Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that remains to be fully understood by experts. However, it is known that sleep is essential for the body and brain to rest, and a good night's sleep is vital for overall health and well-being. During sleep, the body cycles between non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep, characterised by rapid eye movement, increased brain activity, and temporary muscle paralysis, plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. Scientific research has linked sufficient REM sleep to improved learning, mood regulation, and protection against dementia. REM sleep typically makes up around 20-25% of total sleep time, and achieving optimal REM sleep is important for maintaining overall health.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
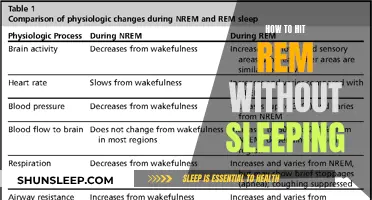
| Eye movement | Rapid |
| Brain activity | More active than in non-REM sleep |
| Muscle tone | Loss of muscle tone |
| Heart rate | Increased |
| Blood pressure | Increased |
| Dreaming | Most dreams occur during this stage |
| Memory | Memories are consolidated |
| Emotional processing | Emotions are processed |
| Brain development | Plays a role in brain development |
| Learning | Improved learning |
| Mood regulation | Improved mood regulation |
| Protection against dementia | Decreased risk of dementia |
What You'll Learn

REM sleep improves learning and memory consolidation
REM sleep is vital for improving learning and memory consolidation. During the REM stage, the brain prunes its synapses, which are the spaces where brain cells communicate with each other. This process enhances memory and problem-solving abilities. Additionally, REM sleep aids in the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. This may explain why newborns require a significant amount of REM sleep.
Research has shown that a lack of REM sleep can interfere with memory formation. Multiple studies on humans and animals suggest that REM sleep deprivation negatively impacts memory. While the specific effects of REM sleep deprivation are still being investigated, it is clear that this stage of sleep is crucial for cognitive performance.
Furthermore, REM sleep plays a role in emotional processing. During this stage, the brain processes emotions and emotional memories, including those associated with fear. This emotional processing during REM sleep may contribute to overall mood regulation, which is critical for daily work performance and quality of life.
Brain Activity During REM Sleep: Activation and Inhibition Explained
You may want to see also

REM sleep aids emotional processing and mood regulation
REM sleep is crucial for emotional processing and mood regulation. During this sleep stage, the brain processes emotions and emotional memories, including those associated with fear. This aids in mood regulation and ensures better mental concentration, which is critical for daily work performance and overall quality of life.
The amygdala, the brain region responsible for processing emotions, is activated during REM sleep. This activation helps in emotional processing and enables individuals to cope with emotions more effectively. The function of dreaming during REM sleep is also linked to emotional processing, as dreams are typically more vivid and intense during this stage.
The negative consequences of insufficient REM sleep highlight the importance of this sleep stage. Lack of REM sleep can lead to difficulty in managing emotions, impaired concentration, a weakened immune system, and feelings of grogginess upon waking. These symptoms underscore the critical role of REM sleep in maintaining emotional equilibrium and overall well-being.
Additionally, REM sleep plays a vital role in brain development, particularly in the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. This may explain why newborns and infants require a significant amount of REM sleep, as their brains are rapidly developing and consolidating new information.
Furthermore, REM sleep is associated with memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain processes and integrates new learnings, motor skills, and experiences from the day, committing some to long-term memory. This process of memory consolidation contributes to improved learning and problem-solving abilities.
Exploring Unique Dreams During REM Sleep
You may want to see also

REM sleep is important for brain development
REM sleep stimulates the areas of the brain that help with learning and memory. During this stage, the brain repairs itself, processes emotional experiences, and transfers short-term memories into long-term memories. Researchers have also found that people who get less REM sleep may have a greater risk of developing dementia later in life.
REM sleep is also important for brain development because it promotes the generation of new brain cells. Studies have shown that being deprived of REM sleep interferes with memory formation and the brain's ability to generate new cells.
REM Sleep: The Energetic Paradox
You may want to see also

REM sleep protects against dementia
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During REM sleep, your eyes move around rapidly in different directions, and your brain is active. Your brain activity is similar to its activity when you’re awake. Dreams typically happen during REM sleep.
REM sleep plays a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. A lack of REM sleep can cause trouble coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and feeling groggy in the morning.
Research has shown that people who get less REM sleep have a greater risk of developing dementia. A study published in the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology found that people who developed dementia spent an average of 17% of their sleep time in REM sleep, compared to 20% for those who did not develop dementia. The results showed that for every percent reduction in REM sleep there was a 9% increase in the risk of dementia.
How to Increase REM Sleep
To increase your REM sleep, you need to get more sleep overall. Here are some ways to improve your sleep:
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Set a sleep schedule and stick to it.
- Avoid nicotine and caffeine.
- Exercise and spend some time outside in natural sunlight every day.
- Avoid alcohol and meals close to bedtime.
- Avoid TV and electronics before bed.
REM sleep is important for brain development and memory consolidation. A lack of REM sleep has been linked to an increased risk of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, it is important to ensure that you are getting enough REM sleep to protect your brain health and reduce your risk of dementia.
Eye Movement in REM Sleep: What Does it Mean?
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep negatively impacts overall health
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that remains to be fully understood by experts. However, it is known that a good night's rest is essential for the body and brain to function properly. Sleep can be divided into two main stages: REM (rapid-eye movement) sleep and non-REM sleep. This response will focus on the negative consequences of insufficient REM sleep.
REM sleep is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it aids in memory consolidation and learning. During this stage, the brain processes and stores new information, improving memory and problem-solving abilities. Secondly, REM sleep plays a role in emotional processing and mood regulation. It helps the brain process emotional experiences and memories, including those associated with fear, and ensures better mental concentration. Thirdly, REM sleep is necessary for healthy brain development, especially in infants and children whose brains are still developing. Newborns spend almost half of their sleep in the REM stage, and this gradually decreases with age.
Lack of REM sleep can have serious negative effects on overall health and well-being. Insufficient REM sleep can lead to difficulty in coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, a weakened immune system, and feelings of grogginess in the morning. Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to the development of various health conditions, including diabetes, depression, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
The negative consequences of inadequate REM sleep extend beyond the individual. For example, sleep deprivation can impair an individual's ability to operate machinery or drive safely, posing a risk to others. Additionally, the economic impact of sleep deprivation is significant, with lost productivity and healthcare costs associated with sleep disorders amounting to billions of dollars annually.
To mitigate the negative impacts of insufficient REM sleep, it is essential to prioritize sleep hygiene and maintain a consistent sleep schedule. This includes practices such as winding down before bed, avoiding caffeine and nicotine, and limiting screen time close to bedtime. By improving sleep quality and duration, individuals can enhance their overall health and reduce the risks associated with inadequate REM sleep.
Understanding REM Sleep: Tracking Techniques and Insights
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During this stage of sleep, your eyes move rapidly in different directions, and your brain is active. Your brain activity is similar to its activity when you’re awake. Dreams typically happen during REM sleep.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory consolidation, mood regulation, brain development, and emotional processing. It also stimulates the areas of your brain that help with learning and memory.
Lack of REM sleep can lead to trouble coping with emotions, difficulty concentrating, a weakened immune system, and grogginess in the morning.