Many users encounter a common issue when trying to wake up their desktop computer from sleep mode: the power button doesn't seem to work. This can be frustrating, especially when you need to access important files or applications. Understanding why this happens and how to resolve it is essential for anyone who relies on their desktop for work or personal use. In this paragraph, we'll explore the reasons behind this problem and provide practical solutions to help you get your computer back up and running smoothly.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Method | Pressing the power button on the computer |
| Effect | Waking the computer from sleep mode |
| Purpose | To resume the computer's operation after it has been in a low-power state |
| User Interaction | Physical action required; no software automation needed |
| System Compatibility | Most modern desktop computers with Windows, macOS, or Linux operating systems |
| Potential Issues | May cause unexpected behavior if the system is not properly configured; can lead to system hangs or crashes if done incorrectly |
| Alternative Methods | Using keyboard shortcuts (e.g., Windows key + X, then selecting "Restart"), or software tools to manage power settings |
What You'll Learn
- Power Button Functionality: Understanding how the power button interacts with the system during sleep
- Sleep States: Exploring the different sleep states and their impact on the desktop
- Wake-Up Commands: Identifying the specific commands that trigger the desktop to wake from sleep
- Power Management Settings: Adjusting settings to control wake-up behavior and power consumption
- Hardware Interventions: Exploring hardware solutions to wake the desktop from sleep

Power Button Functionality: Understanding how the power button interacts with the system during sleep
The power button on a desktop computer is a critical component that facilitates interaction between the user and the system, especially when it comes to managing power states. When a computer enters sleep mode, it is a power-saving state where the system temporarily halts many background processes and displays, conserving energy. However, the user still needs a way to wake the system back up, and this is where the power button plays a crucial role.
When you press the power button on a sleeping desktop, it triggers a series of events that bring the system back to a fully operational state. The button's functionality is designed to communicate with the computer's hardware and software, initiating a process that resumes normal operations. This process involves several steps, starting with the hardware components.
Upon pressing the power button, the computer's motherboard receives the signal and initiates a power-on sequence. This sequence includes powering up the CPU, RAM, and other essential components. The system then begins to boot up, starting with the basic input/output system (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), which is responsible for initializing hardware and setting up the system for the operating system. During this phase, the power button's interaction with the system is direct and immediate, ensuring a swift response.
As the system boots, it loads the operating system, and the user interface comes back to life. The power button's functionality extends beyond just powering on; it also allows for various power management options. For instance, a long press or a double-tap on the power button might initiate a shutdown or restart, respectively, providing users with quick access to these essential system functions. This level of control is particularly useful for users who want to manage their computer's power state efficiently without relying on the graphical user interface.
Understanding the power button's functionality is essential for users who want to optimize their computer's performance and manage power consumption. By knowing how the power button interacts with the system during sleep, users can take advantage of its versatility, ensuring their desktop is ready for use whenever needed. This knowledge also empowers users to troubleshoot issues related to power management, making their computing experience more efficient and user-friendly.
Sleep Tech's Impact: Do Sleep Wake Cases Hurt Your Battery?
You may want to see also

Sleep States: Exploring the different sleep states and their impact on the desktop
The concept of sleep states is an essential aspect of computer management, especially for desktop systems, as it allows for efficient power management and improved performance. When a desktop enters sleep mode, it transitions through various stages, each with its own set of characteristics and implications. Understanding these sleep states is crucial for users who want to optimize their desktop's power usage and ensure a seamless experience.
In the first sleep state, known as "Standby" or "S1," the desktop system remains in a low-power state while retaining its memory and context. During this state, the processor, memory, and other components are powered down, but the system can quickly resume normal operation. This is a common power-saving mode, especially when the user is away from the desk for a short period. When the power button is pressed, the system can wake up almost instantly, making it ideal for quick access without the need for lengthy boot-up processes.
The next sleep state is called "Sleep" or "S2." Here, the desktop system powers down most components, including the processor and hard drive, but retains power to the RAM. This state is more energy-efficient than Standby but still allows for faster wake-up times compared to deeper sleep modes. When the system enters Sleep mode, it can be woken up by a simple keystroke or a mouse click, making it convenient for users who want to minimize power consumption without sacrificing responsiveness.
A more advanced sleep state is "Hibernation" or "S3." In this mode, the desktop system saves the current state of the operating system and applications to a file on the hard drive, then powers down all non-essential components. Hibernation is particularly useful for laptops, as it allows them to be completely shut down without losing any data. However, for desktops, it might be less practical due to the need for a dedicated hibernation file. When the system hibernates, it requires a full boot-up process to resume, which can be slower than Standby or Sleep modes.
The final sleep state is "Off," where the desktop system is completely powered down, and all components are disconnected. This state is the most energy-efficient but also the least convenient for quick access. When the system is in this mode, pressing the power button will not wake it up until it is manually restarted. This state is often used when the desktop is not in use for an extended period and requires a complete reset of the system.
Understanding these sleep states empowers users to make informed decisions about their desktop's power management. By choosing the appropriate sleep mode, users can balance energy efficiency, convenience, and performance. For instance, Standby and Sleep modes offer a good compromise between power savings and quick wake-up times, while Hibernation is ideal for those who want to ensure data retention during extended periods of inactivity.
Newborn Sleep: When to Wake Your Baby and When to Let Them Rest
You may want to see also

Wake-Up Commands: Identifying the specific commands that trigger the desktop to wake from sleep
When it comes to waking up a desktop computer from sleep mode, the power button is often the go-to method. However, the process can vary depending on the operating system and hardware configuration. Here's a breakdown of the wake-up commands and how they work:
Power Button Press: The most common and straightforward method is to simply press the power button. This action sends a signal to the computer's motherboard, indicating that it should exit sleep mode and resume normal operation. The computer may take a few seconds to boot up, but this method is generally reliable and user-friendly.
Keyboard Shortcuts: Some operating systems offer keyboard shortcuts to wake up the computer. For example, on Windows, pressing the 'Shift' + 'Sleep' buttons simultaneously can wake the computer from sleep. Similarly, on macOS, holding down the 'Control' and 'Shift' keys while pressing the power button can achieve the same result. These shortcuts provide a quick way to wake the computer without having to navigate through the graphical user interface.
External Devices: In certain scenarios, connecting an external device can trigger the wake-up process. For instance, plugging in a USB drive or an external hard drive can sometimes wake the computer from sleep. This is particularly useful when you need to access data on an external storage device without fully powering down the system.
Network Connection: Another wake-up command is establishing a network connection. When a computer is in sleep mode, it may disconnect from the network. By reconnecting to a Wi-Fi network or plugging in an Ethernet cable, the computer can be woken up. This is especially relevant for laptops or desktop computers that rely on network connectivity for internet access or remote control.
It's important to note that the specific wake-up commands may vary depending on the hardware manufacturer and the operating system version. Some computers might require additional steps or have unique wake-up methods. Understanding these commands can be crucial for efficient computer management and troubleshooting.
Deep Sleep, Wake-Up Calls: The Watchdog Effect
You may want to see also

Power Management Settings: Adjusting settings to control wake-up behavior and power consumption
When it comes to managing the power settings on your desktop computer, you have the ability to fine-tune its behavior to ensure it meets your specific needs. One crucial aspect is controlling how your computer wakes up from sleep mode, and this is where the power management settings come into play. By adjusting these settings, you can customize the wake-up process and optimize power consumption, ensuring your computer operates efficiently.
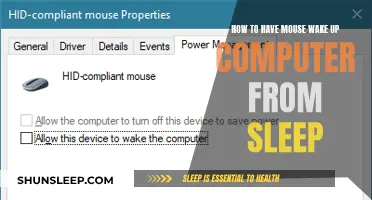
The power management settings allow you to define the conditions under which your computer should wake up. For instance, you can set the power button to wake the computer from sleep when pressed, which is useful for quick access. However, you might also want to restrict wake-up events to specific scenarios, such as when a network connection is established or a particular peripheral device is connected. This level of control ensures that your computer remains in a power-saving state until it's truly needed, reducing unnecessary power consumption.
To access these settings, navigate to the power management options in your computer's control panel or system preferences. Here, you'll find various tabs or categories dedicated to power-related configurations. Look for sections like 'Sleep' or 'Power Options', where you can find detailed settings to manage wake-up behavior. You might be able to set specific wake-up triggers, such as enabling the computer to wake up when a network cable is plugged in or when a USB device is connected.
Additionally, you can adjust the power plan or profile to customize the computer's behavior. Different power plans offer varying levels of performance and power-saving options. For example, a 'Balanced' plan might provide a middle ground between performance and energy efficiency, allowing the computer to wake up quickly when needed while still conserving power during idle time. On the other hand, a 'Power Saver' plan could prioritize energy efficiency, putting the computer into a deeper sleep state and requiring more deliberate actions to wake it up.
By exploring and modifying these power management settings, you can take control of your computer's wake-up behavior and overall power consumption. This ensures that your desktop computer operates efficiently, meeting your requirements while minimizing unnecessary energy usage. Remember, the goal is to find the right balance between performance and power-saving modes to suit your specific desktop computing needs.
Gentle Tips for Waking a Child from Deep Slumber
You may want to see also

Hardware Interventions: Exploring hardware solutions to wake the desktop from sleep
When it comes to waking up a desktop computer from sleep mode using the power button, it's important to understand the underlying hardware mechanisms. The process involves a combination of hardware components and their interactions. Here, we delve into the hardware interventions that can help achieve this task.
One potential solution lies in the power management settings of the computer's BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). Accessing the BIOS setup can provide a way to modify power-related configurations. By enabling specific options, such as "Power-on Auto Execution" or "Power-on Self-Test," you can instruct the system to wake up from sleep when the power button is pressed. This method requires a certain level of technical expertise, as it involves navigating through the BIOS interface and making precise adjustments.
Another hardware-related approach involves the use of a dedicated wake-on-button module. These modules are designed to wake up the computer specifically when the power button is pressed. They often require a hardware modification, such as soldering a small circuit board onto the computer's motherboard. This intervention ensures that the power button triggers the desired action, even when the system is in a deep sleep state. It's crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and consult technical resources when implementing this solution.
Additionally, examining the computer's power supply unit (PSU) can be beneficial. The PSU plays a critical role in managing power delivery to the system. By ensuring that the PSU is functioning correctly and providing stable power, you can minimize the chances of unexpected sleep states. Cleaning or replacing the PSU's filters and ensuring proper ventilation can contribute to maintaining optimal power delivery, which may indirectly help in waking the computer from sleep.
In some cases, the issue might stem from the computer's hardware itself. It is worth inspecting the computer's internal components, especially the RAM and storage drives. Sometimes, a loose connection or a faulty component can cause the system to enter an unresponsive sleep state. Careful inspection and potential troubleshooting of these components can be part of the solution, ensuring that the hardware is functioning as expected.
Sleepless Nights: Strategies to Conquer Insomnia and Rise Early
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The power button on your desktop computer is a hardware-level control that can force a system restart or a wake from sleep, even if the operating system is unresponsive or frozen. This method can be useful when the computer is in a deep sleep state and requires an immediate response.
When you press the power button, it sends a signal to the computer's motherboard, which then triggers a hardware reset. This action can help resolve issues related to software locks or unresponsive applications, allowing the system to resume normal operation.
No, using the power button for this purpose is not harmful to your computer. It is a standard function of desktop hardware and can be a quick solution when other wake methods fail. However, excessive and forceful pressing might cause physical damage, so it's recommended to use it gently.
Yes, you can often adjust the power button's functionality in the computer's BIOS or UEFI settings. This allows you to choose between different power states, such as hibernate, sleep, or shutdown, and even set a custom action for the power button. It provides more control over your system's power management.