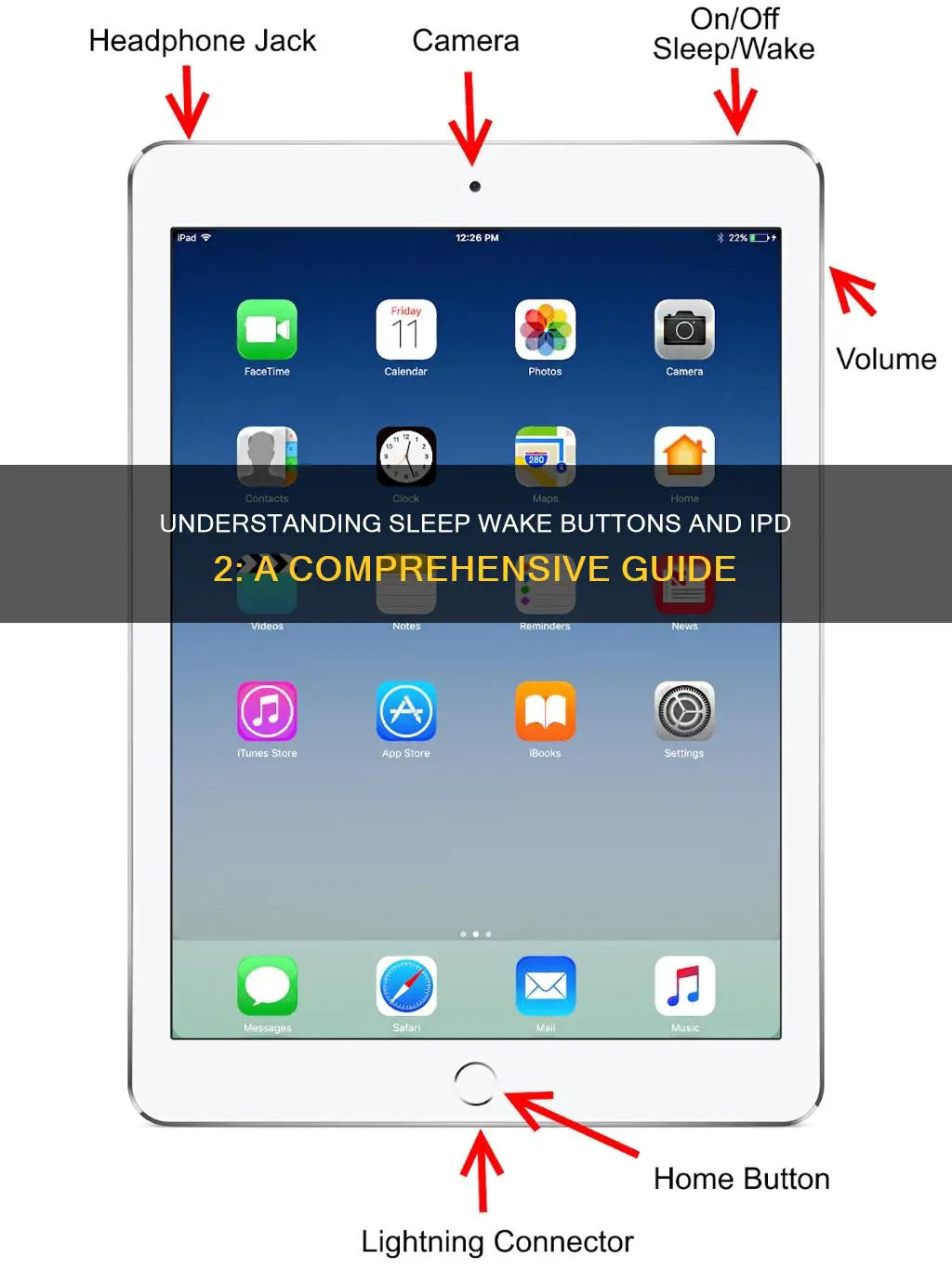
The Sleep/Wake Button and I/O Port (IPD 2) is a crucial component in modern electronic devices, particularly smartphones and tablets. This button serves as a dual-purpose control, allowing users to easily switch between sleep and wake modes, as well as providing a dedicated input/output port for various functions. Understanding its functionality and impact on device operation is essential for optimizing user experience and ensuring efficient device management.
What You'll Learn
- Sleep Wake Button: A physical or virtual button that triggers sleep or wake modes on a device
- I/O Ports: Input/Output ports for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and external displays
- Power Management: Controls power states, including sleep, hibernate, and power-off modes
- IPD (Input/Output Device): Hardware components that interact with the user, like touchscreens and keyboards
- BIOS/UEFI: Firmware that initializes hardware during startup, managing sleep/wake functions

Sleep Wake Button: A physical or virtual button that triggers sleep or wake modes on a device
The Sleep Wake Button is a crucial feature on many electronic devices, offering a simple yet effective way to control power states. This button, whether physical or virtual, serves as a direct interface for users to initiate sleep or wake modes on their gadgets. When a user presses the Sleep Wake Button, it sends a signal to the device's operating system, prompting it to transition from an active state to a power-saving mode or vice versa. This mechanism is fundamental in modern technology, ensuring that devices can be easily managed and their energy consumption optimized.
In the context of IPD 2 (presumably referring to a specific device or a version of a product), the Sleep Wake Button plays a pivotal role in user experience. It allows for quick and intuitive control, especially in scenarios where users might be in a hurry or require immediate access to a particular function. For instance, on a smartphone, pressing this button can instantly put the device to sleep, preventing accidental taps or notifications during a meeting or while driving. Similarly, on a computer, it can initiate a quick sleep mode, saving power and reducing wear and tear on the hardware.
The design of the Sleep Wake Button varies across different devices. On some smartphones, it is a physical button located on the side or top of the device, providing a tactile feedback mechanism. This physical button is often used in conjunction with a power menu or settings to offer users multiple ways to manage their device's power state. In contrast, other devices, especially those with touch-sensitive interfaces, rely on a virtual Sleep Wake Button, which is an on-screen icon or gesture. This virtual button is often part of a larger control panel, allowing users to customize its behavior and placement.
The functionality of the Sleep Wake Button extends beyond mere power management. It can also be programmed to perform specific tasks when activated. For example, on a smart speaker, pressing this button might initiate a voice assistant, ready to respond to user commands. On a tablet, it could launch a specific app or put the device into presentation mode. The versatility of this button is a testament to its importance in modern device design, where user-friendliness and efficiency are paramount.
In summary, the Sleep Wake Button is an essential component of device interaction, providing a direct and efficient way to manage power states. Its physical or virtual nature allows for quick access, ensuring that users can easily transition their devices between active and sleep modes. With its ability to be customized and programmed, this button enhances the overall user experience, making technology more intuitive and responsive to individual needs.
When Your Child Has a Fever: Waking or Not Waking?
You may want to see also

I/O Ports: Input/Output ports for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and external displays
I/O ports, short for Input/Output ports, are essential interfaces on computers and other electronic devices that facilitate communication between the device and external peripherals. These ports enable users to connect a variety of devices, such as keyboards, mice, printers, scanners, and external displays, to the computer system. Each I/O port serves a specific purpose, providing a pathway for data transfer between the device and the connected peripherals.
The most common types of I/O ports include USB (Universal Serial Bus), HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface), DisplayPort, Ethernet, and audio jacks. USB ports are versatile and widely used for connecting keyboards, mice, external hard drives, and various other peripherals. HDMI ports are crucial for connecting high-definition displays, such as modern TVs and monitors, allowing for the transmission of video and audio signals. DisplayPort offers similar functionality to HDMI but often provides higher resolutions and refresh rates. Ethernet ports are used for wired network connections, ensuring a stable and fast internet connection. Audio jacks, typically in the form of 3.5mm mini-jacks, are used for connecting headphones, speakers, and microphones.
I/O ports are designed with specific standards and specifications to ensure compatibility and ease of use. For example, USB ports follow a standardized protocol that defines the data transfer rates, power requirements, and connector types. This standardization allows for a wide range of peripherals to be connected to a single USB port, making it a versatile and widely adopted interface. Similarly, HDMI and DisplayPort have their own specifications, ensuring optimal video and audio quality when connecting to compatible displays.
When connecting peripherals, it's important to match the type of I/O port on the device with the port on the peripheral. For instance, using a USB keyboard with a computer that only has HDMI ports would require an adapter or a different keyboard with an HDMI connection. Modern devices often feature a combination of I/O ports to accommodate various peripherals, ensuring flexibility and convenience for users.
In summary, I/O ports are critical components that enable the connection of peripherals to computers and other devices. They provide the necessary pathways for data transfer, allowing users to interact with their devices and peripherals seamlessly. Understanding the different types of I/O ports and their specifications is essential for ensuring compatibility and optimizing the user experience when connecting external devices.
Helping a Sleep Walker: When and How to Intervene Safely
You may want to see also

Power Management: Controls power states, including sleep, hibernate, and power-off modes
The Sleep/Wake button is a crucial component in managing power states on electronic devices, especially those with advanced power management systems like the IPD 2 (Intelligent Power Device). This button is designed to control the device's power consumption and performance, allowing users to switch between different power modes efficiently. When you press the Sleep/Wake button, the device enters a specific power state, optimizing its energy usage and potentially extending battery life.
In the context of power management, the Sleep mode is a low-power state where the device's performance is significantly reduced, and power consumption is minimized. During Sleep, the device can still retain some data in its memory, ensuring that it can quickly resume its previous state when awakened. This is particularly useful for laptops, tablets, and smartphones, as it allows users to leave their devices in a low-power state without losing their current work or media session. The Sleep/Wake button triggers this mode, ensuring the device can enter a deep sleep state while still being responsive to user inputs.
Hibernate mode is another critical power state that the Sleep/Wake button can activate. This mode is similar to Sleep but takes power management a step further. When the device hibernates, it saves the current system state, including the operating system and open applications, to a hard drive or solid-state drive. This process ensures that the device can be restored to its exact state when it wakes up, providing a seamless user experience. Hibernate mode is ideal for laptops and computers, as it allows users to shut down the device completely while preserving their work, making it a powerful tool for power management.
The Power-off mode, as the name suggests, completely powers down the device, cutting off all power to the system. This mode is essential for devices with removable batteries, as it ensures the battery is not drained when not in use. When in Power-off mode, the device's internal components are shut down, and it requires a manual restart to turn it back on. The Sleep/Wake button can initiate this mode, providing users with a quick and convenient way to ensure their device is in a secure and energy-efficient state when not in use.
In summary, the Sleep/Wake button is a vital interface for power management, offering users control over various power states. It enables devices to enter Sleep or Hibernate modes, reducing power consumption and preserving system states. Additionally, the Power-off mode, triggered by this button, ensures the device is completely powered down when not required. Understanding these power management functions is essential for optimizing device performance and battery life, especially with advanced power-saving technologies like IPD 2.
Awakening the Slumbering: Strategies to Revive Your Body's Sleeping Parts
You may want to see also

IPD (Input/Output Device): Hardware components that interact with the user, like touchscreens and keyboards
The Sleep/Wake button is a crucial component of many electronic devices, especially those with touch-based interfaces. It serves as a primary input mechanism for users to initiate specific actions, such as powering on or off the device, putting it into a sleep mode, or triggering a quick action like taking a screenshot. This button is often located on the side or top of the device, making it easily accessible to the user. Its functionality is essential for providing a seamless user experience, ensuring that users can control their devices efficiently without relying on complex menus or gestures.
Input/Output (I/O) devices, or Input/Output (I/O) interfaces, are hardware components that facilitate communication between a computer or electronic device and its user. These devices enable users to input data, commands, or instructions into the system and receive output, such as visual or auditory feedback. I/O devices play a vital role in enhancing user interaction and making technology more accessible and user-friendly.
One of the most common I/O devices is the touchscreen, which has revolutionized user interaction with mobile devices and tablets. Touchscreens allow users to interact with the device by touching the screen directly, making it intuitive and efficient. They respond to various touch inputs, such as taps, swipes, and gestures, enabling users to navigate through menus, select options, and perform actions with a simple touch. This technology has become ubiquitous in modern smartphones and tablets, offering a natural and intuitive way to interact with digital content.
Keyboards are another essential I/O device, providing a traditional input method for text input and command execution. They offer a more precise and efficient way to input data compared to touch-based interfaces, especially for tasks requiring accurate typing or complex commands. Modern keyboards often include additional features like backlighting, customizable keys, and multimedia controls, enhancing their functionality and user experience.
In the context of IPD (Input/Output Device), the Sleep/Wake button can be considered a specialized input mechanism. It is designed to provide a quick and convenient way to control the device's power state, ensuring that users can easily manage their devices without navigating through complex menus. This button's functionality is often integrated with the device's operating system, allowing for seamless power management and user control.
Awakening Love: Strategies to Revive Your Sleeping Heart
You may want to see also

BIOS/UEFI: Firmware that initializes hardware during startup, managing sleep/wake functions
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) are essential components of a computer's firmware, which is a type of software that is embedded in the hardware and initializes the system during the startup process. These firmware systems play a critical role in managing the hardware components of a computer, including the sleep and wake functions. When a computer is powered on, the BIOS or UEFI firmware is the first software to execute, performing a series of tasks to initialize the hardware and prepare the system for the operating system. This initialization process involves recognizing and configuring various hardware components, such as the CPU, memory, storage devices, and input/output peripherals.
One of the key responsibilities of the BIOS/UEFI firmware is to manage the sleep and wake functions of a computer. When a user puts the computer into a sleep or hibernate state, the firmware saves the current state of the system, including the state of the CPU, memory, and open applications, to a designated storage area. This allows the computer to quickly resume its previous state when awakened, providing a seamless user experience. The firmware ensures that the system's hardware is properly configured to support the sleep mode, including adjusting power settings and disabling unnecessary peripherals to conserve energy.
During the startup process, the BIOS/UEFI firmware initializes the hardware and loads the operating system into memory. It also provides a user interface, often referred to as the BIOS setup or UEFI setup, which allows users to configure various system settings, including those related to power management. In this setup, users can adjust the sleep and wake settings, such as specifying the time after which the computer should enter sleep mode or defining the behavior of the sleep/wake button. This button is a physical input device that allows users to manually control the sleep and wake functions of the computer, providing an additional layer of convenience and control.
The sleep/wake button is connected to the BIOS/UEFI firmware, which interprets the button's input and executes the corresponding actions. When the button is pressed, the firmware responds by saving the current system state, powering down the display and certain peripherals, and entering the specified sleep mode. To wake the computer, the user can press the button again, and the firmware will restore the system from the saved state, bringing the computer back to its previous operational state. This process is managed by the firmware, ensuring that the hardware is configured correctly and that the system resumes its normal operation efficiently.
In summary, the BIOS/UEFI firmware is a critical component that initializes hardware during startup and manages various system functions, including sleep and wake operations. It works in conjunction with the sleep/wake button to provide users with the ability to control and customize their computer's power state. Understanding the role of these firmware systems and their interaction with physical input devices like the sleep/wake button is essential for optimizing system performance and ensuring a smooth user experience.
Should You Wake a Sick Toddler? Navigating Sleep and Illness
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Sleep/Wake Button is a physical button located on the NIPD 2 device, typically found on the side or front panel. It serves as a quick access point to toggle between sleep and wake states, allowing users to easily put the device to sleep or wake it up without relying on software controls.
When pressed, the Sleep/Wake Button triggers a power-off sequence, putting the NIPD 2 into a low-power sleep mode. This button is designed to provide a convenient way to conserve battery life and ensure the device is ready for use when needed.
Yes, the functionality of the Sleep/Wake Button can often be customized through the device's settings. Users may be able to configure the button to perform specific actions, such as launching a particular app, adjusting display settings, or enabling/disabling certain features when pressed.
While the Sleep/Wake Button is a useful feature, it is not always essential for basic device operation. The NIPD 2 may also offer alternative methods to put the device to sleep, such as automatic sleep timers, software shortcuts, or gesture controls, depending on the device's design and operating system.







