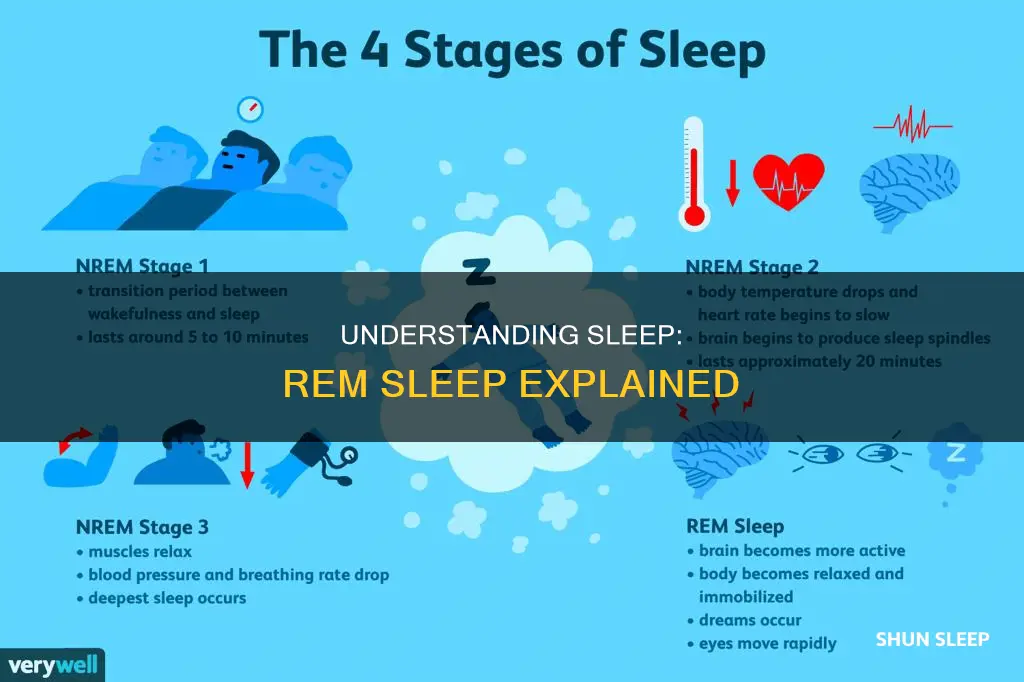
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process, and while you sleep, your body cycles between being awake and asleep. The stages of sleep fall broadly into two categories: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-REM (NREM) sleep. During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly in different directions, and your brain activity is similar to when you are awake. Dreams typically occur during REM sleep. The REM stage accounts for approximately 20-25% of sleep time, while the other 75% is taken up by NREM sleep.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What does REM stand for? | Rapid Eye Movement |
| When does it occur? | 60-90 minutes after falling asleep |
| How often does it occur? | Every 90-120 minutes |
| How long does it last? | 10 minutes to 1 hour |
| What happens during REM sleep? | Eyes move rapidly, heart rate increases, breathing becomes irregular, brain activity increases |
| What is the function of REM sleep? | Memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, dreaming |
| What happens if you don't get enough REM sleep? | Trouble coping with emotions, trouble concentrating, weakened immune system, feeling groggy in the morning |
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep is the fourth stage of sleep, characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
- During REM sleep, the brain processes emotions, consolidates memories, and repairs itself
- Lack of REM sleep can cause trouble coping with emotions, concentrating, and a weakened immune system
- To increase REM sleep, it is recommended to get more sleep overall, stick to a sleep schedule, and avoid caffeine and alcohol
- REM sleep is also known as paradoxical sleep due to its similarities to a wakeful state

REM sleep is the fourth stage of sleep, characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth and final stage of sleep. It is preceded by three stages of non-REM sleep, which is characterised by non-rapid eye movement. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly and the muscles become temporarily paralysed. This is thought to be a protective measure to prevent sleepers from acting out their dreams.
REM sleep is also characterised by irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. The brain activity during this stage is similar to that of a wakeful state, and dreams that occur during REM sleep are usually more vivid.
The first cycle of REM sleep occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. Each cycle through the four stages of sleep takes 90 to 120 minutes to complete, and as the cycles continue, they shift towards a higher proportion of REM sleep. The first period of REM sleep typically lasts about 10 minutes, with each subsequent REM stage getting longer, up to an hour.
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming. It is also associated with increased brain temperatures and decreased skin temperatures.
While the precise function of REM sleep is not yet fully understood, several theories have been proposed. One theory, known as the dual-process hypothesis, suggests that the two major phases of sleep (REM and non-REM) correspond to different types of memory consolidation. Another theory, the defensive immobilization hypothesis, suggests that REM sleep is an evolutionary transformation of the defensive mechanism known as the tonic immobility reflex, where animals feign death to avoid detection by predators.
Talking to Someone in REM Sleep: Is it Possible?
You may want to see also

During REM sleep, the brain processes emotions, consolidates memories, and repairs itself
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active and exhibits brain wave activity similar to that of a wakeful state. This stage of sleep is characterised by rapid eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and relaxed muscles.
REM sleep is important for the brain to process emotions, consolidate memories, and repair itself. Firstly, the brain processes emotions during REM sleep. The amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotions, is activated during this stage. Secondly, REM sleep aids in memory consolidation, as the brain processes and commits new learnings and motor skills to memory. Finally, the brain repairs itself during REM sleep. The brain's electrical activity during this stage resembles that of wakefulness, with neurons firing at similar intensities. This heightened brain activity allows for self-repair and recovery, as the brain is more active and energised compared to the non-REM sleep stages.
The first cycle of REM sleep occurs about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. As part of a full night's sleep, individuals cycle through three stages of non-REM sleep followed by a stage of REM sleep. Each cycle through all sleep stages takes 90 to 120 minutes to complete. With each new cycle, the duration of REM sleep increases, with most of it occurring in the second half of the night.
REM sleep plays a crucial role in dreaming, memory, emotional processing, and healthy brain development. It is associated with vivid dreaming and contributes to the consolidation of new information and the processing of emotions. The unique characteristics of REM sleep, including increased brain activity and relaxed muscles, provide an opportunity for the brain to repair and recover, enhancing overall brain function and health.
Enhancing Sleep Quality: Achieving REM Sleep
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep can cause trouble coping with emotions, concentrating, and a weakened immune system
REM stands for rapid eye movement and is the fourth out of four stages of sleep. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly, the heart rate increases, breathing becomes irregular, and the body experiences partial muscle relaxation. Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep per night, which plays a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming.
A lack of REM sleep can lead to difficulty concentrating during the day. Sleep deprivation can cause cognitive performance decline, including problems with memory and other cognitive tasks. This can manifest as forgetfulness or poor memory, and in extreme cases, as brief microsleep episodes during the day.
REM sleep is also associated with emotional processing. A lack of REM sleep can cause irritability and changes in mood.
Finally, a lack of REM sleep can weaken the immune system. Sleep plays a crucial role in the robustness of our immune system, contributing to both innate and adaptive immunity. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the healthy functioning of the immune system, making it easier to get sick and increasing the risk of chronic illnesses such as diabetes and heart problems.
Reducing REM Sleep: Tips to Shorten Your Sleep Duration
You may want to see also

To increase REM sleep, it is recommended to get more sleep overall, stick to a sleep schedule, and avoid caffeine and alcohol
REM stands for rapid eye movement. It is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle, which we enter about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. During REM sleep, the brain is highly active, and the body experiences a temporary loss of muscle tone.
To increase REM sleep, it is recommended to get more sleep overall. This is because the amount of REM sleep we get increases with each cycle of sleep, and the final period may last up to an hour. Here are some tips to help you get more sleep and increase your REM sleep:
Stick to a Sleep Schedule
It is important to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This primes your body for sleep and waking, and an irregular sleep schedule can lead to various issues that impact your physical and mental health.
Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol
Caffeine and alcohol are two common culprits for disrupting sleep. Caffeine interferes with your sleep cycle and should be avoided in the second half of the day. Alcohol delays when you first enter REM sleep and causes you to spend less time in this stage overall.
Get More Sleep Overall
Try to get the recommended 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night. If you are regularly not getting the hours you need, you will miss out on a significant part of REM sleep.
Other Tips
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Add aromatherapy to your bedtime routine.
- Try white noise or earplugs to block out sounds.
- Eat more magnesium-rich foods or take a magnesium supplement.
- Exercise regularly, but several hours before bed.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine, such as reading or taking a warm bath.
Surroundings and REM Sleep: What Do You Know?
You may want to see also

REM sleep is also known as paradoxical sleep due to its similarities to a wakeful state
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth of four stages of sleep. During this stage, the eyes move rapidly, and the brain is active, with brain activity resembling that of a wakeful state. The body, however, is temporarily paralysed, with a loss of muscle tone. This stage of sleep is characterised by irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and vivid dreams.
REM sleep is also known as paradoxical sleep. This is due to its similarities with a wakeful state. While the body is paralysed, the brain exhibits cerebral activity akin to wakefulness. Brain waves during REM sleep are fast, low amplitude, and desynchronized, resembling the patterns seen during wakefulness. The brainstem, in particular the pontine tegmentum and locus coeruleus, is thought to regulate this stage of sleep.
During REM sleep, the body suspends homeostasis, resulting in fluctuations in respiration, thermoregulation, and circulation. The body temperature is not effectively regulated, and organisms become more sensitive to external temperatures. The heart rate, cardiac pressure, cardiac output, and breathing rate also become irregular.
REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, and brain development. It is also associated with dreaming, with most dreams occurring during this stage. While the precise function of REM sleep is not fully understood, it is known to play a crucial role in overall health and well-being.
The amount of REM sleep needed varies across different age groups. Newborns spend up to 50% of their sleep in the REM stage, while adults spend approximately 20-25%. As people age, the proportion of REM sleep remains relatively stable, but the overall amount of sleep decreases.
Tracking REM Sleep: Methods for Understanding Your Sleep Better
You may want to see also







