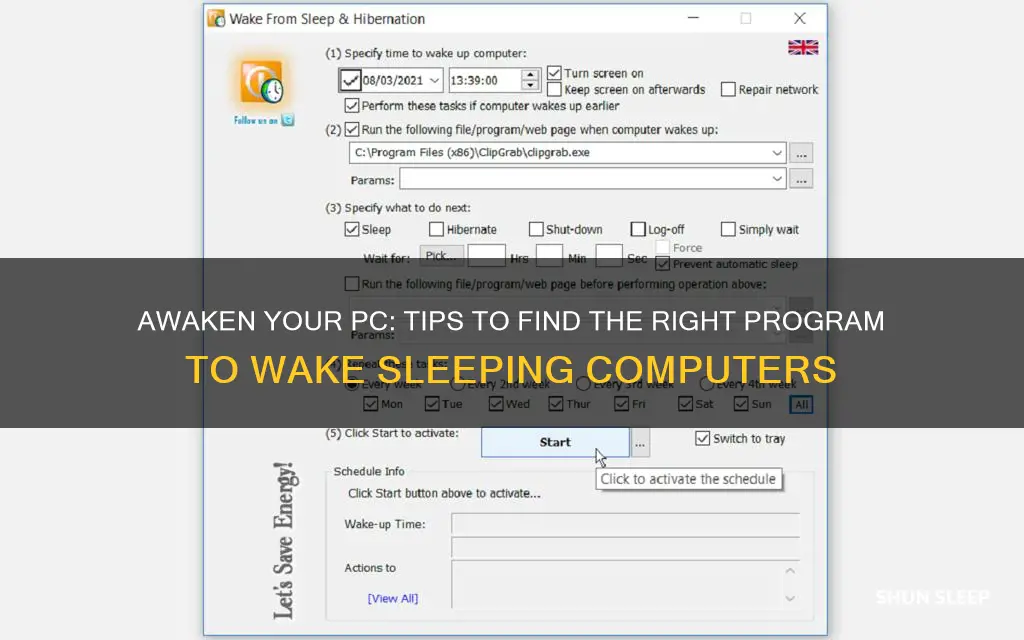
Finding a program that can wake up a sleeping computer can be a useful skill for anyone who wants to ensure their computer is ready for use when they need it. Whether you're a busy professional, a student, or a home user, having a program that can quickly and reliably wake your computer from sleep mode can save you time and frustration. In this guide, we'll explore some of the best methods and tools you can use to find and set up a program that will wake your sleeping computer, ensuring it's always ready for your next task.
What You'll Learn
- Identify Sleep States: Determine which power states your computer enters during sleep, e.g., S1, S3, or S4
- Monitor System Logs: Use system logs to track when the computer transitions into and out of sleep
- Use Task Manager: Check the Task Manager for processes that keep the computer awake
- Check Power Settings: Review power settings to ensure no unnecessary sleep or hibernation is enabled
- Analyze Hardware Sensors: Examine hardware sensors data to identify any issues causing the computer to stay asleep

Identify Sleep States: Determine which power states your computer enters during sleep, e.g., S1, S3, or S4
To identify the specific sleep states your computer enters, you need to examine its power management settings and understand the different levels of sleep modes. These states are often referred to as 'sleep cycles' or 'power states' and are standardized across various computer systems. Here's a breakdown of how to determine these states:
Check Power Management Settings: Start by accessing your computer's power settings. The method for this varies depending on your operating system. For Windows, you can typically find these settings by right-clicking on the battery icon in the system tray and selecting 'Power Options'. On macOS, go to 'System Preferences' and then 'Energy Saver'. Here, you'll find detailed information about your computer's power management behavior. Look for sections related to 'Sleep' or 'Power States' to identify the specific modes your system uses.
Understand Sleep States: There are several sleep states, each with its own characteristics:
- S1 (Active State): This is the least aggressive sleep state, where the computer remains powered on and can quickly resume operations. It involves minimal power consumption and is often used for tasks that require quick access to data.
- S3 (Hibernation): S3 sleep is a deeper state where the computer saves the current state of memory to disk and powers down, consuming very little power. It's ideal for long periods of inactivity.
- S4 (Soft Off): S4 is a fully powered-off state, but it can be quickly resumed. It's a more aggressive power-saving mode compared to S3.
Monitor System Behavior: Pay attention to how your computer behaves during sleep. For example, if you notice that your computer quickly resumes from sleep, it's likely in the S1 state. If it takes a noticeable amount of time to wake up, it might be in S3 or S4. You can also use system monitoring tools to track power usage and identify the specific sleep states your computer enters.
Use Diagnostic Tools: Some operating systems provide built-in diagnostic tools to help identify sleep states. For instance, Windows includes a 'Power Troubleshooter' that can help diagnose and fix power-related issues, including sleep state identification. These tools can provide valuable insights into your computer's power management behavior.
By understanding these sleep states and monitoring your computer's behavior, you can effectively identify the specific power states it enters during sleep, which is crucial for finding and implementing the right program to wake your sleeping computer.
Power Button Magic: Unlocking Sleep Mode Secrets
You may want to see also

Monitor System Logs: Use system logs to track when the computer transitions into and out of sleep
To effectively monitor your computer's sleep states and identify the programs that wake it up, you can leverage system logs. These logs provide a detailed record of system activities, including power management events. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use system logs for this purpose:
Accessing System Logs:
Start by accessing your system's logs. The location and format of logs can vary depending on your operating system. For Windows, you can use the Event Viewer, which provides a comprehensive view of system events. Open Event Viewer and navigate to the "Windows Logs" section. Here, you'll find various logs, including "System," "Application," and "Power." For macOS, you can use the "Console" application, which displays system logs in real-time.
Identifying Sleep Transitions:
Look for events related to power management and sleep states. These events often provide valuable information about when the computer enters and exits sleep modes. In Windows, search for events with keywords like "Sleep," "Hibernation," or "Power Management." These events typically include details such as the time of the transition, the power state, and the duration. On macOS, you might find similar events under the "Power" log, indicating when the system transitions to or from sleep.
Analyzing Log Content:
Pay close attention to the log messages. They often contain crucial details about the programs or processes involved in waking the computer. For instance, a log entry might state, "Program X initiated a wake-up call at 10:30 AM." Look for patterns or specific programs that consistently trigger these events. You can also use filtering options in your log viewer to narrow down the results and focus on relevant entries.
Troubleshooting and Identifying Programs:
If you suspect a particular program is causing frequent wake-ups, you can correlate the log entries with the program's usage. For example, if a specific application is running when the computer wakes up, it's a strong indicator of its involvement. Additionally, you can use the log data to troubleshoot and identify any issues related to power management. By analyzing the timing and frequency of these events, you can pinpoint the programs or processes that are causing the computer to wake up from sleep.
Remember, system logs provide a historical record, allowing you to review past events and identify patterns. This method is particularly useful for troubleshooting and understanding the behavior of your computer's power management system. By monitoring these logs regularly, you can gain insights into the programs that interact with the system and potentially optimize your computer's power usage.
Awakening Windows 10: Tips for a Smooth Wake-Up
You may want to see also

Use Task Manager: Check the Task Manager for processes that keep the computer awake
To identify the programs or processes that might be keeping your computer awake, you can utilize the Task Manager, a powerful tool available on most Windows operating systems. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use the Task Manager to find these processes:
- Right-click on the taskbar, which is the bar at the bottom of your screen, to open the Task Manager. You can also access it by pressing the 'Ctrl + Shift + Esc' keys on your keyboard simultaneously. This will display a list of all running processes and applications.
- Navigate to the 'Processes' tab, which provides a comprehensive view of all the active processes on your system. Here, you'll see a list of processes, each with its name, CPU usage, memory usage, and other details. Look for any processes that are using a significant amount of CPU or memory, as these could be the culprits keeping your computer awake.
- In the 'Processes' tab, you can also sort the list by various columns, such as CPU, Memory, or Name, to make it easier to identify any unusual or resource-intensive processes. Look for any unfamiliar or unexpected applications that are consuming a lot of resources.
- If you find a process that seems to be causing your computer to stay awake, you can right-click on it and select 'End Task' to force it to stop. However, exercise caution when doing this, as it might disrupt the normal functioning of your computer or certain applications. It's recommended to research the process or application first to ensure it's not essential for your system's stability.
- Additionally, you can explore the 'Details' tab in the Task Manager, which provides a more comprehensive view of all processes, including those that are not visible in the main list. This can be useful if you suspect a background process or service is keeping your computer awake.
By regularly checking the Task Manager, you can identify and manage the processes that consume excessive resources, potentially resolving the issue of your computer waking up from sleep mode. This method is a straightforward way to troubleshoot and optimize your system's performance.
Whoop's Impact: Can It Wake You Up from Light Sleep?
You may want to see also

Check Power Settings: Review power settings to ensure no unnecessary sleep or hibernation is enabled
When your computer goes to sleep or hibernates, it's important to understand the underlying reasons and settings that trigger these actions. One crucial aspect to examine is the power settings on your device. By reviewing and adjusting these settings, you can ensure that your computer remains responsive and doesn't fall into an unintended sleep state.
The power settings in your computer's operating system play a pivotal role in determining when the machine enters a sleep or hibernation mode. These settings often include options to adjust the display timeout, system sleep duration, and hibernation file location. It is essential to check and customize these parameters to prevent unnecessary sleep or hibernation.
To begin, access the power settings on your computer. The location of these settings may vary depending on your operating system. For Windows users, you can typically find them in the Control Panel under 'Power Options'. On macOS, go to 'System Preferences' and then 'Energy Saver'. Here, you'll have the ability to customize various power-related settings.
Within these power settings, look for options related to sleep and hibernation. Ensure that the system is configured to wake up when needed, such as when a specific program is launched or a network connection is established. Disable any unnecessary sleep or hibernation triggers that might cause the computer to enter an unintended sleep state. For instance, you might want to disable the display sleep setting if you frequently use your computer for extended periods without needing to save power.
Additionally, consider the power plan you are using. Different power plans offer varying levels of performance and power-saving features. Select a plan that aligns with your usage patterns, ensuring it doesn't inadvertently trigger sleep or hibernation. By carefully reviewing and adjusting these power settings, you can effectively manage your computer's behavior and ensure it remains responsive and ready for use when needed.
Understanding Bird Sleep Patterns: Tips to Gently Awaken Your Feathered Friend
You may want to see also

Analyze Hardware Sensors: Examine hardware sensors data to identify any issues causing the computer to stay asleep
To troubleshoot a computer that remains asleep, it's crucial to delve into the hardware sensors and their data. These sensors provide valuable insights into the system's health and can often reveal the root cause of the issue. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to analyze hardware sensor data to identify potential problems:
- Identify Relevant Sensors: Begin by understanding the hardware sensors your computer utilizes. Common sensors include temperature sensors, fan speed sensors, CPU/GPU temperature sensors, and power supply sensors. Each sensor type monitors specific components and their operating conditions. For instance, temperature sensors track the heat generated by the CPU and GPU, while fan speed sensors ensure adequate cooling by adjusting fan rotation.
- Access Sensor Data: Most modern operating systems provide a way to access hardware sensor data. This can be done through the system's built-in monitoring tools or third-party software. Look for options like "System Monitor," "Task Manager," or "Hardware Monitor" in your operating system's settings. These tools display real-time sensor readings, allowing you to analyze their behavior.
- Check for Anomalies: Examine the sensor data for any unusual or abnormal readings. For example, if the CPU temperature sensor consistently shows a temperature significantly higher than the expected range, it could indicate a potential overheating issue. Similarly, if the fan speed sensor reads a constant zero, it might suggest a faulty fan. Look for patterns or trends that deviate from the normal operating range.
- Compare with Historical Data: If possible, compare the current sensor data with historical readings. This can help identify if the issue is recent or has been ongoing. For instance, if the temperature sensor data shows a steady increase over time, it could indicate a failing cooling system. Comparing current and historical data can provide valuable context for troubleshooting.
- Eliminate External Factors: While analyzing sensor data, consider other potential factors that might affect the computer's sleep state. External factors such as power supply issues, faulty peripherals, or software conflicts can impact the system's behavior. Ensure that the computer is not experiencing any external interference or power-related problems that could be causing it to stay asleep.
By thoroughly examining hardware sensor data, you can gain valuable insights into the computer's internal health and identify specific issues related to its sleep state. This approach allows for a more targeted and effective troubleshooting process, helping you find the program or solution needed to wake the sleeping computer.
Coffee's Power: Can It Break Your Sleep Cycle?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To identify the program responsible for waking your computer, you can use the Task Manager or Activity Monitor. On Windows, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager, and then look for the program that has the highest CPU or memory usage when your computer transitions from sleep to active state. On a Mac, open Activity Monitor (found in Applications > Utilities) and examine the processes running at that time.
Yes, you can configure your computer's power settings to control which programs can wake it. On Windows, go to Settings > System > Power & sleep, and then click 'Additional power settings'. Here, you can create a power plan that allows you to specify which programs can wake your computer. On a Mac, navigate to System Preferences > Energy Saver, and adjust the settings to control which applications can wake your machine.
Absolutely! There are several third-party tools available that can help you monitor and manage power-related activities. For example, 'PowerToys' by Microsoft offers a feature called 'Sleep Watchdog' that can notify you when a program is about to wake your computer. Other tools like 'Sleep Timer' or 'Sleep Switch' provide similar functionality, allowing you to set specific conditions for your computer to remain asleep.