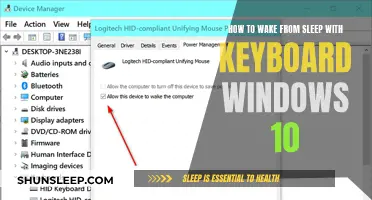
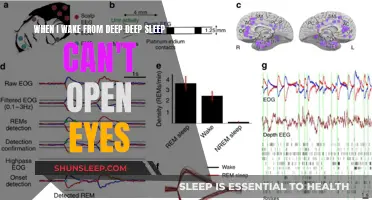
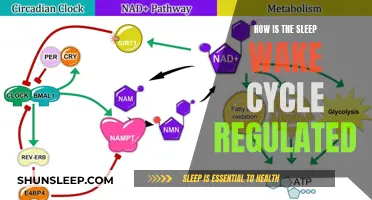
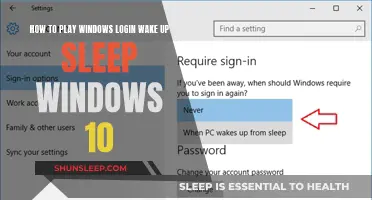
What if you wake up from a deep slumber, only to find that your world has changed? Perhaps time has passed you by, or you've been transported to a different realm. Maybe you've lost memories or gained new ones. This scenario explores the intriguing possibilities of waking up to a different reality, where your past, present, and future might be forever altered. It's a thought-provoking question that delves into the mysteries of sleep and the potential consequences of a sudden awakening.
What You'll Learn
- Dreams and Lucidity: Exploring the nature of dreams and the experience of waking up lucidly
- Sleep Disorders: Understanding conditions like sleep apnea and narcolepsy and their impact
- Brain Activity: Analyzing brain waves during deep sleep and their role in memory consolidation
- Health Benefits: Discussing the restorative power of deep sleep and its impact on overall health
- Sleep Stages: Exploring the different stages of sleep and their unique characteristics

Dreams and Lucidity: Exploring the nature of dreams and the experience of waking up lucidly
The concept of lucid dreaming, where one becomes aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state, is a fascinating phenomenon that has intrigued both scientists and dream enthusiasts alike. When you wake up from a deep sleep, it can sometimes feel like you've only just begun to explore the realm of dreams. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to take control of their dreams, manipulate the environment, and even interact with dream characters, offering a unique and empowering experience. This state of awareness during dreaming can provide valuable insights into the nature of consciousness and the mind's capabilities.
Exploring the nature of dreams and achieving lucidity can be a rewarding journey. It often begins with understanding the different stages of sleep. During deep sleep, the body repairs and restores itself, and this is where many vivid and memorable dreams occur. The transition from deep sleep to lighter stages is a crucial moment for lucid dreaming. As you start to awaken, you can try to recognize the dream environment and your own state of mind. This involves paying attention to the details around you, such as the setting, the people or objects in the dream, and your own emotions and thoughts. By becoming aware of these elements, you can make a conscious decision to remain lucid and potentially influence the dream's direction.
Lucid dreaming is a skill that can be cultivated and improved over time. One common technique is reality testing, which involves regularly questioning your surroundings throughout the day. This practice helps develop a habit of questioning and can translate into the dream world, where you might ask yourself, "Am I dreaming?" or "Is this real?" These questions can prompt a shift in consciousness, allowing you to wake up lucidly within the dream. Additionally, keeping a dream journal can be immensely helpful. Writing down your dreams immediately upon waking can improve dream recall and provide valuable information about recurring themes and symbols, which are often associated with lucid dreams.
The experience of waking up lucidly can be both exhilarating and transformative. It provides a sense of empowerment, as you realize you have the ability to influence and control your dreams. This awareness can extend beyond the dream world and impact your waking life, fostering a heightened sense of self-awareness and creativity. Lucid dreaming has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits, including the treatment of nightmares and the exploration of personal issues in a safe, controlled environment. It encourages individuals to confront their fears and desires, offering a unique form of self-exploration.
In summary, exploring the nature of dreams and achieving lucidity is an intriguing journey that can unlock a new dimension of self-discovery. By understanding the sleep stages, practicing reality testing, and maintaining a dream journal, individuals can increase their chances of experiencing lucid dreams. Waking up lucidly from deep sleep provides a unique opportunity to explore the boundaries of consciousness and the power of the mind, offering a blend of excitement and self-reflection that continues to captivate researchers and dream enthusiasts worldwide.
Revive Your App's Potential: Strategies to Wake Up Sleeping Apps
You may want to see also

Sleep Disorders: Understanding conditions like sleep apnea and narcolepsy and their impact
Sleep disorders are a group of conditions that affect the quality and duration of sleep, often leading to significant daytime impairment and reduced overall health. Two of the most well-known sleep disorders are sleep apnea and narcolepsy, each with distinct characteristics and impacts on an individual's life.
Sleep Apnea: This disorder is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, often occurring multiple times throughout the night. These pauses, known as apneas, can last for a few seconds to minutes and are typically accompanied by a gasping or choking sensation. Sleep apnea is a serious condition that can lead to fragmented sleep, leaving individuals feeling exhausted during the day. It is caused by the collapse of the upper airway, often due to the relaxation of the throat muscles. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type, where the airway is physically blocked, while central sleep apnea involves a disruption in the brain's signaling to the muscles that control breathing. The impact of sleep apnea can be far-reaching, including excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and an increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
Narcolepsy: In contrast, narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Individuals with narcolepsy experience sudden and intense episodes of sleepiness, often falling asleep involuntarily during the day. These episodes can be triggered by physical activity or emotional stress. One of the key features of narcolepsy is cataplexy, a sudden loss of muscle tone, which can range from a slight limp to full-body collapse. This disorder can significantly impact daily life, affecting work, social interactions, and overall quality of life. Narcolepsy is often associated with a lack of the neurotransmitter orexin, which helps regulate wakefulness and sleep.
Both sleep apnea and narcolepsy require medical attention and management. Treatment options for sleep apnea include continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, and lifestyle changes. For narcolepsy, medications and sleep hygiene practices are commonly recommended. Early diagnosis and proper management of these disorders can significantly improve the lives of those affected, ensuring they can achieve better sleep quality and overall well-being. Understanding these conditions is crucial in promoting awareness and encouraging individuals to seek help for sleep-related issues.
Can Another Computer Wake Up from Sleep? Exploring the Possibilities
You may want to see also

Brain Activity: Analyzing brain waves during deep sleep and their role in memory consolidation
The concept of deep sleep and its impact on memory has captivated scientists for decades, leading to extensive research on brain activity during this restorative phase. Deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), is characterized by slow, high-amplitude brain waves, which are crucial for various physiological processes, including memory consolidation. When we delve into the realm of deep sleep, our brains undergo a complex dance of neural activity, which plays a pivotal role in strengthening our memories.
During deep sleep, the brain exhibits distinct patterns of electrical activity, primarily in the form of slow delta waves (0.5-4 Hz) and, to a lesser extent, theta waves (4-8 Hz). These waves are generated by the synchronous firing of neurons in specific brain regions, notably the hippocampus and the amygdala, which are integral to memory processing. The hippocampus, in particular, is renowned for its role in converting short-term memories into long-term ones, a process that is intricately linked to deep sleep. As we transition into deep sleep, the brain's frequency of these slow waves increases, creating a rhythmic pattern that facilitates the consolidation of memories.
Research has shown that the intensity and frequency of these deep sleep brain waves are directly proportional to the amount of memory consolidation that occurs. When an individual is in a deep sleep state, the brain's ability to strengthen neural connections and reinforce memory pathways is heightened. This process is essential for the transformation of newly acquired information into long-term, stable memories, ensuring that we can recall them when needed. The more profound the sleep, the more effective the memory consolidation, as evidenced by studies comparing different sleep stages.
The role of deep sleep in memory consolidation is further supported by experiments involving sleep deprivation. When individuals are deprived of deep sleep, their ability to recall and process information is significantly impaired. This impairment is not limited to declarative memories (facts and events) but also extends to procedural memories (skills and habits). The lack of deep sleep disrupts the brain's natural rhythm, hindering the formation of new memory traces and the strengthening of existing ones.
Understanding the intricate relationship between deep sleep and memory has practical implications. For instance, ensuring adequate deep sleep through proper sleep hygiene and managing sleep disorders can significantly enhance cognitive performance and memory retention. Additionally, the study of brain activity during deep sleep provides valuable insights into the neural mechanisms underlying memory, offering potential avenues for developing novel therapeutic approaches to improve memory function in various clinical conditions.
Recognizing Sleep Wake Disturbances: Signs and Solutions
You may want to see also

Health Benefits: Discussing the restorative power of deep sleep and its impact on overall health
The concept of deep sleep, often referred to as slow-wave sleep (SWS), is a fascinating aspect of our nightly routine. It is a phase of sleep characterized by slow, rhythmic brain waves and is crucial for our overall health and well-being. When we delve into the realm of deep sleep, our bodies undergo a transformative process that offers a multitude of health benefits.
One of the most significant advantages of deep sleep is its restorative nature. During this phase, the body repairs and rejuvenates itself. It is a time when physical and mental restoration takes center stage. Deep sleep triggers the release of growth hormones, which are essential for tissue repair and the maintenance of a healthy immune system. This process is particularly vital for athletes and individuals engaged in physically demanding activities, as it aids in muscle recovery and reduces the risk of injury. Moreover, it plays a pivotal role in maintaining cognitive function. Adequate deep sleep has been linked to improved concentration, enhanced memory retention, and better problem-solving abilities. It essentially provides the brain with a much-needed boost, ensuring optimal cognitive performance.
The impact of deep sleep on overall health is profound. It is closely associated with improved cardiovascular health. Studies suggest that individuals who consistently achieve deep sleep have a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke. This is attributed to the regulation of stress hormones and the promotion of healthy blood pressure levels. Additionally, it contributes to emotional well-being. Deep sleep helps regulate emotions and is linked to a lower risk of depression and anxiety disorders. It provides a sense of calm and balance, allowing individuals to approach their daily lives with a clearer mind and improved emotional resilience.
Furthermore, the quality of deep sleep can influence weight management and metabolic health. Research indicates that individuals with higher SWS percentages tend to have better insulin sensitivity and a reduced risk of obesity. This is because deep sleep influences the body's ability to process glucose and regulate appetite hormones, thus promoting a healthy metabolism.
In conclusion, deep sleep is a powerful ally in our pursuit of optimal health. Its restorative properties impact both physical and mental well-being, offering a range of benefits that contribute to a healthier and more vibrant life. Understanding the importance of this sleep stage encourages individuals to prioritize healthy sleep habits, ensuring they unlock the full potential of their nightly rest.
Tesla Model 3's Awakening: Unlocking the Secrets of Sleep Mode
You may want to see also

Sleep Stages: Exploring the different stages of sleep and their unique characteristics
The human sleep cycle is a fascinating process, consisting of multiple stages that play a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. Understanding these stages can provide valuable insights into why we sleep and how it impacts our daily lives. Sleep is typically divided into two main types: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, each with distinct characteristics and functions.
During the initial stages of sleep, we enter the NREM sleep phase, which is further divided into three levels. The first stage is a transition period where brain activity slows down, and the body begins to relax. Here, individuals may experience light sleep, where they can be easily awakened. As the sleep progresses, muscle activity slows, and the body temperature and heart rate drop. This is the stage where it becomes increasingly difficult to wake someone up, and it is often referred to as 'deep sleep' or 'slow-wave sleep.' This deep sleep is crucial for restorative functions, as it allows the body to repair tissues, synthesize proteins, and release important hormones.
The second stage of NREM sleep is characterized by the appearance of sleep spindles, which are brief bursts of rapid brain wave activity. These spindles are essential for memory consolidation, particularly for procedural and declarative memories. As the sleep advances, the third stage of NREM sleep is marked by the presence of delta waves, which are high-amplitude, slow brain waves. This stage is often associated with the most restorative sleep, and individuals are typically in a very deep sleep, making it challenging to wake them.
Moving into the REM sleep stage, this is when most of our dreaming occurs, and brain activity is similar to that during wakefulness. The eyes scurry rapidly behind closed lids, and breathing is irregular. This stage is crucial for emotional processing, memory consolidation, and creativity. It is also the stage where most of our REM behavior disorder (RBD) episodes occur, where individuals may act out their dreams, sometimes with violent movements.
Understanding these sleep stages is essential as it highlights the importance of a full sleep cycle. Waking up during deep sleep or the REM stage can disrupt the natural progression of sleep, leading to decreased sleep quality and potential health issues. It is recommended to aim for uninterrupted sleep to ensure all stages are completed, promoting optimal physical and mental restoration.
iPad Sleep/Wake Button: Location and Functionality Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Waking up from a deep sleep can be a bit jarring, but it's a natural part of the sleep cycle. You might feel disoriented and take a few moments to orient yourself. It's common to experience a brief period of confusion or a sense of disconnection from your surroundings. As you become more alert, your senses will gradually come back to you, and you'll start to feel more aware of your environment.
Generally, waking up from deep sleep is not associated with significant health risks. However, frequent disruptions during deep sleep can impact your overall sleep quality. This may lead to feelings of fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. Ensuring a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can help improve your sleep and reduce the likelihood of waking up from deep sleep.
Deep sleep is a crucial stage for restorative processes, and it's natural to experience some awakenings. However, you can minimize disruptions by maintaining a comfortable sleep environment. Keep the room dark, quiet, and at a pleasant temperature. Avoid stimulating activities before bed, and establish a regular sleep routine. If you tend to wake up frequently, consider using a white noise machine or earplugs to block out sudden noises.
Yes, it is quite common to experience vivid and memorable dreams during the transition from deep sleep to lighter sleep stages. This is because the brain is more active and processing information during this time. If you're interested in exploring your dreams further, keep a dream journal by your bed to jot down any dreams you recall upon waking.
If you consistently wake up from deep sleep and feel unrested, it might be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. They can evaluate your sleep patterns and provide personalized advice. This may include recommendations for sleep hygiene, such as improving your sleep environment, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and adopting relaxation techniques before bed.