Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. While sleeping, the body cycles between REM (rapid eye movement) and non-REM sleep. During the REM stage, the eyes move rapidly and the brain is active, similar to when awake. Dreams typically occur during this stage, and the muscles become temporarily paralysed to prevent people from acting them out. REM sleep is important for learning and memory, and insufficient REM sleep can lead to negative consequences for overall health and brain function. Understanding the REM stage of sleep is crucial to optimising sleep quality and overall well-being.
What You'll Learn

REM sleep is important for brain health and function
Secondly, REM sleep aids in mood regulation by helping the brain process emotional memories, including those associated with fear. This emotional processing during REM sleep may also contribute to improved mental health and emotional well-being.
Thirdly, REM sleep is crucial for brain development, especially in infants and children. Newborns spend a significant amount of their sleep time in REM sleep, which is believed to aid in the development of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. The amount of REM sleep needed decreases with age, as the brain becomes more developed.
Finally, REM sleep may offer protection against dementia. Research suggests that reduced REM sleep is associated with an increased risk of developing dementia. Therefore, adequate REM sleep may help lower the chances of cognitive decline and dementia in older adults.
REM Sleep and Stage 4: Are They Connected?
You may want to see also

It helps with learning and memory
REM sleep is vital for learning and memory. During this stage, the brain repairs itself and processes emotional experiences. It also transfers short-term memories into long-term memories. This is known as memory consolidation.
During REM sleep, your brain prunes its synapses, the spaces in which brain cells communicate with one another. This process improves your memory and problem-solving abilities.
REM sleep also plays a role in brain development, particularly the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. This may explain why infants, especially newborns, require so much REM sleep.
Animal and human studies have documented increased REM sleep after learning. In a study of rats, those who learned a new maze spent more time in REM sleep for nearly a week afterward. Another study of healthy college students found that those who napped between tests performed better, and the more time they spent in REM sleep during their nap, the higher their accuracy.
If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience trouble concentrating and coping with emotions. This is because REM sleep stimulates the areas of your brain that help with learning and memory.
The Importance of REM Sleep for Survival
You may want to see also

It aids mood regulation
REM sleep is important for mood regulation as it helps your brain process emotional memories, including those associated with fear. During REM sleep, your brain repairs itself and processes emotional experiences. This is why a lack of REM sleep can cause trouble coping with emotions.
REM sleep is also when most of your dreams occur. Dreams can be involved in emotional processing. The amygdala, the part of the brain that processes emotions, is activated during REM sleep.
REM sleep plays a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night.
REM sleep is one of four stages of sleep. The other three are non-REM sleep stages, during which your brain is less active and your body repairs and regrows tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens your immune system.
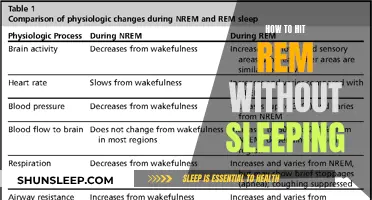
During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly behind your closed eyes, your heart rate speeds up, and your breathing becomes irregular. Your brain is highly active during this stage, and your brain waves become more variable.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory. During this stage, your brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory, maintaining others, and deciding which ones to delete.
Antidepressants and REM Sleep: A Complex Relationship
You may want to see also

It's when most dreams occur
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth of four stages of sleep. It is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity.
During REM sleep, your brain activity is similar to its activity when you are awake. Dreams typically happen during REM sleep, and they can be intense. This is because your brain is more active during this stage of sleep, and your brain waves become more variable.
Your muscles usually go limp during REM sleep, preventing you from acting out your dreams. However, this is not always the case, and some people with REM sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) may shout, punch, kick, or jerk in their sleep, sometimes injuring themselves or their sleep partner.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory. During this stage, your brain repairs itself, processes emotional experiences, and transfers short-term memories into long-term memories. It is also thought to aid in the development of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord.
Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night. Your first REM cycle is typically the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes. Each cycle after that is longer, with the final one lasting up to an hour.
How Pillows Enhance REM Sleep Quality
You may want to see also

It's characterised by rapid eye movement
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is a stage of the sleep cycle, during which the eyes move rapidly behind closed eyelids. This stage is characterised by increased brain activity, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and relaxed muscles.
REM sleep is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle, which is comprised of three non-REM (NREM) stages followed by REM sleep. The sleep cycle repeats throughout the night, with each cycle lasting between 90 and 120 minutes. The first REM cycle is the shortest, lasting around 10 minutes, and each subsequent cycle increases in length, with the final cycle lasting up to an hour.
During REM sleep, the brain activity is similar to that of wakefulness. The brain processes emotions, consolidates memories, and dreams occur. Dreaming is one of the most well-known characteristics of REM sleep, with the majority of dreams taking place during this stage. However, it is important to note that dreams can also occur during non-REM sleep stages.
The eyes move rapidly during REM sleep, giving this stage its name. This rapid eye movement occurs even though the eyes are closed. The direction of eye movement varies, and the muscles in the arms and legs become temporarily paralysed, preventing sleepers from acting out their dreams.
In addition to dreaming, REM sleep plays a crucial role in several other functions. These include memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and learning. The brain prunes its synapses, improving memory and problem-solving abilities, and processes emotional memories, including those associated with fear.
The amount of REM sleep needed varies with age. Newborns spend approximately half their sleep time in REM sleep, which gradually decreases to around 20% by the age of 20. In older adults, this percentage decreases slightly, with individuals aged 80 spending about 17% of their sleep time in REM.
Actigraphy: Measuring REM Sleep Accurately?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. It is a stage of sleep during which your eyes move rapidly in different directions and your brain is active.
The amount of REM sleep you need varies depending on your age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, while by age 20, most people spend just over 20% of their total sleep time in REM sleep.
REM sleep plays a key role in brain health and function. It improves learning and problem-solving abilities, helps with mood regulation, and is thought to aid in brain development.
To increase your REM sleep, you need to get more sleep overall. Sticking to a sleep schedule, limiting alcohol and caffeine, and relaxing before bed can all help improve your sleep.