Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. During sleep, the body cycles between different stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages of increasing depth, with the deepest stage being crucial for tissue repair, immune system strengthening, and muscle relaxation. REM sleep, on the other hand, is characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and dreaming. While both types of sleep are important, the question arises as to whether REM sleep or level 4 sleep, the deepest stage of NREM sleep, is more beneficial for overall health and well-being.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
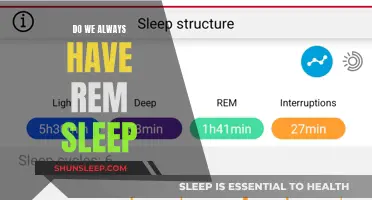
| Number of sleep cycles per night | 4-5 |
| Percentage of sleep time that is REM sleep | 20-25% |
| First REM stage duration | 10 minutes |
| Final REM stage duration | Up to 1 hour |
| REM sleep benefits | Improved learning, mood regulation, brain development, protection against dementia |
| REM sleep deprivation symptoms | Trouble coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, weakened immune system, feeling groggy |
What You'll Learn

REM sleep is important for brain development and preventing dementia
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and repair. While all stages of sleep are important, REM sleep, in particular, has been linked to brain development and the prevention of dementia.
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth stage of sleep, characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. It typically occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep and is associated with dreaming and memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, committing some to memory and deciding which ones to delete.
REM sleep is crucial for brain development, especially in infants and children whose brains are still developing. Newborn babies spend up to eight hours in REM sleep each day, and this decreases to an average of two hours per night by adulthood. Animal studies have shown that REM sleep is important for neuronal development, with researchers finding that it helps to prune and maintain new synapses in the developing brain. This process is vital for normal neuronal circuit development and cognitive improvement.
Furthermore, REM sleep may play a role in preventing dementia. A study published in the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology found that people who got less REM sleep had a greater risk of developing dementia, including Alzheimer's disease. The results indicated that for every percent reduction in REM sleep, there was a 9% increase in the risk of dementia. While the reasons for this link are not yet fully understood, it highlights the importance of REM sleep in maintaining brain health.
In summary, REM sleep is essential for brain development, especially during infancy and childhood. It also plays a role in memory consolidation and emotional processing, which may contribute to its protective effect against dementia. While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between REM sleep and brain health, it is clear that getting adequate REM sleep is vital for overall wellbeing.
Signs You've Entered REM Sleep and How to Recognize Them
You may want to see also

REM sleep improves learning and problem-solving abilities
REM sleep is vital for learning and problem-solving abilities. During REM sleep, the brain is active, and dreams typically occur. This stage of sleep stimulates the areas of the brain that aid in learning and memory. The brain repairs itself and processes emotions, transferring short-term memories into long-term ones.
REM sleep is also when the brain replenishes neurotransmitters that organise neural networks essential for learning, performance, and problem-solving. Sleep spindles, or spikes of neural activity, occur during this stage and are believed to play a key role in helping people learn and remember how to perform physical tasks.
Research has shown that REM sleep improves the ability to solve complex problems. In one study, participants were woken up during REM sleep and could solve 15 to 35% more puzzles than when awakened during non-REM sleep. They also performed better than they did during the day. This indicates that REM sleep plays a significant role in enhancing creative problem-solving skills.
Additionally, sleep in general helps to strengthen memories formed throughout the day and link them to existing ones. A full night of sleep, including REM sleep, can aid in problem-solving by connecting related memories in unexpected ways.
While all stages of sleep are important, REM sleep stands out for its role in cognitive enhancement and emotional processing. By getting sufficient REM sleep, individuals can improve their learning and problem-solving abilities, ultimately enhancing their overall well-being.
Impaired REM Sleep: Understanding Alzheimer's Impact
You may want to see also

REM sleep helps regulate your mood
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process, and researchers are still trying to understand how and why we sleep and what happens to us while we do.
There are two types of sleep: REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and non-REM sleep. During REM sleep, your brain is active and dreams typically happen. Non-REM sleep has four stages, the third of which is deep sleep. Deep sleep is essential for health and well-being.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory, and non-REM sleep is when your body repairs and regrows tissues. Both are important because while you’re asleep, your brain and body are busy repairing and strengthening things as well as processing memories.
REM sleep is when we tend to dream, and the deepest non-REM sleep is when the body relaxes fully and repairs itself. Dreaming is important for processing emotions and experts believe it helps you process emotions. Dreaming may be functional to process negative emotional experiences. It has also been assumed to have a role in integrating traumatic and other distressing memories into our long-term memory.
REM sleep appears to facilitate cognitive distortions of anxiety and depression. Depressed/anxious participants were significantly less positive and significantly more negative after awakenings from REM sleep vs non-REM sleep.
REM sleep deprivation in depressed patients is known to (temporarily) alleviate depression in some patients. REM sleep suppression increases general negative affect, enhances amygdala responses and alters its functional connectivity with anterior cingulate cortex during passively experienced experimental social exclusion.
REM sleep is important for regulating your mood. If you don’t get enough REM sleep, you may have trouble coping with emotions, concentrating, and experience a weakened immune system and grogginess in the morning.
REM sleep deprivation affects emotional reactivity and social function. Without enough healthy sleep, negative emotional reactivity seems to be significantly enhanced and positive reactions to positive events are often subdued.
REM sleep deprivation is both a common symptom of and risk factor for a range of psychiatric disorders including anxiety and mood disorders. Sleep disturbances not only restrict our daily well-being and social functioning but may even have a prognostic significance in the evolution of affective disorders like depression.
Healthy sleep repairs adaptive processing and functional brain activity, integrity of the medial prefrontal cortex-amygdala connections important in emotion regulation processes.
REM sleep deprivation diminishes the capacity to regulate emotion. Women sleeping 6-8 h seemed to be more able to regulate their emotions in their waking lives.
REM sleep deprivation can make it more difficult to fall asleep, but it might help regulate emotions to a greater extent, so that they are less likely to disrupt sleep during the night, leading to increased sleep duration, reduced sleep fragmentation and improved sleep quality.
REM sleep deprivation can lead to a decrease in accepting blame. It has been found that sleep deprivation leads to a decrease in accepting blame.
REM sleep deprivation can lead to an increase in extra-punitive responses, which reflects the tendency to show direct blame or hostility towards people or objects in the environment.
Both REM and non-REM sleep are important for your health and well-being. While non-REM sleep is when your body repairs itself, REM sleep is important for learning and memory and regulating your mood.
Track REM Sleep: Fitbit Alta HR Tips and Tricks
You may want to see also

REM sleep is when your body repairs and strengthens itself
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and mind. During sleep, our body cycles through different stages, including REM (rapid eye movement) sleep and non-REM sleep. While all stages of sleep are important, REM sleep stands out as a period when the body repairs and strengthens itself.
REM sleep is characterised by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, and a faster heart rate. It usually occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep and becomes longer with each subsequent cycle. During REM sleep, the body repairs and strengthens itself in several ways. Firstly, it is a time when the body repairs and regrows tissues, a vital process for maintaining overall health. Secondly, REM sleep promotes the building of bone and muscle, ensuring structural integrity and strength. Thirdly, it strengthens the immune system, our body's defence mechanism against diseases and infections.
In addition to physical repairs and strengthening, REM sleep also contributes to mental and emotional health. This stage of sleep is associated with dreaming, which is believed to aid in emotional processing and mood regulation. The brain's amygdala, responsible for processing emotions, is active during REM sleep. Furthermore, REM sleep supports memory consolidation by processing new information and converting short-term memories into long-term ones.
The amount of REM sleep needed varies with age. Newborns spend about half their sleep time in REM sleep, which gradually decreases to about 20% by adulthood. Older adults experience a slight decline, with approximately 17% of their sleep being REM sleep by the age of 80.
While the body repairs and strengthens itself during REM sleep, it is important to note that this is just one aspect of the complex sleep cycle. Non-REM sleep, particularly the deep sleep stage, also plays a crucial role in the body's recovery and regeneration process.
Hallucinogens and REM Sleep: A Complex Relationship
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep can cause trouble concentrating and coping with emotions
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that scientists are still trying to fully understand. It is known, however, that sleep is essential for the body and brain to function properly.
REM sleep is the fourth stage of sleep, characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. During this stage, the brain is highly active, and dreams are more vivid. REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming.
If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience symptoms such as trouble coping with emotions and concentrating, as well as a weakened immune system and feelings of grogginess in the morning.
The Impact of Lack of REM Sleep on Emotional Coping and Concentration
During REM sleep, the brain processes emotions and consolidates memories. This stage of sleep is crucial for emotional regulation and cognitive function. When you don't get enough REM sleep, you may find it challenging to cope with your emotions effectively. You might feel more irritable, anxious, or depressed, and have trouble managing your emotional responses to different situations.
Additionally, the lack of REM sleep can lead to difficulties with concentration and memory. This is because REM sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation, the process of storing new information in the brain and making it accessible for retrieval. Without adequate REM sleep, you may experience problems with focus, learning, and retaining information.
Strategies to Increase REM Sleep
To improve your REM sleep, focus on getting more sleep overall and improving your sleep quality. Here are some strategies to help you increase your REM sleep:
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Establish a calming pre-sleep routine to help you unwind and prepare for sleep. This could include activities such as reading, meditation, or listening to soothing music.
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps to regulate your body's internal clock and promote better sleep.
- Avoid stimulants: Steer clear of nicotine and caffeine, especially close to bedtime, as these substances can interfere with your sleep.
- Get regular exercise and sunlight: Engage in physical activity and spend time outdoors daily. Exercise can help tire your body, making it easier to fall asleep, and natural sunlight exposure helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle.
- Avoid alcohol and heavy meals close to bedtime: Consuming alcohol or large meals before bed can disrupt your sleep. Opt for a light snack if you need something before sleeping.
- Limit screen time before bed: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with your sleep. Avoid watching TV or using electronic devices at least an hour before bedtime.
By implementing these strategies and prioritising sleep, you can increase your chances of getting more restorative REM sleep and improve your overall well-being.
Brain Activity During REM Sleep: Slow or Active?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During this stage, your eyes move rapidly, your brain is active, and your heart rate and blood pressure increase.
Level 4 sleep is the deepest stage of non-REM (NREM) sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep. It is characterised by slow brain waves, decreased heart rate and body temperature, and a loss of muscle tone.
Both stages of sleep are important and serve different purposes. REM sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. Level 4 sleep, on the other hand, is the stage where the body repairs and regenerates tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system.
Lack of REM sleep can lead to trouble coping with emotions, difficulty concentrating, a weakened immune system, and feeling groggy in the morning.
Not getting enough level 4 sleep can result in feeling tired during the day, as this is the stage where the body restores its energy. It can also impact physical and mental health, as the body relies on this stage for tissue repair and immune system enhancement.