REM Sleep or Just a Myth?
You may want to see also

REM sleep is important for brain development and memory consolidation
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the proper functioning of the body and brain. During sleep, the body cycles between non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. While NREM sleep is characterised by slower brain waves and relaxed muscles, REM sleep is marked by rapid eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and heightened brain activity.
REM sleep is crucial for brain development and memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain exhibits increased activity, resembling the brain activity observed during wakefulness. This heightened brain activity serves several important functions, including memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development.
Memory Consolidation:
REM sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation, the process of strengthening and stabilising memories. During this stage, the brain reviews and processes new information, skills, and experiences from the day, deciding what to retain as long-term memories and what to discard. Research has shown that sleep after learning is essential for cementing new information into the brain's architecture, improving memory retention and recall.
Brain Development:
REM sleep is particularly important for brain development in infants and children. Newborns spend a significant amount of their sleep time in the REM stage, which is believed to promote brain development. The amount of REM sleep gradually decreases with age, as the brain matures.
Emotional Processing:
REM sleep also facilitates emotional processing by activating the amygdala, the region of the brain responsible for processing emotions. Dreams, which are typically more vivid during REM sleep, may play a role in this process.
Overall, REM sleep is a critical component of sleep, contributing to memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. By understanding the importance of REM sleep, we can appreciate the complex ways in which sleep supports our cognitive functions and overall well-being.
REM Sleep: Lightest Stage or Deep Sleep's Cousin?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. It is one of the two main stages of sleep, the other being non-REM sleep.
REM sleep occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. Each sleep cycle, which lasts between 80 to 120 minutes, includes a period of REM sleep.
On average, a person experiences four to six cycles of REM sleep per night.
During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly, your heart rate increases, your breathing becomes irregular, and your muscles become temporarily paralysed. Dreaming also typically occurs during this stage.
REM sleep is important for learning, memory, emotional processing, and brain development. It also helps with mood regulation and may offer protection against dementia.







