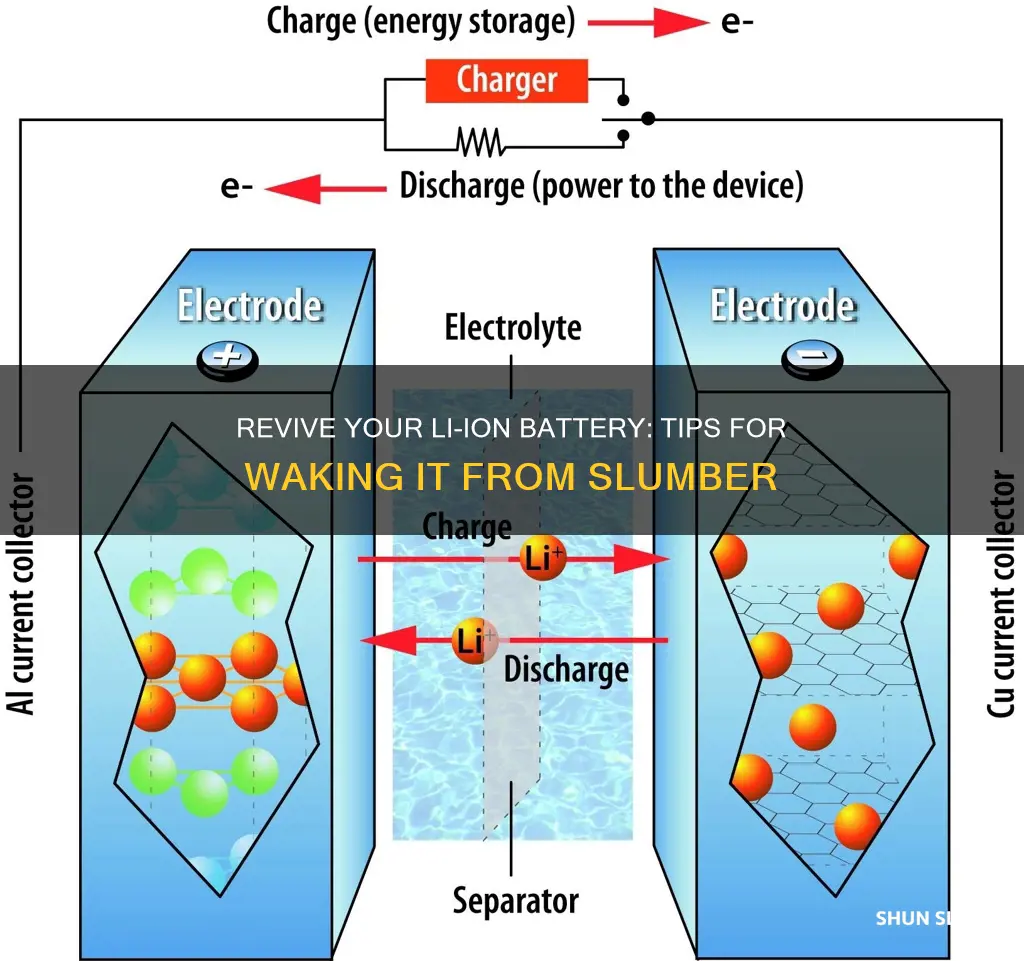
Understanding how to safely and effectively wake a sleeping lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery is crucial for maintaining its performance and longevity. When a Li-ion battery is not in use, it can enter a state of dormancy, where it may not respond to charging or discharging attempts. This phenomenon is often referred to as sleeping and can occur due to various factors, including low temperature, under-voltage, or disuse. To wake a sleeping Li-ion battery, one must employ specific techniques that stimulate the battery to resume its normal operation. This process involves gradually increasing the voltage and current to the battery while monitoring its response to ensure it does not overheat or experience other adverse effects. Properly awakening a sleeping Li-ion battery is essential to prevent damage and ensure its reliability in various applications.
What You'll Learn
- Initial Charge: Apply a gentle, controlled current to restore capacity
- Temperature Control: Optimize temperature to enhance performance and safety
- Voltage Regulation: Maintain a steady voltage to prevent over- or under-charging
- Current Limiting: Use a low current charge to avoid damage
- Discharge Management: Monitor and control discharge to prevent deep discharge

Initial Charge: Apply a gentle, controlled current to restore capacity
When dealing with a seemingly dormant lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery, the initial step to revive its functionality is to initiate a controlled and gentle charging process. This methodical approach aims to stimulate the battery's internal mechanisms and restore its capacity. The key here is to apply a low-voltage current that is carefully regulated to avoid any potential damage. By doing so, you are essentially providing a gentle nudge to the battery, encouraging it to resume its normal operation.
The process begins with connecting the Li-ion battery to a suitable charger designed for its specific voltage and current requirements. It is crucial to use a charger that matches the battery's specifications to ensure safe and effective charging. The charging current should be kept at a very low level, often referred to as a 'trickle charge,' which is significantly lower than the battery's typical operating current. This cautious approach prevents any sudden surges in voltage, which could potentially harm the battery's delicate components.
Over the course of several hours, this gentle current will initiate a series of reactions within the battery. It will begin to restore the chemical balance within the cells, gradually bringing the battery back to life. The charging process should be closely monitored to ensure it remains within the safe parameters. It is essential to avoid overcharging, as this can lead to unnecessary stress on the battery and potentially cause damage.
During this initial charge, it is recommended to keep the battery at room temperature. Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can hinder the charging process and may even lead to permanent damage. Maintaining a moderate temperature range allows the battery to respond optimally to the gentle current.
In summary, the initial charge for a 'sleeping' Li-ion battery involves a meticulous application of a controlled, low-voltage current. This methodical approach aims to revive the battery's capacity without causing any harm. By following this process, you can effectively bring a dormant Li-ion battery back to a state where it can be utilized for its intended purpose.
Mastering the Art of Deep Sleep: Tips to Stay Asleep
You may want to see also

Temperature Control: Optimize temperature to enhance performance and safety
Temperature control is a critical aspect of managing and optimizing the performance and safety of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. These batteries are highly sensitive to temperature variations, and maintaining an optimal temperature range is essential for their longevity and efficient operation. Here's an overview of how temperature control can be optimized for Li-ion batteries:
Understanding Temperature Sensitivity: Li-ion batteries have a narrow temperature operating window. They typically perform best between 15°C and 35°C (59°F to 95°F). Operating outside this range can lead to decreased performance and potential safety hazards. Low temperatures can cause the battery to enter a 'sleeping' state, where it may not be able to provide the required power, while high temperatures can accelerate degradation and even lead to thermal runaway.
Thermal Management Techniques: To optimize temperature control, various thermal management strategies can be employed:
- Cooling Systems: In high-performance applications, active cooling systems can be utilized. These systems use heat sinks, fans, or liquid cooling to dissipate heat and maintain a lower temperature. This is especially important in electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems where multiple batteries are packed closely together.
- Thermal Insulation: Proper insulation can prevent heat loss and maintain the desired temperature. This is often used in battery packs to minimize temperature fluctuations and ensure consistent performance.
- Temperature Monitoring: Advanced temperature sensors are employed to monitor the battery's temperature continuously. These sensors provide real-time data, allowing for quick detection of any temperature anomalies and enabling prompt action.
Optimizing Performance: Temperature control directly impacts the performance of Li-ion batteries:
- Increased Efficiency: Operating within the optimal temperature range ensures that the battery operates at its highest efficiency. This results in improved power output and reduced energy losses.
- Extended Cycle Life: Controlling temperature helps minimize stress on the battery's electrochemical components, leading to longer cycle life and reduced capacity fade over time.
- Enhanced Safety: Maintaining a safe temperature range prevents the formation of thermal runaway conditions. This is crucial for safety, especially in high-energy density applications.
Safety Considerations: Temperature control is vital for safety:
- Overheating Prevention: High temperatures can cause thermal stress and potentially lead to battery failure. Implementing cooling systems and monitoring temperature helps prevent overheating.
- Thermal Runaway Mitigation: In the event of a short circuit or other fault conditions, temperature control measures can help mitigate thermal runaway, a dangerous situation where the battery's temperature rapidly rises.
- Fire and Explosion Prevention: Proper temperature management reduces the risk of fire and explosion, which can occur if the battery's temperature exceeds safe limits.
By implementing effective temperature control strategies, it is possible to optimize the performance and safety of Li-ion batteries, ensuring they operate efficiently and reliably across various applications. This includes managing the temperature during charging and discharging cycles and considering environmental conditions to provide a comprehensive approach to battery management.
Eyelid Lifts: The Science of Waking Up a Sleeping Person
You may want to see also

Voltage Regulation: Maintain a steady voltage to prevent over- or under-charging
Voltage regulation is a critical aspect of managing and maintaining the health of a lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery. When a Li-ion battery is 'sleeping' or in a dormant state, it requires careful handling to ensure it awakens properly and performs optimally. One of the key principles to follow is maintaining a steady voltage during the charging process.
Over-charging a Li-ion battery can lead to several issues. Firstly, it can cause the battery to heat up excessively, potentially leading to thermal runaway, a dangerous situation where the battery's temperature rises uncontrollably. This can result in damage to the battery cells and even pose a fire hazard. Secondly, over-charging can cause the formation of a solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer, which can hinder the battery's performance and reduce its overall lifespan. The SEI layer is a protective barrier that forms on the anode during the initial charging cycles, and while it is beneficial in preventing side reactions, excessive charging can lead to its degradation.
On the other hand, under-charging, or not providing enough current to the battery, can also be detrimental. Under-charging may result in the battery not reaching a full charge, leaving it in a semi-dormant state. This can lead to increased internal resistance, affecting the battery's ability to deliver power efficiently. Over time, under-charging can cause the battery to lose its capacity and become less reliable.
To maintain a steady voltage, it is essential to use a controlled charging algorithm. This algorithm should monitor the battery's voltage and current levels throughout the charging process. By adjusting the charging rate and voltage, the algorithm ensures that the battery charges at a safe and optimal pace. A common technique is to use a constant-current charging phase followed by a constant-voltage phase. During the constant-current phase, the charger provides a fixed amount of current to the battery until it reaches a certain voltage threshold. Then, in the constant-voltage phase, the charger maintains this voltage while gradually reducing the current as the battery nears full capacity.
Additionally, using a smart charger with voltage regulation capabilities is highly recommended. These chargers can automatically adjust the charging parameters based on the battery's characteristics, ensuring a safe and efficient charging process. They often include features like trickle charging, which provides a slow and steady charge to maintain the battery's health without over-charging.
In summary, voltage regulation is vital to prevent over- or under-charging a Li-ion battery. By employing controlled charging algorithms and utilizing smart chargers, one can ensure that the battery awakens from its sleeping state, ready to provide reliable power while maintaining its longevity and performance.
The Prince's Slumber: A Tale of Awakening
You may want to see also

Current Limiting: Use a low current charge to avoid damage
When dealing with a seemingly dormant lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery, it's crucial to approach the process with care and precision to avoid any potential damage. One of the key strategies to revive a sleeping Li-ion battery is through current limiting. This technique involves using a low-current charge to gently coax the battery back to life.
The primary goal here is to prevent over-current conditions, which can lead to excessive heat generation and potential damage to the battery's cells. Li-ion batteries are sensitive to high currents, and applying a rapid, high-current charge can cause irreversible harm. Instead, a slow and controlled approach is recommended.
To implement current limiting, you can use a charger specifically designed for Li-ion batteries. These chargers often have built-in safety features that regulate the charging current. Set the charger to a low-current setting, typically around 0.5 to 1 ampere, which is significantly lower than the typical charging current. This slow charge rate allows the battery to absorb the current gradually, reducing the risk of overheating or other adverse effects.
During the charging process, it's essential to monitor the battery's response. If the battery shows signs of life, such as an increase in voltage or current, it's a positive indicator. However, if the battery remains unresponsive, a longer charging period with the low-current setting might be necessary. Patience is key here, as rushing the process could lead to further issues.
Remember, the current-limiting technique is a delicate balance between revival and potential harm. It requires careful observation and adjustment to ensure the battery's health is not compromised. By using a low-current charge, you can effectively wake a sleeping Li-ion battery while minimizing the risk of damage.
Regain Control: Tips to Reset Your Sleep-Wake Cycle
You may want to see also

Discharge Management: Monitor and control discharge to prevent deep discharge
Discharge management is a critical aspect of maintaining the health and longevity of a lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery. It involves monitoring and controlling the discharge process to ensure the battery operates within safe and optimal parameters. Proper discharge management is essential to prevent deep discharge, which can lead to irreversible damage and reduced battery life.
One key method to manage discharge is by implementing a smart charging system. This system employs advanced algorithms and sensors to monitor the battery's state of charge (SoC) and state of health (SoH). By continuously tracking the battery's performance, the system can adjust charging parameters in real-time. For instance, if the battery is almost fully charged, the system can reduce the charging current to prevent overcharging, which can cause unnecessary stress on the battery cells. Similarly, if the battery is low on power, the system can provide a gentle boost to maintain a healthy discharge rate.
Another effective strategy is to use a battery management system (BMS) that incorporates a discharge control mechanism. The BMS can be programmed to set specific discharge cut-off thresholds. When the battery's voltage drops below a certain level, the BMS triggers a cutoff, preventing further discharge. This ensures that the battery is not drained to an unsafe level, especially during periods of inactivity or when the device is not in use. By implementing such thresholds, you can effectively manage the discharge process and protect the battery from deep discharge.
Additionally, users can employ a technique known as 'top-up charging' to manage discharge. This involves regularly providing a small amount of power to the battery, even when it's not fully discharged. Top-up charging helps maintain the battery's charge level and prevents it from reaching a critically low state. It is particularly useful for batteries that are not frequently used or are stored for extended periods, ensuring they remain in a healthy state.
In summary, discharge management is a vital practice to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of Li-ion batteries. By employing smart charging systems, BMS with discharge control, and top-up charging techniques, one can effectively monitor and control the discharge process. These methods collectively help prevent deep discharge, reduce battery wear, and ensure the battery operates within safe limits, ultimately extending its overall lifespan.
Uncover the Secrets: Waking Up a Sleeper Agent's Blackout
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Li-ion batteries can enter a low-power state, often referred to as a "sleep mode," when they are not in use for an extended period. To wake it up, ensure the battery is at room temperature and apply a gentle charge. Avoid overcharging, as it may damage the battery.
Reviving a sleeping Li-ion battery involves a process called "reconditioning." You can use a specialized battery charger designed for Li-ion batteries and follow the manufacturer's instructions. This process may require multiple cycles of charging and discharging to restore the battery's capacity.
While a regular charger might work, it's not recommended. Standard chargers may not provide the precise voltage and current levels required to safely awaken a sleeping Li-ion battery. Using the correct charger designed for Li-ion batteries is essential to avoid potential damage.
The charging time depends on the battery's capacity and the charger's specifications. As a general guideline, charge the battery for at least 2-3 hours. However, it's crucial to monitor the charging process and prevent overcharging, as it can lead to safety hazards.
Yes, a sleeping Li-ion battery may exhibit low voltage, reduced capacity, or difficulty holding a charge. You might also notice a decrease in the battery's performance when you try to use it. Regularly checking the battery's health and monitoring its behavior can help identify if it needs to be awakened.