Many users want to prevent their PCs from waking up from sleep mode due to certain events or programs. This guide will explore various methods to limit and control PC wake-up behavior, ensuring a more stable and energy-efficient computing experience. We'll cover system settings, software solutions, and hardware considerations to help you manage and restrict unnecessary wake-ups.
What You'll Learn
- Power Settings: Adjust power options to limit background processes and device wake-ups
- Sleep Timer: Set a timer to automatically put the PC to sleep after a period of inactivity
- Network Management: Disable unnecessary network connections to prevent wake-ups from network activity
- USB Control: Block USB devices from waking up the PC when plugged in
- BIOS/UEFI Settings: Modify hardware settings to restrict wake-up sources and power management

Power Settings: Adjust power options to limit background processes and device wake-ups
To effectively manage your computer's sleep behavior and reduce unnecessary wake-ups, you should delve into the power settings and explore the various options available. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to achieve this:
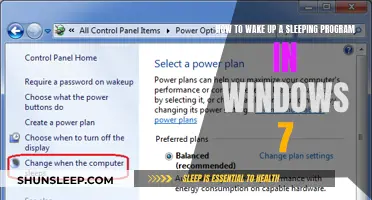
Accessing Power Settings: Begin by opening the Power Settings window. This can typically be found in the Control Panel or by searching for "Power Options" in the Start menu. Here, you'll find a range of settings to customize your computer's power behavior.
Adjusting Power Plan: Select the "Choose what closing the lid does to your device" option. This setting allows you to control the behavior of your PC when the lid is closed. Choose the "Turn off" or "Hibernate" option to ensure your computer enters a deep sleep state, minimizing power consumption and preventing unnecessary wake-ups. You can also set the time delay before the computer goes to sleep, giving you more control over when it enters this state.
Managing Background Processes: Within the Power Settings, locate the "Sleep" or "Energy Saver" settings. Here, you can configure how your computer manages power-hungry background processes. Disable unnecessary features like automatic brightness adjustment, which can cause frequent wake-ups. You can also set the computer to turn off Wi-Fi or Bluetooth when not in use, reducing power consumption and the likelihood of device wake-ups.
Customizing Power Options: Explore the advanced power settings to fine-tune your computer's behavior. You can set the computer to turn off hard drives, close programs, and shut down after a certain period of inactivity. These settings ensure that your PC remains in a low-power state, reducing the chances of unexpected wake-ups. Additionally, consider disabling unnecessary startup programs to minimize power usage during idle time.
By carefully adjusting these power settings, you can significantly limit the number of times your computer wakes up from sleep. This not only improves energy efficiency but also enhances overall system performance by reducing the impact of background processes and unnecessary device activations. Remember to experiment with different settings to find the optimal configuration for your specific needs.
Mastering Sleep: Disabling Wake-from-Sleep via Power Button
You may want to see also

Sleep Timer: Set a timer to automatically put the PC to sleep after a period of inactivity
Setting a sleep timer on your computer is a great way to ensure your PC automatically enters a power-saving state after a period of inactivity, thus limiting the chances of it waking up unexpectedly. This feature is particularly useful for laptops and desktop computers that are often left unattended. Here's a step-by-step guide to implementing this:
Step 1: Access Power Settings
Start by opening the 'Control Panel' on your Windows computer. You can do this by searching for 'Control Panel' in the Start menu. In the Control Panel, look for the 'Power Options' or 'Power Settings' and click on it. On a Mac, you can access 'Energy Saver' preferences from the System Preferences.
Step 2: Adjust Sleep Settings
Within the power settings, locate the 'Sleep' or 'Energy Saver' settings. Here, you'll find various options to customize the behavior of your computer when it's inactive. Look for a setting labeled 'Time to sleep' or 'After' followed by a duration. This setting determines how long the computer should wait for inactivity before entering the sleep mode. You can set this timer to a duration that suits your needs, such as 15 minutes, 30 minutes, or even longer if you're comfortable with it.
Step 3: Customize Additional Settings (Optional)
Depending on your operating system, you might have additional customization options. For example, on Windows, you can choose to 'Turn off display' after a certain period of inactivity, which further reduces power consumption. You can also set the computer to 'Hibernate' instead of sleep, which saves the current state of your work and powers down the computer, allowing for a quicker resume when you return.
Step 4: Test and Adjust
After setting the sleep timer, test it by leaving your computer idle for the specified duration. Check if it indeed powers down or enters sleep mode as expected. If you need to adjust the timer, simply modify the setting and repeat the test until you find the perfect balance between convenience and energy savings.
By implementing a sleep timer, you can effectively manage your computer's power state, ensuring it remains in a low-power mode when not in use, thus reducing energy consumption and potentially extending the lifespan of your hardware. This simple setting can contribute to a more efficient and environmentally friendly computing experience.
The Sleep Switch: Unlocking the Brain's Control Center
You may want to see also

Network Management: Disable unnecessary network connections to prevent wake-ups from network activity
In the realm of network management, one of the key strategies to prevent unnecessary wake-ups from sleep mode is to disable any unused or unnecessary network connections. This practice is particularly crucial for laptops and computers that are designed to conserve power and remain in a low-power state when not in active use. By minimizing the number of active network interfaces, you can significantly reduce the chances of your computer waking up due to network-related activities.
The process of disabling unnecessary network connections begins with identifying the network interfaces available on your system. These interfaces can include Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth, and even certain USB devices that support network connectivity. It is essential to understand that each of these interfaces has the potential to trigger a system wake-up if they are set to a power-saving mode or are actively searching for connections.
Once you have identified the interfaces, the next step is to disable those that are not required for your current task or daily usage. For example, if you are primarily using a wired Ethernet connection for internet access and have no need for Wi-Fi, it would be beneficial to disable the Wi-Fi adapter. Similarly, if Bluetooth is not in use, it can be turned off to eliminate any potential power consumption and wake-up triggers.
To disable these interfaces, you can access your computer's network settings and locate the respective interface settings. Here, you will find options to enable or disable the interface and set its power management preferences. It is recommended to disable the interface entirely or set it to a power-saving mode that does not require frequent wake-ups. Some operating systems provide tools or utilities specifically designed for network management, allowing for easier control and customization of these settings.
By implementing this network management technique, you can effectively reduce the number of potential wake-up triggers, ensuring that your computer remains in a power-saving state for extended periods. This approach is particularly useful for users who prioritize energy efficiency and want to minimize any unnecessary interruptions to their workflow. Regularly reviewing and adjusting network connections can contribute to a more stable and power-efficient computing experience.
The Science Behind the Struggle: Why Waking Up is So Tough
You may want to see also

USB Control: Block USB devices from waking up the PC when plugged in
To prevent your PC from waking up from sleep mode when a USB device is plugged in, you can utilize the built-in power management settings in your operating system. Here's a step-by-step guide to achieving this:
- Access Power Settings: Start by opening the Power Settings panel. In Windows, you can do this by searching for "Power Options" in the Start menu or by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting "Power Options." On a Mac, go to System Preferences > Energy Saver.
- Configure Sleep Settings: Navigate to the "Sleep" or "Energy Saver" settings. Here, you'll find options to customize how your PC behaves when it enters sleep mode. Look for a section related to "Power-on behavior" or "When plugged in."
- Disable Wake on USB: Within the power settings, locate the option to disable "Wake on USB." This setting controls whether the PC should wake up when a USB device is connected. You can typically find this option under advanced power settings or device power management. Select the appropriate USB device(s) and choose the "Do not wake" option. This ensures that the PC remains asleep even if a USB device is plugged in.
- Additional Customization: Depending on your operating system, you might have further customization options. For example, in Windows, you can set specific USB devices to wake the PC if needed, while others are blocked. This allows for more granular control over which USB devices trigger a wake event.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage USB device wake-up behavior, ensuring your PC remains in a power-saving state when not in use. This is particularly useful for laptops or desktop computers with multiple USB ports, as it helps conserve power and extend battery life or reduce energy consumption. Remember to adjust these settings according to your specific requirements and the devices you connect to your PC.
Overwatch Anna's Sleep Paralysis: Can You Wake Her?
You may want to see also

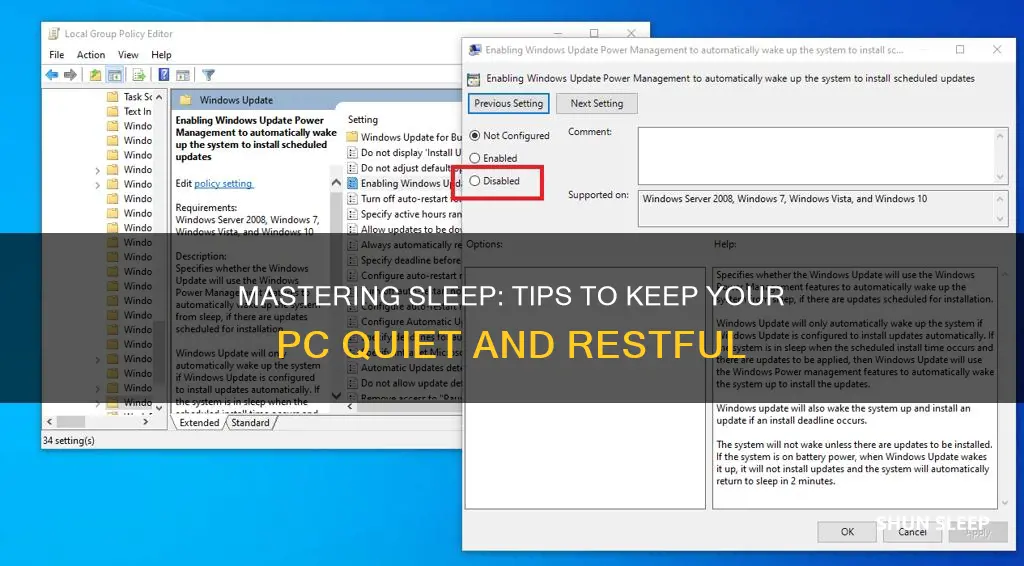
BIOS/UEFI Settings: Modify hardware settings to restrict wake-up sources and power management
To effectively limit your PC's ability to wake up from sleep mode, you need to delve into the BIOS or UEFI settings, which control the hardware's fundamental operations. Here's a step-by-step guide to modifying these settings to restrict wake-up sources and optimize power management:
Accessing the BIOS/UEFI:
The first step is to access your computer's BIOS or UEFI setup. This process varies depending on your PC's manufacturer. Typically, you can access it by pressing a specific key (often F2, F10, or Del) repeatedly during the boot process. Once inside, navigate through the menus using the arrow keys and select the appropriate settings using the numeric keypad.
Locating Power Management Settings:
Look for the "Power Management" or "Power Options" menu. This section will vary depending on your BIOS/UEFI version and manufacturer. Here, you'll find settings related to power-saving modes and hardware wake-up sources.
Restricting Wake-Up Sources:
- Disable Unnecessary Devices: Identify and disable any devices that shouldn't wake your PC from sleep. This includes peripherals like USB devices, network adapters, and Bluetooth. Only keep essential devices enabled.
- Configure Wake-Up Timers: Some BIOS/UEFI versions allow you to set wake-up timers. You can disable these timers entirely to prevent any scheduled wake-ups.
- Advanced Power Management: Explore advanced power management settings. Look for options like "Power-off on sleep" or "Deep sleep" to ensure your PC enters a deeper sleep state that requires fewer wake-up sources.
Optimizing Power Management:
- Adjust Sleep/Hibernate Settings: Configure your PC to use sleep mode instead of hibernation whenever possible. Sleep mode retains your system state and requires less power to wake up.
- CPU Power Management: Modify CPU power settings to limit performance when the PC is asleep. This reduces power consumption and further minimizes wake-up triggers.
- Monitor Power-Saving States: Familiarize yourself with the different power-saving states (S1, S3, S4, etc.) offered by your BIOS/UEFI. Choose the most appropriate state for your needs to balance power savings and wake-up reliability.
Saving and Exiting:
After making the necessary adjustments, remember to save your settings and exit the BIOS/UEFI. This often involves selecting an "OK" or "Apply" option and then exiting the setup. Your PC will reboot with the new power management settings in effect.
Troubleshooting Tips: Reviving a Sluggish Printer
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To minimize wake-ups, you can adjust power settings by accessing the 'Power Options' in your PC's settings. Look for the 'Sleep' or 'Energy Saver' settings and adjust the time limits for sleep, hibernate, and shutdown. You can set these to never sleep or hibernate, or set longer durations to reduce the chances of the system waking up.
Yes, you can manage which devices and applications are allowed to wake up your PC. Go to the 'Device Manager' and locate the device you want to control. Right-click and select 'Properties', then go to the 'Power Management' tab. Here, you can uncheck the option that allows the device to wake the computer. Repeat this process for all devices you want to restrict.
Absolutely! There are various third-party software tools available that can help manage power settings and restrict wake-ups. These tools often provide more granular control over power options and can be useful for advanced users. Some popular options include 'Sleep Asynchroneous' and 'PowerToys', which offer features to disable specific hardware and software from waking the PC.