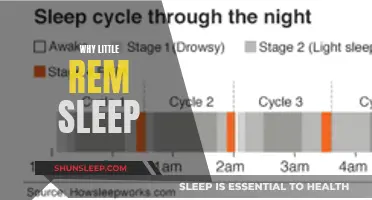
Sleep is a complex and mysterious body process that is essential for health and wellbeing. A good night's sleep is dependent on several factors, including the number of sleep cycles and the quality of sleep within each cycle. On average, a person goes through four to six sleep cycles per night, with each cycle lasting around 90 minutes. Each cycle consists of three stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and a final stage of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. While the amount of sleep needed varies from person to person, understanding the sleep cycle and ensuring adequate time in each stage is crucial for feeling rested and maintaining overall health.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of sleep cycles per night | 4-6 |
| Length of each sleep cycle | 90-120 minutes |
| First sleep cycle length | 70-100 minutes |
| Later sleep cycle length | 90-120 minutes |
| REM sleep | 25% of total sleep time |
| Deep sleep | 25% of total sleep time |
| Light sleep | No minimum requirement |
What You'll Learn

REM sleep is important for learning and memory
Sleep plays a critical role in learning and memory, and this is particularly true of REM sleep. During the REM stage, the brain is active, and dreams typically occur. This stage of sleep stimulates the areas of the brain that aid in learning and memory. Here are some reasons why REM sleep is important for learning and memory:
Memory Consolidation and Recall
REM sleep helps to strengthen and consolidate memories formed throughout the day. It facilitates the transfer of short-term memories from the motor cortex to the temporal lobe, converting them into long-term memories. This process, known as memory consolidation, ensures that new information is stored in the architecture of the brain, making it easier to recall.
Emotional Processing
REM sleep is also crucial for processing emotional experiences and regulating emotions. It helps to reduce the intensity of emotions associated with memories, particularly traumatic or intense ones. This emotional processing aspect of REM sleep can contribute to overall emotional well-being and mental health.
Creative Problem-Solving
In addition to enhancing memory, REM sleep improves creative problem-solving abilities. Research has shown that participants who were woken up during REM sleep performed better on anagram puzzles than those awakened during non-REM sleep or during the daytime. This suggests that REM sleep may play a significant role in improving complex problem-solving skills.
Brain Maintenance
During REM sleep, the brain reorganizes and catalogs memories and learned information. This process is akin to a librarian sorting and shelving books, making it easier to access and retrieve information. It helps integrate new knowledge and improves the ability to recall and utilize that knowledge creatively.
Sleep Spindles
REM sleep is characterized by sleep spindles, which are spikes of neural activity or bursts of brain waves. These sleep spindles are believed to play a crucial role in learning and memory consolidation, especially for physical tasks. They occur during the REM phase, which usually happens towards the end of the night when dreaming is most likely to occur.
In conclusion, REM sleep is essential for learning and memory. It strengthens memory recall, facilitates the conversion of short-term memories into long-term ones, enhances creative problem-solving skills, and contributes to emotional well-being. By understanding the importance of REM sleep, individuals can prioritize their sleep to optimize their cognitive abilities and overall well-being.
EMG Readings: Are We Active During REM Sleep?
You may want to see also

Non-REM sleep is when the body repairs and regrows tissues
Sleep is a complex and mysterious process that is essential for the body and brain to rest and recover. While asleep, the body cycles through different stages of sleep, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages of increasing depth: N1, N2, and N3.
NREM sleep, particularly the deep sleep of the N3 stage, is crucial for the body's physical restoration. During this stage, various bodily functions slow down or stop, allowing the body to repair and regrow tissues, build bone and muscle, and strengthen the immune system. This stage is characterised by slow brain waves, known as delta waves, and even slower oscillations, called slow oscillations. These slow waves are believed to be responsible for the regenerative process that occurs during deep sleep.
The body releases growth hormones during N3 sleep, facilitating tissue repair and the building of bone and muscle. Additionally, this stage of sleep helps regulate glucose metabolism, immune system functioning, hormone release, and memory consolidation. Getting enough N3 sleep is vital for waking up feeling rested and energised.
As people age, they tend to sleep more lightly and experience a decrease in the amount of deep sleep they get. However, studies show that older adults still require the same amount of total sleep as when they were younger. Overall, the recommended amount of sleep for adults is 7 to 9 hours per night, with about 25% of that time spent in the deep sleep stage.
REM Sleep Disorder: Negative Impact on OSA Patients
You may want to see also

Sleep cycles can vary from person to person
Firstly, age plays a significant role in the variation of sleep cycles. Newborns, for instance, spend a lot more time in the REM stage, which can be up to 50% of their sleep. As people get older, they tend to sleep more lightly and experience shorter periods of sleep. Older adults, in particular, tend to spend less time in REM sleep.
Recent sleep patterns can also impact sleep cycles. Irregular or insufficient sleep over an extended period can lead to an abnormal sleep cycle. Additionally, alcohol consumption can alter sleep architecture, reducing REM sleep early in the night and causing a REM sleep rebound as the alcohol wears off.
Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome, can interrupt healthy sleep cycles and cause multiple awakenings. Furthermore, factors like depression, traumatic brain injuries, medications, and circadian rhythm disorders can also affect sleep quality and the time spent in each sleep stage.
It is important to note that sleep cycles can even vary from night to night for the same person due to various factors, including age, recent sleep patterns, and alcohol consumption.
REM Sleep: Easily Awakened or Deep Sleeper?
You may want to see also

Sleep is important for the immune system
During sleep, the body repairs and regrows tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. This is because sleep plays a crucial role in the robustness of the immune system, contributing to both innate and adaptive immunity. Sleep also helps to regulate the production of cytokines, which are proteins that act as messengers for the immune system.
Additionally, sleep has been shown to improve the effects of vaccines, indicating its benefits for adaptive immunity. Studies have found that when individuals do not get enough sleep after receiving a vaccine, their immune response is weaker, and they may require a second dose. Sleep also plays a role in the formation of immunological memory, which is the immune system's ability to recognize and react to dangerous antigens.
Furthermore, sleep helps to regulate the production of hormones such as melatonin, which is adept at counteracting the stress that can come from inflammation during sleep. Getting sufficient sleep facilitates a delicate balance of immune function that is vital for overall health.
Overall, sleep is crucial for the proper functioning of the immune system, and a lack of sleep can have negative consequences on both physical and mental health.
REM vs NREM: Understanding Sleep Stages Better
You may want to see also

Lack of REM sleep can cause grogginess and trouble concentrating
A good night's sleep is essential for our health and well-being. Sleep occurs in cycles, and a healthy adult will typically go through four to five cycles per night. Each cycle includes three stages of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and a stage of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
REM sleep is important for learning and memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain is active and dreams occur. While the purpose of REM sleep is still unknown, a lack of it can lead to grogginess and trouble concentrating the next day.
If you don't get enough REM sleep, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Feeling groggy in the morning
- Trouble concentrating
- Weakened immune system
- Mood changes
- Fatigue
- Problems with memory and other cognitive tasks
To increase your REM sleep, you need to get more sleep overall. Here are some tips to improve your sleep:
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Set a sleep schedule and stick to it.
- Avoid nicotine, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Exercise and spend time outdoors during the day.
- Avoid TV and electronics before bed.
- Avoid heavy meals close to bedtime.
Do Bats Experience REM Sleep?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
REM stands for rapid eye movement. During REM sleep, your eyes move rapidly in different directions, and your brain is active. It is similar to when you are awake. Dreams typically happen during REM sleep.
Non-REM sleep is when your brain is not as active. In the deeper stages of non-REM sleep, your heart rate and body temperature decrease, and your breathing slows down.
On average, there are four to six sleep cycles per night.
Each sleep cycle lasts between 80 to 120 minutes.
During the deep stages of non-REM sleep, the body repairs and regrows tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens your immune system. During REM sleep, your brain is highly active, and this stage is associated with dreaming, learning, and memory.