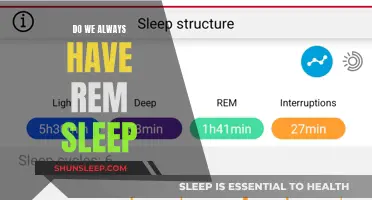
Sleep is a complex and dynamic process that affects how we function in ways scientists are only beginning to understand. Sleep is divided into two stages: REM (rapid eye movement) and NREM (non-rapid eye movement). NREM is further split into three parts: starting to fall asleep, light sleep, and deep sleep. During a typical night, your sleep alternates through cycles of REM and NREM sleep about every 90 minutes. The REM stage accounts for approximately 25% of sleep time, while the NREM stage takes up the other 75%.
REM sleep is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity. Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Eyes | Move rapidly in different directions |
| Brain Activity | More similar to when awake |
| Dreams | Typically occur during this stage |
| Heart Rate | Increases |
| Blood Pressure | Increases |
| Breathing | Becomes irregular and erratic |
| Muscles | Become temporarily paralysed |
What You'll Learn
- REM sleep is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
- Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night
- REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming
- You can increase your REM sleep by getting more sleep overall, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding nicotine and caffeine
- REM sleep is also known as active sleep, desynchronized sleep, paradoxical sleep, and dream sleep

REM sleep is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity
REM sleep is one of the most fascinating stages of sleep, as it is so different from other stages. During REM sleep, the eyes move rapidly, the brain is highly active, and the body experiences a temporary loss of muscle tone. This stage is characterised by relaxed muscles, quick eye movement, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and increased brain activity.
During REM sleep, your eyes will dart rapidly from side to side behind closed eyelids. Your heart rate speeds up and your breathing becomes irregular, with a faster and more erratic pattern. Your muscles become temporarily paralysed, which is thought to be a protective measure to stop you from acting out your dreams and injuring yourself. However, this hypothesis is being questioned as it is now known that dreams can occur during non-REM sleep, when the body is not paralysed.
REM sleep usually occurs around 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. The first cycle is the shortest, lasting about 10 minutes, with each subsequent cycle getting longer, up to an hour. You will experience several REM cycles throughout the night, with most of your REM sleep taking place in the second half of the night.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory, as well as emotional processing and brain development. It plays a significant role in helping your brain consolidate and process new information, ensuring better mental concentration and mood regulation. A lack of REM sleep can have serious negative effects on overall health, including brain function and cellular repair.
If you want to increase your REM sleep, you need to get more sleep overall. Sticking to a sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can all help improve your sleep.
How to Induce REM Sleep Without Falling Asleep
You may want to see also

Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night
REM sleep is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle, during which the eyes move rapidly, the brain is active, and dreaming occurs. The first REM cycle of the night is the shortest, lasting around 10 minutes, while the final one may last up to an hour. The average adult experiences three to five cycles per night, with each cycle lasting 90 to 120 minutes.
If you're concerned about your sleep patterns or feel you're not getting enough REM sleep, it's important to speak with a healthcare professional. They can help you understand the impact of your sleep habits on your overall health and provide guidance on improving your sleep quality.
The Intriguing World of REM Sleep: A Visual Guide
You may want to see also

REM sleep is important for memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming
During REM sleep, the brain processes new learnings and motor skills from the day, deciding which ones to commit to memory, maintain, and which ones to delete. REM sleep is also when the brain transfers short-term memories into long-term memories.
REM sleep is also when the brain processes emotions. The amygdala, the part of the brain that processes emotions, activates during REM sleep. Dreams, which are more vivid during REM sleep, may also be involved in emotional processing.
REM sleep may also promote brain development. Newborns spend most of their sleep time in REM, and animals born with less developed brains, such as humans and puppies, spend even more time in REM sleep during infancy than those born with more developed brains, like horses and birds.
Finally, REM sleep is when most dreams occur. The dreams that occur during REM sleep tend to be more vivid than those that occur during non-REM sleep.
Understanding Sleep: The Pre-REM Stage Explained
You may want to see also

You can increase your REM sleep by getting more sleep overall, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding nicotine and caffeine
REM sleep is the fourth and final stage of the sleep cycle, which we first enter about 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. It is characterised by rapid eye movement, increased brain activity, irregular breathing, an elevated heart rate, and relaxed muscles. Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night, which plays a role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, brain development, and dreaming.
If you want to increase your REM sleep, try the following:
Get more sleep overall
Since REM sleep occurs mostly during the second half of the sleep period, sleeping for a longer period will allow time to complete all the REM sleep cycles. Most adults need seven to nine hours of sleep every night.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine
Try activities such as taking a warm bath, listening to relaxing music, or reading a book.
Avoid nicotine and caffeine
Both substances can interfere with your sleep, especially if consumed in the evening or close to your desired sleep period.
Other tips
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom environment.
- Avoid bright lights, TV, and electronics before bed.
- Avoid alcohol before bed.
Recognizing REM Sleep: Signs and Brain Activity
You may want to see also

REM sleep is also known as active sleep, desynchronized sleep, paradoxical sleep, and dream sleep
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the fourth of four stages of sleep. During this stage, the eyes move rapidly, the brain is highly active, and the body experiences a temporary loss of muscle tone. This stage of sleep is associated with dreaming and memory consolidation.
REM sleep is also known as active sleep because the brain is highly active during this stage, resembling brain activity when a person is awake. It is called desynchronized sleep because the brain waves during this stage are more variable compared to the slow brain waves of non-REM sleep.
REM sleep is also referred to as paradoxical sleep, a term coined by French researcher Michel Jouvet due to the high brain metabolic demand and the lack of clear benefits to the body during this state. Additionally, the suppression of REM sleep through certain drugs does not seem to have any striking effects on behaviour, memory, or overall health.
Finally, REM sleep is known as dream sleep because it is the stage of sleep where most dreams occur. However, it is important to note that dreams can also occur during non-REM sleep stages.
Sleep Terrors: The Mystery of Non-REM Sleep
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During this stage, your eyes move rapidly in different directions, and your brain is active. Your brain activity is similar to when you're awake, and dreams typically occur during this stage.
Most adults need about two hours of REM sleep each night. However, this can vary depending on age and individual needs.
If you're getting the recommended seven to nine hours of sleep per night, you're likely getting enough REM sleep. However, if you experience symptoms such as trouble coping with emotions, difficulty concentrating, a weakened immune system, or feeling groggy in the morning, you may not be getting enough REM sleep.
To increase your REM sleep, focus on improving your overall sleep quality and duration. This may include creating a relaxing bedtime routine, setting a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, and getting regular exercise.