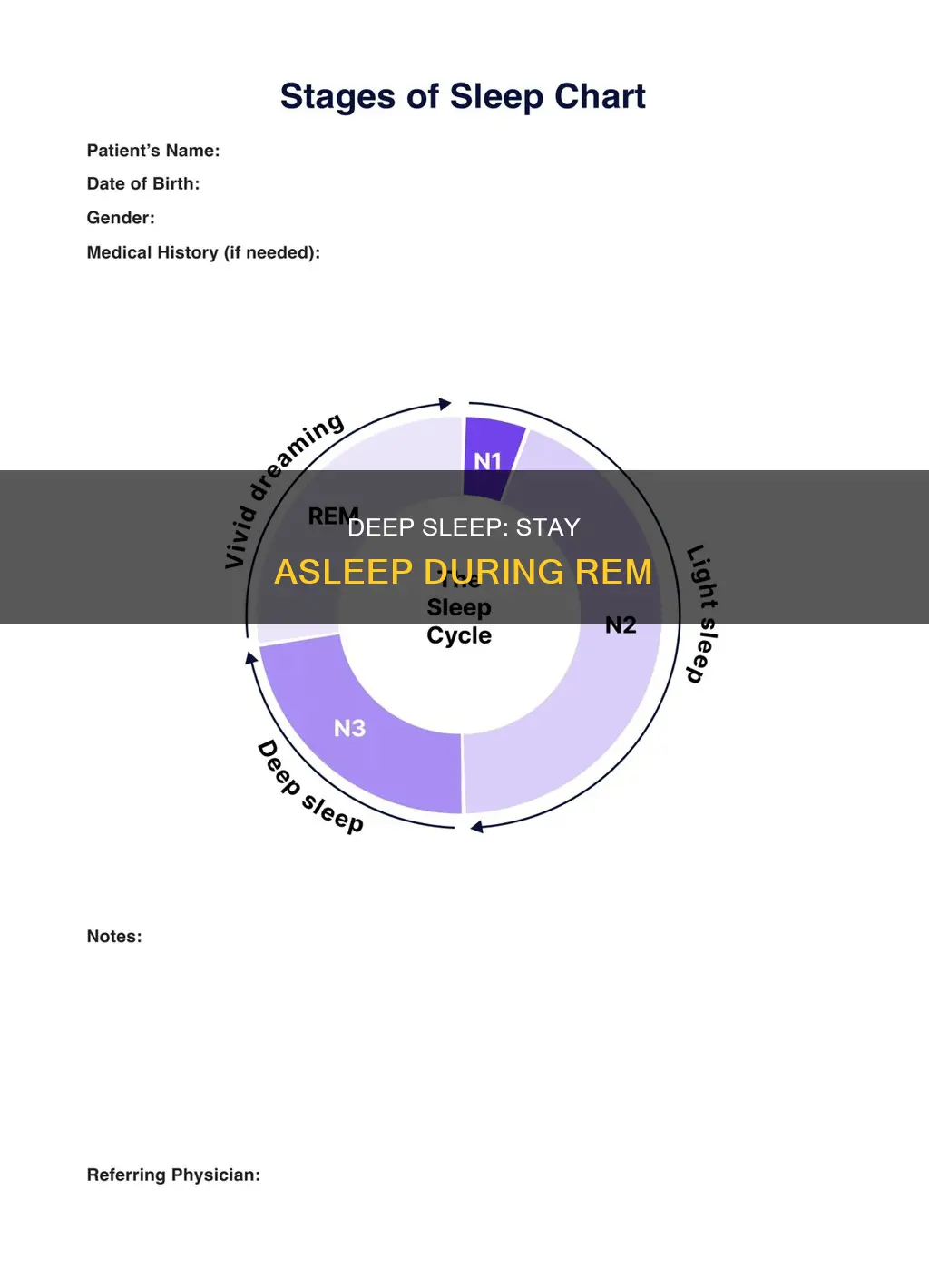
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the human body and brain to rest and recover. While asleep, the brain cycles through various stages, including REM sleep, which is characterised by rapid eye movement, increased brain activity, and dreaming. Waking up during REM sleep can cause disorientation and grogginess that may last throughout the day. To improve sleep quality and ensure you wake up feeling refreshed, it is beneficial to wake up during a period of light, non-REM sleep. This can be achieved by using sleep tracking apps and adopting good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a bedtime routine, and avoiding bright lights and electronics before bed.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Develop and maintain a sleep schedule | Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day |
| Treat sleep disorders | Consult a doctor or sleep specialist to develop a treatment plan |
| Stop taking sleep aids | Consult a doctor about switching medications or lowering your dose |
| Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco | Cut down on these substances and avoid them in the late afternoon or evening |
| Use sleep hygiene techniques | Exercise regularly, maintain a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom, establish a bedtime routine, and keep gadgets and screens out of the bedroom |
What You'll Learn

Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco
Alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco are three substances that are best avoided if you want to get a good night's rest. Drinking a moderate to high amount of alcohol can delay when you first enter REM sleep, and it can also cause you to spend less time in REM sleep overall. Similarly, consuming caffeine and tobacco in the evening or close to your desired sleep period may also interfere with normal progression through the sleep stages.
Caffeine promotes wakefulness by blocking adenosine, a sleep-inducing chemical. It can make it harder to fall asleep and reduce the amount of deep, slow-wave sleep you get, which is critical for feeling refreshed the next day. It is generally recommended to avoid consuming caffeine in the hours leading up to bedtime to minimize the risk of insomnia and promote better sleep quality. If you struggle with sleep, it may be helpful to keep track of the time of day you consume caffeine and how you sleep at night.
Tobacco and other nicotine products have been found to increase the risk of several sleep problems, including snoring and sleep disorders like obstructive sleep apnea and certain parasomnias. Nicotine is a stimulant that works quickly in the body, causing a rapid release of hormones that increase a person's breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate. People who smoke or use nicotine products often report experiencing difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently throughout the night, and overall poorer sleep quality compared to non-smokers. It is important to avoid all nicotine products at least four hours before bed to promote better sleep quantity and quality.
If you are struggling with sleep, it is best to avoid alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, especially in the late afternoon or evening.
REM Sleep: Is It Really Deep Sleep?
You may want to see also

Develop and maintain a sleep schedule
Developing and maintaining a sleep schedule is a crucial step towards achieving better sleep and, consequently, more REM sleep. Here are some tips to help you establish and stick to a sleep schedule:
- Consistency is key: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This consistency helps to regulate your body's internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm. Disrupting this balance with irregular sleep and wake times may confuse your body and interfere with REM sleep regulation.
- Make time for sleep: Choose a bedtime that allows you to get the recommended amount of sleep for your age. For adults, it is generally recommended to get seven to nine hours of sleep each night.
- Establish a bedtime routine: Engage in soothing activities before bed, such as reading or taking a warm bath. This routine will signal to your brain that sleep is approaching, making it easier to fall asleep and maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Avoid bright lights and electronics: Exposure to bright lights or electronic screens before bedtime can disrupt your body's natural sleep-wake functions. It is best to avoid these close to bedtime and create a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom environment.
- Limit naps: While napping can be beneficial, long or frequent naps can affect your sleep quality at night. If you do nap, try to limit them to 20-30 minutes and avoid napping too close to bedtime.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity during the day can improve your sleep quality. However, avoid strenuous exercise close to bedtime, as it may make it harder to fall asleep.
By following these tips and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, you will be well on your way to improving your sleep and getting the REM sleep your body needs.
Dreaming, Memory Consolidation, and REM Sleep
You may want to see also

Treat sleep disorders
Sleep disorders can be treated in a variety of ways. Here are some methods to tackle them:
Develop and Maintain a Sleep Schedule
Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends and holidays. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. This helps to regulate your body's sleep-wake cycle and promote a healthy sleep pattern.
Treat the Underlying Condition
If your sleep disorder is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as sleep apnea or insomnia, seek professional help. A doctor or sleep specialist can help you develop an appropriate treatment plan. For example, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy has been found to effectively treat obstructive sleep apnea, leading to improved mood and higher-quality sleep.
Stop Taking Sleep Aids
Certain medications, such as antidepressants and antipsychotics, can interfere with REM sleep. If you suspect that your medication is affecting your sleep quality, consult your doctor about alternative options or adjusting your dosage.
Avoid Alcohol, Caffeine, and Tobacco
Consuming alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, especially close to bedtime, can disrupt your sleep cycles and reduce the time spent in REM sleep. Try to cut down on these substances, especially in the late afternoon or evening, to improve your sleep quality.
Adopt Sleep Hygiene Practices
Sleep hygiene refers to habits and practices that promote better sleep quality. This includes exercising regularly, maintaining a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom environment, establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, and limiting screen time before bed. These practices can help improve your overall sleep quality and duration.
Seek Professional Help
If you are experiencing frequent sleep disturbances or daytime symptoms such as excessive tiredness, it is important to consult a medical professional. They can help diagnose any underlying conditions and provide personalized treatment options to improve your sleep quality.
Rem's Guide: Navigating the Complexities of Memory
You may want to see also

Stop taking sleep aids
Stopping sleep aids can be a challenging process, and it is important to do it safely and effectively. Here are some detailed instructions and considerations to help you stop taking sleep aids:
Tapering Off
The best way to stop taking sleeping pills or sedatives is to gradually reduce the dosage over time. This process is known as "tapering." It is essential to do this under the guidance of a doctor to ensure your safety and minimize withdrawal symptoms. The tapering process typically takes place over several weeks or months, and there is no one-size-fits-all formula. Your doctor will create a weaning schedule based on the type and amount of drug you are taking, as well as your individual circumstances.
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms can occur when you stop using sleep aids, and they can range from mild to severe. Common withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, irritability, shivering, sweating, gastrointestinal issues, and sleep disturbances. In some cases, withdrawal can lead to seizures, circulation problems, or other life-threatening complications. Medical detox, supervised by a doctor, is the safest way to manage withdrawal symptoms and ensure your health.
Psychological Support
Quitting sleep aids can be emotionally challenging, and it is important to have psychological or therapeutic support during this time. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a recommended form of therapy that can help you develop coping strategies and improve your sleep habits. CBT can also dispel myths about sleep and teach you relaxation techniques. Additionally, having a strong support system of family or friends can make a significant difference in your journey to stop taking sleep aids.
Good Sleep Habits
Developing good sleep habits is crucial when stopping sleep aids. This includes practices such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, reducing screen time before bed, and finding ways to relax before bedtime. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and a comfortable sleep environment can also contribute to improving your sleep quality.
Alternative Treatments
In some cases, alternative treatments or medications may be considered to help with sleep issues. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication or supplement. Antidepressants or antihistamines, for example, may be explored as potential substitutes during the tapering process, although further research is needed in this area.
Remember, stopping sleep aids is a journey, and it may take time and patience. Always prioritize your health and well-being, and don't be afraid to reach out for professional help if needed.
Melatonin and REM Sleep: The Connection and Benefits
You may want to see also

Use sleep hygiene techniques
Sleep hygiene refers to healthy sleep habits that help you get a good night's sleep. It's important because of how crucial getting good sleep is for your mental and physical health, as well as your overall quality of life. Here are some tips to improve your sleep hygiene:
Keep a consistent sleep schedule
Try to sleep and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This reinforces your body's sleep cycle (your internal clock), making it easier to fall asleep and wake up daily. Sticking to a consistent schedule may also help reduce daytime sleepiness.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine
A relaxing bedtime routine helps you unwind and prepares you for sleep. Keeping the routine consistent helps your body recognize that it's bedtime when you start the routine. This may help you fall asleep more quickly. Include activities such as taking a warm bath, gentle stretches, meditation, or listening to soothing music. Start your routine 30 to 60 minutes before bedtime and avoid anything stressful or overly stimulating.
Turn off electronic devices before sleeping
Electronic devices like phones emit blue light, which can reduce melatonin levels in your body. Melatonin is a chemical that controls your sleep/wake cycle, and lower levels can make it harder to fall asleep. Devices with blue light can also keep your brain alert. Keeping your phone near your bed can disrupt your sleep due to message notifications, buzzing, and sudden light.
Exercise regularly
As little as 30 minutes of aerobic exercise per day can improve your sleep quality and overall health. Exercising outdoors may further enhance these benefits, as exposure to natural light helps regulate your sleep cycle. However, avoid exercising within a couple of hours of bedtime, as it may increase your energy levels and body temperature, making it harder to fall asleep.
Make your sleep environment comfortable
A bedroom temperature between 60 and 67°F (15.6 and 19.4°C) is optimal for most people. Ensure you have a comfortable mattress, pillows, and bed linens. If you're a light sleeper or have noisy neighbours, consider earplugs or a white noise machine. Use blackout curtains or an eye mask to keep your sleep environment dark.
Use your bed only for sleep and sex
Using your bed for activities like reading, working, or watching TV may disrupt your brain's association between your bed and sleep. Even reading can be disruptive if it keeps your brain alert. Try reading on the couch before moving to your bed.
Dreams and REM Sleep: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To avoid waking up during REM sleep, you can try to limit your exposure to outside stimuli such as noise, artificial light, or a partner's movements. Creating a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom environment can help to minimise interruptions.
To get more REM sleep, it is important to develop and maintain a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends. You should also avoid substances such as alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, especially in the evening or close to your desired sleep time. Additionally, adopting sleep hygiene habits such as regular exercise, a bedtime routine, and keeping gadgets out of the bedroom can improve sleep quality.
If you are not getting enough REM sleep, you may experience symptoms of sleep deprivation such as difficulty concentrating during the day, excessive daytime sleepiness, and forgetfulness or poor memory. Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to health conditions like diabetes, depression, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.







