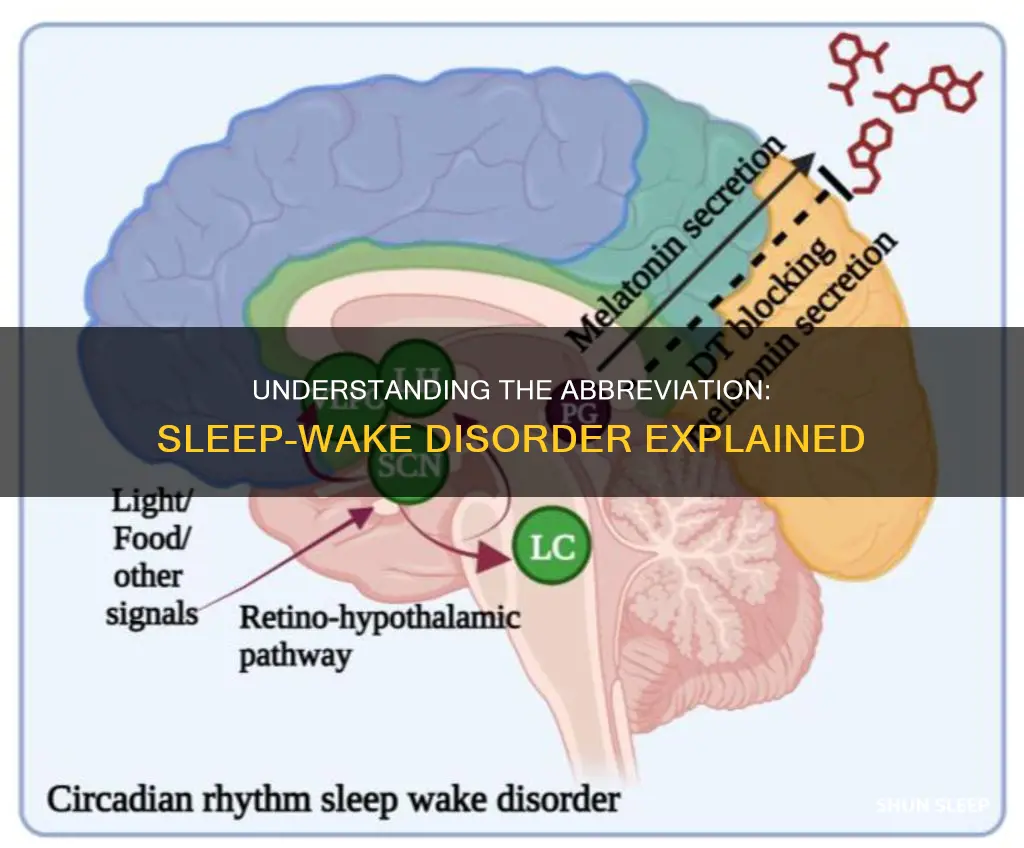
Sleep-wake disorders are a group of conditions that affect the normal sleep-wake cycle, causing disruptions in an individual's ability to fall asleep, stay asleep, or wake up at appropriate times. These disorders can significantly impact a person's daily functioning and quality of life. The abbreviation for sleep-wake disorders is often referred to as SWSD. Understanding the various types and causes of these disorders is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment, as it can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Abbreviation | SWSD |
| Medical Term | Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorder |
| Definition | A neurological condition affecting the sleep-wake cycle, often leading to insomnia, hypersomnia, and irregular sleep patterns. |
| Symptoms | Insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, irregular sleep schedules, and difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. |
| Causes | Genetic factors, brain disorders, medications, and environmental factors. |
| Diagnosis | Sleep studies, patient history, and physical examination. |
| Treatment | Cognitive-behavioral therapy, sleep hygiene education, and sometimes medication. |
| Prevalence | Affects around 1-2% of the population. |
| Types | Non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder, advanced sleep-wake phase disorder, and delayed sleep-phase syndrome. |
What You'll Learn
- Medical Abbreviations: Sleep-wake disorders often use medical abbreviations like insomnia (INS) and narcolepsy (NAR)
- Psychiatric Disorders: Abbreviations like SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder) and SAD (Schizophrenia) are used in sleep-wake disorders
- Neurological Disorders: Narcolepsy (NAR) and REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) are common abbreviations in sleep-wake disorders
- Sleep-Wake Cycle: Abbreviations like SWS (Slow-Wave Sleep) and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep are used to describe sleep stages
- Sleep Disorders: Abbreviations like insomnia (INS) and sleep apnea (SA) are used to describe specific sleep disorders

Medical Abbreviations: Sleep-wake disorders often use medical abbreviations like insomnia (INS) and narcolepsy (NAR)
Sleep-wake disorders are a group of conditions that affect the natural sleep-wake cycle, often leading to difficulties in falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing excessive daytime sleepiness. These disorders can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and overall health. In the medical field, various abbreviations are used to represent these conditions, providing a concise and standardized way to communicate about specific sleep-related issues.
One of the most common abbreviations for sleep-wake disorders is insomnia, often shortened to INS. Insomnia is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and early-morning awakenings. It can be caused by various factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, or an irregular sleep schedule. The abbreviation INS is widely recognized and used in medical literature and clinical settings to refer to this prevalent sleep condition.
Another important abbreviation is NAR, which stands for narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that affects the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles normally. People with narcolepsy experience excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden muscle weakness (cataplexy), and may have vivid hallucinations or sleep paralysis. The NAR abbreviation helps medical professionals and researchers quickly identify this condition, which often requires specialized treatment approaches.
These abbreviations are just a few examples of the many medical terms used to describe sleep-wake disorders. Other conditions, such as sleep apnea (OSA), restless leg syndrome (RLS), and circadian rhythm disorders, also have their own unique abbreviations. Using these abbreviations in medical records, prescriptions, and research papers ensures clarity and consistency, allowing healthcare providers to efficiently communicate and manage these complex sleep conditions.
Understanding these medical abbreviations is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals living with sleep-wake disorders. It enables better communication, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment planning. When seeking medical advice or discussing sleep-related concerns, being familiar with these abbreviations can facilitate a more efficient and informative conversation with healthcare providers.
The Magic of Aurora's Awakening: Unlocking Sleeping Beauty's Slumber
You may want to see also

Psychiatric Disorders: Abbreviations like SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder) and SAD (Schizophrenia) are used in sleep-wake disorders
The field of psychiatry often utilizes abbreviations to represent specific disorders, and this practice extends to sleep-wake disorders as well. One such example is the abbreviation 'SAD' which can have multiple meanings in the context of sleep-wake disorders. Firstly, Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a well-known condition where individuals experience depressive episodes during specific times of the year, often linked to seasonal changes. This type of SAD can indeed impact sleep patterns, leading to disruptions in sleep-wake cycles. Secondly, 'SAD' can also stand for Schizophrenia, a complex mental health disorder characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and cognitive impairments. While schizophrenia primarily affects thought processes and behavior, it can also influence sleep patterns, making it another relevant abbreviation in the realm of sleep-wake disorders.
In the context of sleep-wake disorders, these abbreviations help professionals and researchers quickly identify and communicate specific conditions. For instance, when a patient presents with symptoms of seasonal mood changes affecting their sleep, the diagnosis of SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder) can be made, allowing for targeted treatment approaches. Similarly, recognizing schizophrenia as a potential sleep-wake disorder can guide appropriate interventions.
The use of abbreviations like SAD in sleep-wake disorders is a practical approach to streamline medical communication and documentation. It enables healthcare providers to quickly convey the nature of a patient's condition, facilitating efficient decision-making and treatment planning. This is particularly important in the field of psychiatry, where accurate and timely diagnoses are crucial for effective patient care.
Furthermore, these abbreviations often provide a standardized way of referring to specific disorders, ensuring consistency in research, clinical practice, and patient education. For instance, using 'SAD' for Seasonal Affective Disorder allows for a clear distinction from other potential causes of sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or sleep apnea. This clarity is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies.
In summary, the use of abbreviations like SAD in sleep-wake disorders is a common and practical approach in psychiatric practice. It enables healthcare professionals to efficiently communicate and manage various sleep-related conditions, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care and support. Understanding these abbreviations is crucial for anyone involved in the diagnosis and treatment of sleep-wake disorders, as it facilitates effective collaboration and patient management.
Understanding Sleep-Wake Patterns in Vegetative States: A Complex Mystery
You may want to see also

Neurological Disorders: Narcolepsy (NAR) and REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) are common abbreviations in sleep-wake disorders
Narcolepsy (NAR) and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) are two distinct but interconnected neurological conditions that fall under the umbrella of sleep-wake disorders. These disorders significantly impact an individual's sleep-wake cycle, often leading to excessive daytime sleepiness, disrupted nighttime sleep, and a variety of other symptoms. Understanding these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden muscle weakness (cataplexy), sleep paralysis, and hallucinations. It is caused by a lack of orexin (also known as hypocretin) neurons in the brain, which regulate wakefulness and sleep cycles. NAR can be either primary or secondary, with the former being more common and often inherited. Symptoms typically appear in early adulthood, but they can also develop later in life. Treatment focuses on improving wakefulness and managing other symptoms, and may include stimulant medications, sleep hygiene practices, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) is a parasomnia disorder that affects the regulation of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Individuals with RBD act out their dreams during REM sleep, often resulting in violent movements, shouting, or even falling out of bed. This disorder can lead to injuries and is often associated with other neurological conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, and REM sleep behavior disorder with hallucinations. RBD is more common in older adults and can significantly impact quality of life. Treatment may involve medications to reduce muscle tone and cognitive-behavioral therapy to manage the behavioral aspects of the disorder.
Both NAR and RBD can have a profound impact on an individual's daily life, affecting their ability to work, socialize, and maintain relationships. The overlap in symptoms and the potential for comorbid conditions make accurate diagnosis and management essential. A comprehensive evaluation by a sleep specialist or neurologist is recommended to determine the specific type of sleep-wake disorder and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In summary, narcolepsy and REM sleep behavior disorder are two significant neurological conditions that fall under the category of sleep-wake disorders. They share some commonalities, such as disrupted sleep patterns and excessive daytime sleepiness, but also have distinct features. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking professional help is crucial for effective management and improving the quality of life for those affected by these disorders.
Revive Your MacBook Pro: Tips to Wake Mojave from Sleep
You may want to see also

Sleep-Wake Cycle: Abbreviations like SWS (Slow-Wave Sleep) and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep are used to describe sleep stages
The sleep-wake cycle is a complex process that regulates our sleep and wakefulness throughout the day. It is a natural rhythm that our bodies follow, and it is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. This cycle is characterized by different stages of sleep, each with its own unique features and functions. To understand these stages, various abbreviations are used to describe the different types of sleep.
One of the most well-known abbreviations is SWS, which stands for Slow-Wave Sleep. This stage is also known as non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and is characterized by slow, high-amplitude brain waves. SWS is further divided into three stages, with stage 3 being the deepest and most restorative. During this stage, the body repairs and regenerates tissues, synthesizes hormones, and strengthens the immune system. It is essential for physical health and plays a vital role in learning and memory consolidation.
Another critical aspect of the sleep-wake cycle is REM sleep, which is abbreviated as REM. This stage is easily recognizable due to the rapid eye movements and increased brain activity. REM sleep is associated with dreaming and is crucial for emotional processing and memory consolidation, especially for procedural memories and skills. It is also believed to be involved in emotional regulation and the processing of stressful experiences.
These abbreviations, SWS and REM, are essential in understanding the different stages of sleep and their respective functions. They provide a concise way to describe the complex processes occurring during sleep, allowing researchers, medical professionals, and individuals to communicate effectively about sleep disorders and the impact of sleep on overall health.
In the context of sleep-wake disorders, these abbreviations become even more significant. For example, individuals with insomnia may experience difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep, often leading to SWS and REM sleep disturbances. Similarly, conditions like narcolepsy, where people experience excessive daytime sleepiness, can be linked to disruptions in the REM sleep cycle. Understanding these abbreviations and their implications is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and management of sleep-related disorders.
Newborn Sleep Tips: Gentle Strategies for Waking Up Your Little One
You may want to see also

Sleep Disorders: Abbreviations like insomnia (INS) and sleep apnea (SA) are used to describe specific sleep disorders
Sleep disorders are a group of conditions that affect the quality and duration of sleep, often leading to significant daytime impairment and reduced quality of life. These disorders are typically categorized based on their symptoms and the underlying causes. One of the most common methods to classify sleep disorders is through the use of specific abbreviations, which provide a concise and standardized way to refer to these conditions.
Insomnia (INS) is a well-known sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. It can be further divided into different types, such as insomnia related to another health issue, insomnia with hypnagogic hallucinations, and insomnia without hypnagogic hallucinations. This disorder is often abbreviated as 'INS' in medical literature and clinical settings, making it easier for healthcare professionals to communicate and diagnose the condition.
Sleep apnea, on the other hand, is a more complex disorder. It is abbreviated as 'SA' and refers to a group of disorders characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses, called apneas, can occur repeatedly throughout the night, leading to fragmented sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness. There are several types of sleep apnea, including obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea, and complex sleep apnea, each with its own distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
Other sleep disorders also have their own unique abbreviations. For example, narcolepsy, a chronic neurological disorder affecting the control of sleep and wakefulness, is often abbreviated as 'NAR'. Restless legs syndrome (RLS), a sensory disorder causing an irresistible urge to move the legs, is commonly referred to as 'RLS'. These abbreviations help in streamlining medical documentation, research, and patient care.
Understanding these abbreviations is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. It allows for efficient communication, ensuring that specific sleep disorders are accurately identified and managed. Additionally, these abbreviations facilitate research and the sharing of knowledge among medical professionals, contributing to better patient outcomes and a deeper understanding of sleep disorders.
Unveiling Sleep Study Secrets: Waking Up or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The term "sleep-wake disorder" is often abbreviated as SWD.
Yes, sleep-wake disorders encompass a range of conditions, including insomnia, hypersomnia, narcolepsy, and circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders. Each type has its own unique characteristics and may be abbreviated differently, but SWD is a common overarching term.
In medical literature, SWD is frequently used as an abbreviation for sleep-wake disorders to represent the collective group of these conditions. It is a concise way to refer to the various sleep disturbances and their associated disorders.







