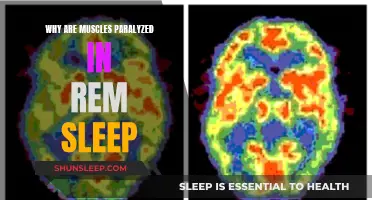
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is a recurring sleep state during which most dreaming occurs. During this state, the eyes move rapidly under closed eyelids, and the skeletal muscles are deeply relaxed. While there are no direct synonyms for REM sleep, it is associated with other terms such as paradoxical sleep, rapid eye movement, and non-REM sleep.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Other Name | Rapid Eye Movement Sleep |
| Dreaming | Yes |
| Brain Activity | High |
| Eye Movement | Rapid |
| Muscle State | Atonia (temporary paralysis) |
| Purpose | Memory formation, emotional processing, brain development, learning, memory consolidation, and creativity |
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep is critical for memory formation, emotional processing, and brain development
- REM sleep is characterised by high levels of brain activity and vivid dreaming
- The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes
- REM sleep is also known as paradoxical sleep because it involves seemingly contradictory states of an active mind and a sleeping body
- REM sleep deprivation may increase the likelihood of chronic conditions such as stress disorders and obesity

REM sleep is critical for memory formation, emotional processing, and brain development
REM sleep, short for rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth and final stage of sleep. It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. During REM sleep, the brain processes emotions and consolidates memories. Dreaming, which is more vivid in REM sleep, may also be involved in emotional processing.
Healthy sleep is fundamental for well-being. Sleep loss negatively impacts cognitive processing and emotional reactivity, as well as social behaviour, leading to feelings of loneliness. Sleep disturbances are a hallmark of mood disorders, and alterations in REM sleep architecture are particularly prominent in mental disorders such as major depression, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
REM sleep is also important for brain development, with newborns spending most of their sleep time in this stage. Researchers hypothesise that REM sleep promotes brain development, as animals born with less developed brains, such as humans and puppies, spend more time in REM sleep during infancy than those with more developed brains, like horses and birds.
Additionally, studies have shown that REM sleep deprivation interferes with memory formation. While the memory problems associated with a loss of REM sleep could be due to overall sleep disruption, REM sleep deprivation has been found to disrupt the brain's ability to generate new cells.
Understanding Delta Sleep: REM or Non-REM?
You may want to see also

REM sleep is characterised by high levels of brain activity and vivid dreaming
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth of four stages of sleep. During this stage, the eyes move rapidly, and brain activity is high, resembling the brain activity of someone who is awake.
REM sleep is also characterised by irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and vivid dreaming. The dreams that occur during REM sleep are usually more vivid than those that occur during non-REM sleep. This is because, during REM sleep, the brain is highly active and brain waves are more variable.
REM sleep is important for several reasons. Firstly, it plays a role in memory consolidation, with the brain processing new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, and deciding which ones to delete. Secondly, it is important for emotional processing. The amygdala, the part of the brain that processes emotions, is activated during REM sleep. Thirdly, REM sleep is important for brain development, with newborns spending most of their sleep time in this stage. Finally, it helps prepare the body for wakefulness, which may explain why it becomes easier to wake someone up during this stage.
On average, adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night.
Hormones: The REM Sleep Regulators
You may want to see also

The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is a sleep stage during which dreaming normally occurs. It is also critical for memory formation, emotional processing, and brain development.
During REM sleep, brain activity picks up, nearing levels seen when a person is awake. Simultaneously, the body experiences atonia, a temporary paralysis of the muscles, except for the eyes and the muscles that control breathing. Even though the eyes are closed, they can be seen moving quickly, which is how this stage gets its name.
REM sleep is believed to be essential for cognitive functions like memory, learning, and creativity. It is known for the most vivid dreams, which can be explained by the significant increase in brain activity. While dreams can occur in any sleep stage, they are less common and less intense during non-REM periods.
Under normal circumstances, a person does not enter the REM sleep stage until they have been asleep for about 90 minutes. As the night progresses, REM stages lengthen, especially during the second half. While the first REM stage may only last a few minutes, later stages can last for around an hour. In total, REM stages make up approximately 25% of sleep in adults.
Understanding the sleep cycle and its stages is crucial for promoting healthy sleep and addressing sleep disorders. By recognizing the importance of REM sleep and its unique characteristics, individuals can better appreciate the complex and restorative nature of sleep.
Get to REM Sleep Faster: Tips for Better Rest
You may want to see also

REM sleep is also known as paradoxical sleep because it involves seemingly contradictory states of an active mind and a sleeping body
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process, and the term "REM sleep" refers to the stage of sleep where most dreams occur. REM stands for "rapid eye movement", referring to the movement of the eyes behind closed eyelids during this sleep stage. It is also known as "paradoxical sleep", a term coined by French researcher Dr. Michel Jouvet in the 1950s.
The paradoxical nature of REM sleep lies in the contradictory states it involves. While the body is in a sleeping state, the mind is active, resembling the brain activity seen during waking hours. This stage of sleep is associated with vivid dreams, as the thalamus—a part of the brain responsible for processing sensory information—is active during REM sleep, contributing to the rich sensory experiences of dreaming.
REM sleep is also characterised by muscle atonia, or temporary paralysis, which prevents sleepers from acting out their dreams. This state of muscle atonia is disrupted in certain sleep disorders, such as REM sleep behaviour disorder, where individuals may act out their dreams, sometimes violently.
The purpose of REM sleep is still debated, but it is associated with several important functions, including learning, memory consolidation, and creativity. Most people complete four to six cycles of REM sleep each night, making up about 25% of total sleep time.
In summary, REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is aptly named paradoxical sleep due to the contradictory states of an active mind and a sleeping body. This stage of sleep is crucial for various cognitive functions and is when most dreaming occurs.
Tracking REM Sleep: Samsung Fit 2 Guide
You may want to see also

REM sleep deprivation may increase the likelihood of chronic conditions such as stress disorders and obesity
Sleep is highly conserved across evolution, suggesting vital biological functions that are yet to be fully understood. Sleep deprivation and stress have a reciprocal relationship. Sleep loss can lead to fatigue, irritability, changes in mood and memory, and issues with cognition and problem-solving. It can also affect cardiovascular health and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, cancer, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases.
REM sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of certain chronic conditions, such as stress disorders and obesity. Studies have shown that REM sleep deprivation can lead to hyperalgesia and increased pain sensitivity. It can also affect the regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, which is important for memory and learning. Additionally, REM sleep deprivation has been associated with increased anxiety and You may want to see also REM sleep is short for rapid eye movement sleep. Some synonyms for REM sleep are paradoxical sleep, rapid eye movement, and rapid eye movement sleep. REM sleep is a recurring sleep state during which dreaming occurs. It is characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and increased brain activity. REM sleep typically totals about two hours a night for adults, accounting for about 20-25% of total sleep. In infants, roughly 50% of sleep is REM sleep. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly under closed lids, and the skeletal muscles are deeply relaxed. There is also increased brain activity, accelerated respiration, and a faster heart rate.Lucid Dreaming: Rapid REM Sleep Gateway?
Frequently asked questions