Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process, and while it may seem like a simple concept, it is anything but. When we sleep, we cycle through different stages of sleep, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three or four stages, depending on the source, with the deepest sleep occurring during the last stage. During NREM sleep, the body repairs tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. On the other hand, REM sleep is when most dreams occur, and it is associated with learning, memory, and mood regulation. Throughout the night, our sleep cycles between NREM and REM sleep, with each cycle lasting around 90 to 120 minutes. While the purpose of this cyclical pattern is not yet fully understood, disruptions in sleep cycles can lead to sleep disorders.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of stages | 3 |
| First stage | Light sleep, slow eye movement, easy to wake up |
| Second stage | Light sleep, heart rate and breathing slow down, body temperature drops |
| Third stage | Deep sleep, harder to wake up, disoriented if woken up |
| Dreaming | Occurs in both REM and NREM sleep |
| Muscle paralysis | Occurs in REM sleep |
| Eye movement | Rapid in REM sleep, slow in NREM sleep |
| Brain activity | More active in REM sleep |
| Heart rate | Quickens in REM sleep |
| Blood pressure | Drops in NREM sleep |
| Breathing | Slows down in NREM sleep |
| Memory consolidation | Occurs in NREM sleep |
What You'll Learn
- NREM sleep is split into three stages: N1, N2, and N3
- During NREM sleep, various bodily functions slow down or stop, allowing for repair and restoration
- Dreaming occurs during both REM and NREM sleep
- NREM sleep is important for physical and mental restoration
- NREM sleep is associated with declarative memory consolidation

NREM sleep is split into three stages: N1, N2, and N3
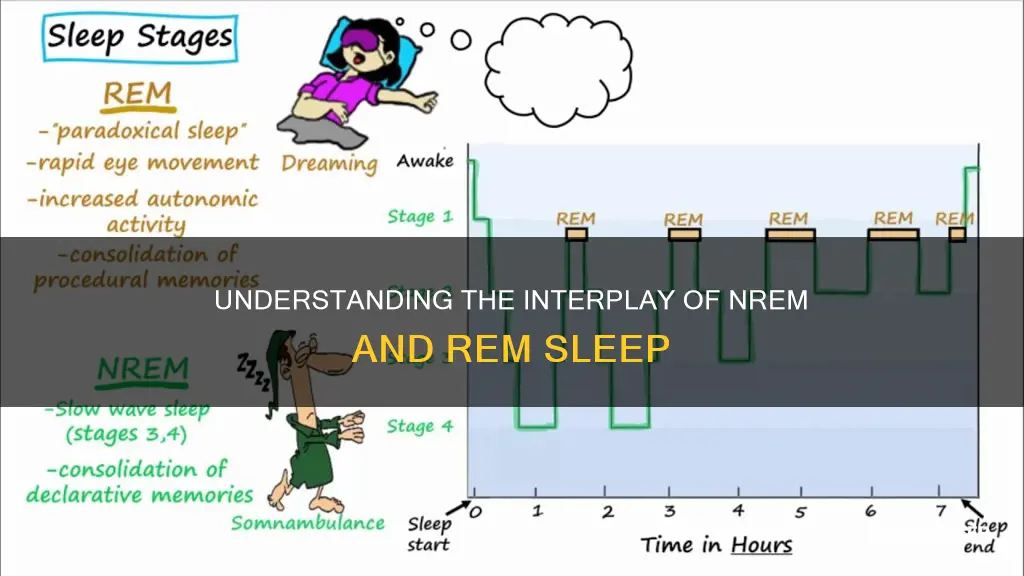
NREM sleep is split into three distinct stages: N1, N2, and N3. Each stage is characterised by unique mental processes, but they all share a tendency for the sleeper to experience slowed breathing, muscle activity, heartbeat, and brain waves.
N1
N1 is the lightest stage of sleep, usually lasting only a few minutes. During this stage, eye movements are slow and rolling, and the heartbeat and breathing slow down. Muscles begin to relax, and the brain produces low-amplitude mixed-frequency waves in the theta range (4 to 7 Hz).
N2
N2 is a light sleep, but deeper than N1. This stage accounts for about 45% of total sleep time and is considered a lighter stage of sleep from which you can be awakened easily. During N2, the heartbeat and breathing slow down further, and body temperature drops. Two distinct brain wave features appear for the first time: sleep spindles and K-complexes.
N3
N3 is the deepest stage of NREM sleep. It is also known as slow-wave, or delta, sleep. This stage is the most difficult to awaken from, and if someone is woken up during this stage, they will likely experience sleep inertia, a state of confusion or "mental fog" that can last up to 30 minutes. During N3, the heartbeat and breathing are at their slowest, and the body is fully relaxed. The brain produces delta brain waves, which are slower brain waves that indicate healing and restorative sleep. It is during this stage that the body performs important health-promoting functions, such as tissue repair and growth, cell regeneration, and strengthening of the immune system.
The Mystery of Missing REM Sleep: What's Keeping Me Awake?
You may want to see also

During NREM sleep, various bodily functions slow down or stop, allowing for repair and restoration
During NREM sleep, the body powers down and various bodily functions slow down or stop altogether, allowing for repair and restoration. This is the time when the body and brain use less energy, giving cells the chance to resupply and stock up for the next day.
In the first stage of NREM sleep, heartbeat, eye movements, brain waves, and breathing activity begin to slow down. Motor movements also decrease, although muscle twitches called hypnic jerks may occur. This stage usually lasts only a few minutes.
The second stage of NREM sleep is characterised by a continued slowing of heartbeat, breathing, muscle activity, and eye movements. The body temperature also drops during this stage. Brain waves slow down further, and two unique types of brain activity appear: sleep spindles and K-complexes. Sleep spindles are essential for memory and learning, while K-complexes may play a role in maintaining sleep and waking the sleeper up if the brain perceives a stimulus as dangerous.
The third stage of NREM sleep is the deep sleep stage, during which the body repairs and regenerates itself. The heartbeat, breathing, muscle activity, and brain waves are at their slowest during this stage. The body releases growth hormones and carries out tissue, muscle, and bone repair. Deep sleep is also thought to help regulate glucose metabolism, immune system functioning, hormone release, and memory.
Weed and Sleep: Does Cannabis Affect Your REM Sleep?
You may want to see also

Dreaming occurs during both REM and NREM sleep
During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyes, the heart rate speeds up, and breathing becomes irregular. The brain is highly active during this stage, and there is a temporary loss of muscle tone. This stage is associated with dreaming, memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development.
On the other hand, NREM sleep is divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3, with N3 being the deepest. During NREM sleep, various bodily functions slow down or stop altogether, allowing for repair and restoration. In the deepest stage of NREM sleep, the body repairs and regenerates tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system.
While dreaming occurs during both REM and NREM sleep, the nature of dreams can differ between the two stages. Dreams during REM sleep tend to be more vivid and emotionally intense, while dreams during NREM sleep are often more mundane and less memorable. Additionally, the mental activity during NREM sleep is thought-like, while dreams during REM sleep include hallucinatory and bizarre content.
The occurrence of dreaming during both REM and NREM sleep suggests the involvement of two different mind generators, with NREM dreams simulating friendly interactions and REM dreams expressing aggressive tendencies. Furthermore, studies have shown that the mechanisms that create REM sleep cause changes in one's sleep experience, leading to sub-cortical activation during NREM sleep that results in dreaming during the morning hours.
Does ZzzQuil Help You Get a Good Night's Rest?
You may want to see also

NREM sleep is important for physical and mental restoration
Sleep is a highly active process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and repair. Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep is a vital part of the sleep cycle, consisting of three stages: N1, N2, and N3, with N3 being the deepest. NREM sleep accounts for 75% to 80% of total sleep time and is crucial for physical and mental restoration.
During NREM sleep, various bodily functions slow down or stop, allowing for repair and regeneration. In the first stage, heartbeat, eye movements, brain waves, and breathing activity begin to slow, and muscle movements decrease. The second stage is marked by a continued slowing of these functions, as well as a reduction in body temperature. The third stage, or deep sleep, is when the body and brain undergo the most critical regeneration. This is when the body releases growth hormones, repairs tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system.
NREM sleep is essential for physical recovery and memory consolidation. Studies have shown that during this stage, the brain consolidates new memories and skills, optimising mental pathways for future learning. It plays a role in both declarative memory (recalling information) and procedural memory (learning new tasks). Sleep spindles and slow waves during NREM sleep are believed to strengthen neural connections and prepare pathways for the next day.
Additionally, NREM sleep contributes to physical growth and repair. The brain uses less energy during this stage, allowing for restoration. Disruptions in NREM sleep, such as insomnia or sleep disorders, can interfere with this process and impact fat metabolism and cardiovascular health.
In summary, NREM sleep is crucial for physical and mental restoration. It allows the body to repair and regenerate, while also consolidating memories and optimising mental pathways. Disruptions to NREM sleep can have negative consequences for physical and mental health, highlighting the importance of adequate sleep for overall well-being.
Muscle Movement During REM Sleep: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

NREM sleep is associated with declarative memory consolidation
During NREM sleep, the brain consolidates new memories and skills into a more durable format. It also optimises mental pathways for future learning. Specific patterns during NREM sleep are associated with better working memory, verbal fluency, motor learning, and word retrieval.
According to the active systems consolidation theory, declarative memory is consolidated and integrated into existing knowledge networks, especially during non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Declarative memory, or episodic memory, is strengthened by the overlapping reactivation of neurons in shared elements in the brain, which leads to a greater strengthening of commonalities. This process is known as the information overlap to abstract (IOtA) model.
During NREM sleep, the ensemble neuronal processes in the hippocampus, thalamus, and neocortex are assumed to be important for systems memory consolidation. Some studies assume that both REM and NREM sleep are necessary for integrating newly acquired memory into the existing memory network. Memory stabilisation occurs during NREM sleep, especially during slow wave sleep (SWS), while memory modification and integration into the existing knowledge base may occur during REM sleep.
The contribution of slow wave sleep to the optimisation of these pathways can be conceived as a recovery period from the day's learning. Researchers propose that more slow wave sleep is needed to recover after either more time spent awake or a more intensive learning process.
Power Nap: REM Sleep Needed or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep is an essential part of the sleep cycle. It involves three stages: N1, N2, and N3, with N3 being the deepest. NREM sleep stages are vital for physical and mental restoration.
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly and your brain is active. Your brain activity is similar to its activity when you’re awake. Dreams typically happen during REM sleep.
NREM and REM sleep do not overlap. Over the course of a period of sleep, NREM and REM sleep alternate cyclically. A sleep episode begins with a short period of NREM sleep, progressing through stages 1 to 3, followed by a shorter period of REM sleep, and then the cycle starts over again.
The function of alternations between NREM and REM sleep is not yet fully understood. However, irregular cycling and/or absent sleep stages are associated with sleep disorders.







