Sleep is vital for our health and well-being. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adults should get at least 7 to 9 hours of sleep every night. However, many people do not meet these recommendations, and sleep deprivation can have significant negative consequences. So, what happens if you don't sleep for a day? Is it fine to stay awake for 24 hours?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Time without sleep | 24 hours |
| Health problems | No major health problems |
| Cognitive effects | Similar to having a blood alcohol concentration of 0.10% |
| Risk | Increased risk of errors and accidents |
| Feelings | Tired, exhausted, "off" |
| Performance | Reduced reaction time, impaired judgment and decision-making, diminished memory and attention, impaired vision, hearing and hand-eye coordination, tremors and muscle tension |
| Hormones | Increased stress hormones, e.g. cortisol and adrenaline |
What You'll Learn

Sleep deprivation can occur after 24 hours without sleep
Sleep deprivation can occur after just 24 hours without sleep. While the effects of sleep deprivation vary from person to person, there are some common symptoms that people may experience after a day without sleep.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), staying awake for 24 hours has similar effects to having a blood alcohol concentration of 0.10%, which is above the legal driving limit. This can lead to impaired judgment, memory, and hand-eye coordination, as well as increased stress hormone levels such as cortisol and adrenaline. These physical and mental impairments can increase the risk of accidents and errors, especially in complex or dangerous tasks.
In addition to the cognitive effects, going without sleep for 24 hours can also impact your mood and emotional state. Research suggests that people may start to feel more anxious or agitated, and their performance on tasks continues to decline, making them more prone to errors.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation can affect your visual perception. People may experience trouble with depth perception and accurately perceiving the shape and size of objects.
It's important to note that the effects of sleep deprivation become more severe with each additional hour of wakefulness. While going without sleep for 24 hours may not have long-term health consequences, it can have significant negative short-term impacts on your physical and mental well-being.
Don't Sleep on Me, Kay? I'm a Night Owl!
You may want to see also

Sleep deprivation can cause cognitive impairment
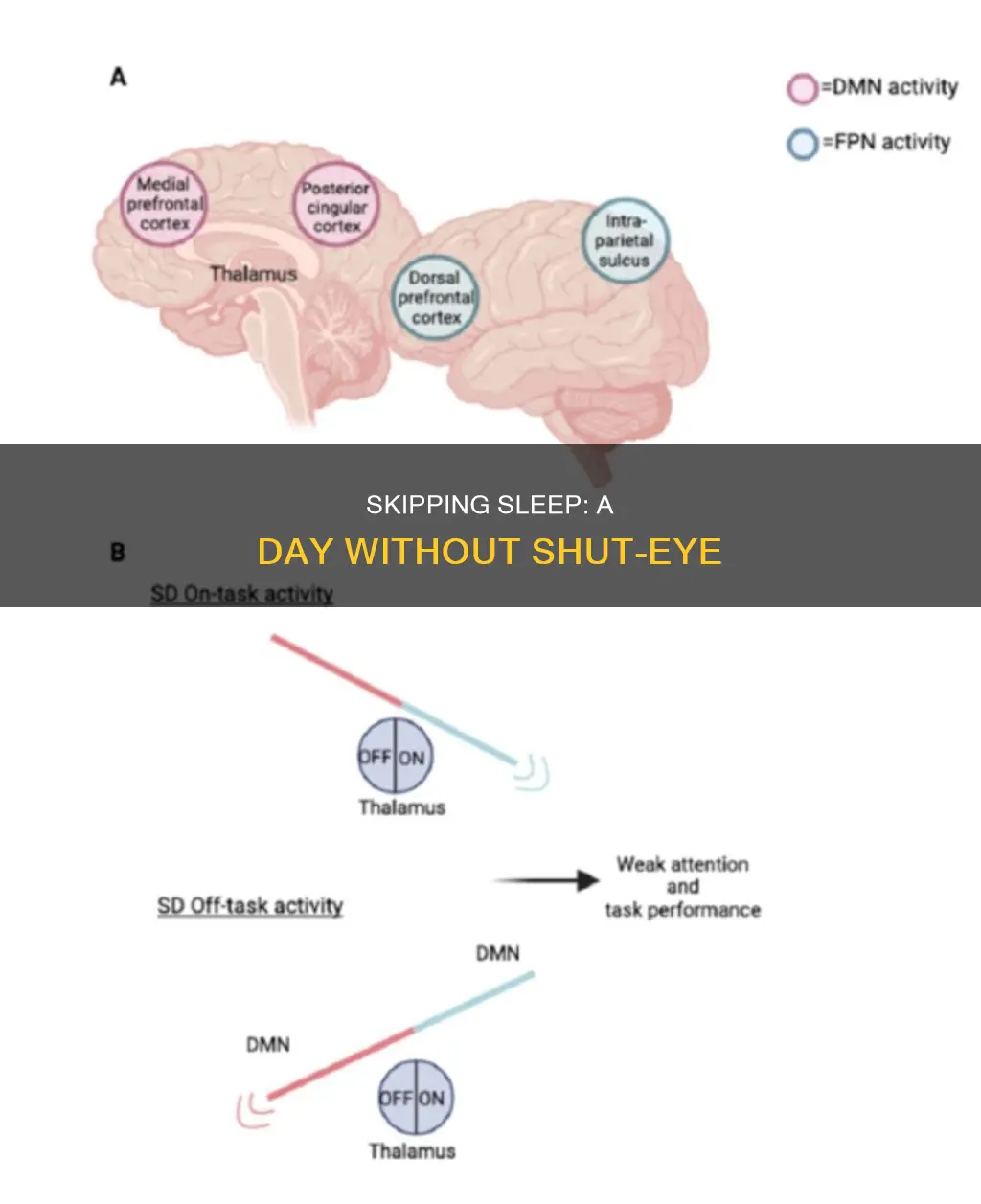
Sleep deprivation can cause a range of cognitive impairments, affecting your brain's performance and function. Here are some ways in which a lack of sleep can impact your cognitive abilities:
- Attention and Working Memory: Sleep deprivation impairs your ability to focus and maintain attention. It also disrupts your working memory, making it challenging to hold and manipulate information in your mind.
- Alertness and Vigilance: Sleep-deprived individuals experience reduced alertness and vigilance, increasing the risk of accidents and errors in everyday tasks.
- Decision-Making and Judgment: Lack of sleep can lead to impaired judgment and risky decision-making. It disrupts the connection between the amygdala and the medial prefrontal cortex, affecting your ability to make rational decisions and social judgments.
- Memory: Sleep is crucial for memory consolidation. Sleep deprivation interferes with the process, making it difficult to form and retain memories. It particularly affects episodic and declarative memory.
- Creativity and Problem-Solving: Sleep deprivation hinders creativity and problem-solving abilities. It disrupts the restructuring and reorganization of information in the brain, making it challenging to connect ideas and find innovative solutions.
- Emotional Processing: Insufficient sleep alters how emotional information is processed. It impairs the ability to recognize and respond appropriately to emotional cues, potentially leading to risky choices and impaired social interactions.
- Language and Speech: Sleep deprivation can impact your language and speech. It disrupts the normal release of specific neurotransmitters, affecting your ability to produce speech effectively.
- Motor Skills: Lack of sleep can lead to reduced coordination and impaired motor skills. This includes a decline in tasks requiring visuomotor performance, such as digit symbol substitution or letter cancellation tasks.
- Higher-Order Cognitive Functions: Sleep deprivation can also impact more complex cognitive functions. It may increase rigid thinking, perseveration errors, and difficulties in utilizing new information for innovative decision-making.
It is important to note that the effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance can vary between individuals. Age, gender, and other factors may influence how sleep deprivation impacts cognition. However, overall, sleep deprivation has a detrimental effect on various aspects of cognitive function.
Lack of Sleep: Aging Faster and the Science Behind It
You may want to see also

Sleep deprivation can increase the risk of accidents
After 24 hours without sleep, you will experience reduced reaction time, impaired judgment and decision-making, diminished memory and attention, impaired vision, hearing and hand-eye coordination, and tremors and muscle tension. These effects will make you more prone to accidents, especially when driving or operating heavy machinery.
The longer you stay awake, the more severe the symptoms of sleep deprivation become, and the higher the risk of accidents. After 36 hours without sleep, you will experience a greater physical impact, with higher levels of inflammatory markers in the blood. Your body will be under considerable stress, with hormone imbalances and a slowed metabolism. By 48 hours without sleep, you are likely to experience microsleep, which can be extremely dangerous if it occurs while driving or operating machinery.
Chronic sleep deprivation, or regularly getting less than the recommended 7-9 hours of sleep per night, can also increase your risk of accidents over time. It can lead to cognitive impairment and dementia, poor balance and coordination, a weakened immune system, impaired glucose tolerance and Type 2 diabetes, overweight and obesity, high blood pressure, cardiac events, stroke, and depression and other mood disorders.
The Amazon's Snakes: A Sleep-Disturbing Adventure
You may want to see also

Sleep deprivation can lead to health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease
Sleep is an essential bodily function, and going without it for even a day can have detrimental effects on your health and well-being. While you may not die from missing a day's sleep, it can certainly put your life at risk. Sleep deprivation can cause cognitive fatigue, impairing your reaction time, judgment, mood, and decision-making abilities.
Furthermore, sleep loss creates a hormone imbalance that promotes weight gain and obesity. Leptin and ghrelin, the hormones that regulate appetite, are altered when you don't get enough sleep, leading to increased feelings of hunger. Sleep deprivation is also associated with growth hormone deficiency and elevated cortisol levels, both linked to obesity.
Additionally, insufficient sleep can impair metabolism, cause inflammation, and increase your risk of cardiovascular disease. During sleep, your heart rate slows, blood pressure drops, and breathing stabilizes, reducing stress on the heart. Sleep deprivation disrupts this process, leading to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart attacks, and stroke.
The link between sleep deprivation and type 2 diabetes is also well-established. Sleep disturbances are a common but under-recognized factor in type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown that insufficient sleep is associated with decreased insulin sensitivity and impaired glucose tolerance, which are key factors in the development of diabetes.
In summary, sleep deprivation goes beyond feeling tired and cranky. It can have serious health consequences, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Getting adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Avoid Password Resets: Auto-Login Post-Sleep Mode
You may want to see also

Sleep deprivation can affect your mental health
Sleep is critical for both physical and emotional well-being. Sleep deprivation can have a detrimental impact on mental health, and the effects can be severe and intolerable.
Firstly, sleep-deprived individuals are more susceptible to negative emotional responses to stressors and have decreased positive emotions. Sleep helps to maintain cognitive skills such as attention, learning, and memory, and a lack of sleep can make it harder to cope with even minor stressors. Poor sleep can also affect our ability to perceive the world accurately.
Secondly, sleep deprivation can increase the risk of mental health disorders. While insomnia is often a symptom of anxiety and depression, it is now recognized that sleep problems can also contribute to the onset and worsening of these conditions. Sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to experience anxiety and distress, and those with mental health disorders are more likely to suffer from chronic sleep problems, creating a negative feedback loop.
Thirdly, sleep deprivation can trigger mania, psychosis, or paranoia, or worsen existing symptoms. It can also increase the risk of psychotic episodes and make individuals more likely to experience suicidal ideation.
Finally, sleep-deprived individuals may struggle with everyday tasks and experience a decline in their overall functionality. They may have impaired coordination, reduced decision-making skills, and a higher risk of accidents.
In conclusion, sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on mental health, affecting emotional responses, cognitive skills, and the risk of mental health disorders. Addressing sleep problems is critical to maintaining good mental health and alleviating the severity of psychiatric disorders.
Eating Late: A Sleep Dilemma
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Not getting enough sleep can have a negative impact on your health and well-being. After 24 hours without sleep, you may experience anxiety, irritability, and daytime sleepiness. Your judgment, memory, and hand-eye coordination will also be impaired.
Chronic sleep deprivation can increase your risk of developing various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, and diabetes. It can also lead to poor academic performance, problems with interpersonal relationships, and a higher risk of accidents.
While there may be short-term benefits, such as having more time to complete tasks, the risks of sleep deprivation generally outweigh any potential advantages. Staying awake for an extended period can impair your cognitive performance and put you at risk of accidents.
Here are some tips to improve your sleep:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
- Keep your bedroom quiet, dark, and at a comfortable temperature.
- Avoid large meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime.
- Limit screen time at least one hour before bedtime.
- Get regular exercise during the day.







